Abstract
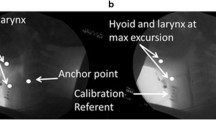
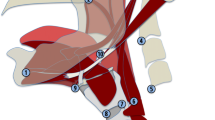
The Dynamic Swallow Study (DSS) is a methodology used to objectively and quantitatively assess swallowing kinematics during Videofluoroscopic Swallow Studies (VFSS). No DSS normative data exist delineating superior and anterior hyoid displacement (Hsup and Hant, respectively), nor the ratio between Hsup and Hant (SAratio). The aims of this study were to (1) establish normative data for Hsup, Hant, and SAratio and (2) assess the effects of age, sex, and bolus size on these measures in non-dysphagic patients, within the context of DSS. VFSSs were reviewed for consecutive elderly (≥ 65 years) and non-elderly (< 65 years) male and female non-dysphagic patients. Measurements of Hsup, Hant, and SAratio were made using a novel measurement methodology within the context of the Dynamic Swallow Study (DSS) protocol. Statistical analysis was performed to establish interaction effects and main effects of age, sex, and bolus size on Hsup, Hant, and SAratio. Descriptive statistics (mean ± standard deviations) are outlined for Hsup, Hant, and SAratio. Hsup was significantly effected by bolus size and age. Additionally, a significant three-way interaction of age, sex, and bolus size was observed. Hant was significantly effected by bolus size and sex, but no two- or three-way interactions were present. Neither bolus size, age, nor sex significantly effected SAratio. Age, sex, and bolus size normative data were established for Hsup, Hant, and SAratio for VFSS kinematic analysis. By outlining these measures, one can more thoroughly evaluate the areas of specific swallowing impairment, better determine the therapy targets, and track changes over time.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pearson WG, Langmore SE, Zumwalt AC. Evaluating the structural properties of suprahyoid muscles and their potential for moving the hyoid. Dysphagia. 2011;26:345–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-010-9315-z.
Robbins J, Hamilton JW, Lof GL, Kempster GB. Oropharyngeal swallowing in normal adults of different ages. Gastroenterology. 1992;103:823–9.
Thompson TZ, Obeidin F, Davidoff AA, et al. Coordinate mapping of hyolaryngeal mechanics in swallowing. J Vis Exp. 2014;87(10):51476. https://doi.org/10.3791/51476.
Molfenter SM, Steele CM. Kinematic and temporal factors associated with penetration-aspiration in swallowing liquids. Dysphagia. 2014;29:269–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-013-9506-5.
Sivarao DV, Goyal RK. Functional anatomy and physiology of the upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Med. 2000;108(4A):27S–37S.
Nishikubo K, Mise K, Ameya M, Hirose K, Kobayashi T, Hyodo M. Quantitative evaluation of age-related alteration of swallowing function: videofluoroscopic and manometric studies. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2014.07.002.
Ekberg O. Closure of the laryngeal vestibule during deglutition. Acta Otolaryngol. 1982;93(1–2):123–9.
Ekberg O, Sigurjónsson SV. Movement of the epiglottis during deglutition - A cineradiographic study. Gastrointest Radiol. 1982;7:101–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01887619.
Steele CM, Bailey GL, Chau T, et al. The relationship between hyoid and laryngeal displacement and swallowing impairment. Clin Otolaryngol. 2011;36:30–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-4486.2010.02219.x.
Kraaijenga SAC, van der Molen L, Heemsbergen WD, Remmerswaal GB, Hilgers GB, van der Brekel MW. Hyoid bone displacement as parameter for swallowing impairment in patients treated for advanced head and neck cancer. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4029-y.
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ. Hyoid movement during swallowing in older patients with dysphagia. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127:1224–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.127.10.1224.
Paik NJ, Kim SJ, Lee HJ, Jeon JY, Lim JY, Han TR. Movement of the hyoid bone and the epiglottis during swallowing in patients with dysphagia from different etiologies. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2008;18:329–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2006.09.011.
Wang TG, Chang YC, Chen WS, Lin PH, Hsiao TY. Reduction in hyoid bone forward movement in irradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;91:926–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2010.02.011.
Ekberg O. Defective closure of the laryngeal vestibule during deglutition. Acta Otolaryngol. 1982;93(1–6):309–17.
Ekberg O. Epiglottic dysfunction during deglutition in patients with dysphagia. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983;109:376–80.
Leonard R, Kendall K. Dysphagia assessment and treatment planning: a team approach. 3rd ed. San Diego: Plural Publishing, Inc.; 2014.
Leonard RJ, Kendall KA, McKenzie S, Gonçalves MI, Walker A. Structural displacements in normal swallowing: a videofluoroscopic study. Dysphagia. 2000;15(3):146–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004550010017.
Molfenter SM, Steele CM. Physiological variability in the deglutition literature: hyoid and laryngeal kinematics. Dysphagia. 2011;26(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-010-9309-x.
Dodds WJ, Man KM, Cook IJ, Kahrilas PJ, Stewart ET, Kern MK. Influence of bolus volume on swallow-induced hyoid movement in normal subjects. Am J Radiol. 1988;150:1307–9.
Leonard R, McKenzie S. Hyoid-bolus transit latencies in normal swallow. Dysphagia. 2006;21:183–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-006-9025-8.
Kim Y, McCullough GH. Maximum hyoid displacement in normal swallowing. Dysphagia. 2008;23(3):274–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9135-y.
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ. Pharyngeal constriction in elderly dysphagic patients compared with young and elderly nondysphagic controls. Dysphagia. 2001;16:272–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-001-0086-4.
Leonard RJ, Kendall KA, Johnson R, McKenzie S. Swallowing in myotonic muscular dystrophy: a videofluoroscopic study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001;82:979–85. https://doi.org/10.1053/apmr.2001.23962.
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ. Videofluoroscopic upper esophageal sphincter function in elderly dysphagic patients. Laryngoscope. 2002;112:332–7.
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ, McKenzie SW. Sequence variability during hypopharyngeal bolus transit. Dysphagia. 2003;18:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-002-0086-z.
Kendall KA, Ellerston J, Heller A, Houtz DR, Zhang C, Presson AP. Objective measures of swallowing function applied to the dysphagia population: a one year experience. Dysphagia. 2016;31:538–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9711-0.
Kendall KA. Oropharyngeal swallowing variability. Laryngoscope. 2002;112(3):547–51. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200203000-00025.
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ, Mckenzie S. Common medical conditions in the elderly: impact on pharyngeal bolus transit. Dysphagia. 2004;19:71–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0502-z.
Leonard R, Kendall KA, Mckenzie S. Structural displacements affecting pharyngeal constriction in nondysphagic elderly and nonelderly adults. Dysphagia. 2004;19:133–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0508-6.
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ, Mckenzie S. Airway protection: evaluation with videofluoroscopy. Dysphagia. 2004;19:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0500-1.
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ. Bolus transit and airway protection coordination in older dysphagic patients. Laryngoscope. 2001;111:2017–21.
Kendall KA, Mckenzie S, Leonard RJ, Gonçalves MI, Walker A. Timing of events in normal swallowing: a videofluoroscopic study. Dysphagia. 2000;15:74–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004550010004.
Crary MA, Carnaby Mann GD, Groher ME. Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86:1516–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2004.11.049.
Rosenbek JC, Robbins J, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996;11:93–8.
Koo TK, Li MY. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med. 2016;15:155–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012.
Ishida R, Palmer JB, Hiiemae KM. Hyoid motion during swallowing: factors affecting forward and upward displacement. Dysphagia. 2002;17(4):262–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-002-0064-5.
Sia I, Carvajal P, Carnaby-Mann GD, Crary MA. Measurement of hyoid and laryngeal displacement in video fluoroscopic swallowing studies: variability, reliability, and measurement error. Dysphagia. 2011;27(2):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-011-9352-2.
Ekberg O. The normal movements of the hyoid bone during swallow. Invest Radiol. 1986;21(5):408–10.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Michelle Troche, PhD, CCC-SLP for contributions to manuscript review and statistical guidance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors James Curtis, Jonelyn Langenstein, and Sarah Schenider declare that they each have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curtis, J., Langenstein, J. & Schneider, S. Superior and Anterior Hyoid Displacement During Swallowing in Non-Dysphagic Individuals. Dysphagia 33, 602–609 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-018-9878-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-018-9878-7