Abstract
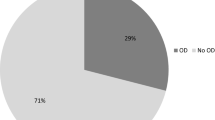
Scientific evidence on the impact of medication on the physiology of swallowing is scarce and mainly based on clinical case reports. To evaluate the association between oropharyngeal dysphagia (OD) and chronic exposure to medication in older patients admitted to the acute geriatric unit (AGU) of a secondary hospital, we performed a retrospective cross-sectional study of 966 patients admitted to an AGU from 2008 to 2011. We reviewed (a) diagnosis of OD (assessed with the volume-viscosity swallow test, V- VST); (b) chronic patient medication classified by anatomical, therapeutic, chemical codes; and (c) demographic and clinical data. A univariate analysis was performed to determine which medications were associated with OD. A multivariate analysis adjusting for confounding clinical factors was performed to identify which of those medications were independently associated with OD. The age of patients included was 85.3 ± 6.37 years and 59.4 % were women. A total of 41.9 % presented OD. We found a possible protective effect of beta blocking agents on OD after the multivariate analysis (OR 0.54, 95 % CI 0.35–0.85). None of the categories of drugs was associated with an altered swallowing function after adjusting for confounding variables. The present study is the first one to widely investigate the association between drugs and OD, increasing understanding of their association. The role of beta blockers in OD needs to be further studied as their potentially beneficial effects on the swallowing function in older patients could help to prevent complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nogueira D, Reis E. Swallowing disorders in nursing home residents: how can the problem be explained? Clinl Interv Aging. 2013;8:221–7.
Cabré M, Serra-Prat M, Force L, Almirall J, Palomera E, Clavé P. Oropharyngeal Dysphagia is a risk factor for readmission for pneumonia in the very elderly persons: observational propsective study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med. 2014;69:330–7.
Serra-Prat M, Hinojosa G, López D, et al. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia and impaired safety and efficacy of swallow in independently living older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(1):186–7.
Smithard D, O’Neill P, Parks C, et al. Complications and outcome after acute stroke. Does dysphagia matter? Stroke. 1996;27:1200–4.
Finestone H, Greene-Finestone L, Wilson E, et al. Prolonged length of stay and reduced functional improvement rate in malnourished stroke rehabilitation patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1996;77:340–5.
Teasell R, McRae M, Marchuk Y, et al. Pneumonia associated with aspiration following stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1996;77:707–9.
Murry T, Carrau R. Clinical management of swallowing disorders. 3rd ed. San Diego: Plural; 2012.
Marik PE, Kaplan D. Aspiration pneumonia and dysphagia in the elderly. Chest. 2003;124:328–36.
Jean A. Brain stem control of swallowing: neuronal network and cellular mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:929–69.
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I. Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114:2226–44.
Carl LL, Johnson PR. Drugs and dysphagia: how medications can affect eating and swallowing. 1st ed. Austin: Pro-Ed; 2006.
Bieger D, Neuhuber W. Neural circuits and mediators regulating swallowing in the brainstem. GI Motility online, 2006. http://www.nature.com/gimo/contents/pt1/full/gimo74.html. Accessed 04 June 2015
Dziewas R, Warnecke T, Schnabel M, et al. Neuroleptic-induced dysphagia: case report and literature review. Dysphagia. 2007;22(1):63–7.
Sokoloff LG, Pavlakovic R. Neuroleptic-induced dysphagia. Dysphagia. 1997;12(4):177–9.
Jt Stewart. Dysphagia associated with risperidone therpay. Dysphagia. 2003;18:274–5.
Loeb M, Becker M, Eady A, et al. Interventions to prevent aspiration pneumonia in older adults: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(7):1018–22.
Fonda D, Schwarts J, Clinnick S. Parkinsonian medication one hour before meals improves symptomatic swallowing: a case study. Dysphagia. 1995;10:165–6.
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. Guidelines for speech-language pathologists performing videofluoroscopic swallowing studies. ASHA Suppl. 2004;24:77–92.
Ebihara T, Takahashi H, Ebihara S, et al. Capsaicin troche for swallowing dysfunction in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(5):824–8.
Ebihara T, Sekizawa K, Nakazawa H, Sasaki H. Capsaicin and swallowing reflex. Lancet. 1994;341:432.
Ebihara T, Ebihara S, Maruyama M, et al. A randomized trial of olfactory stimulation using black pepper oil in older people with swallowing dysfunction. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(9):1401–6.
Rofes L, Arreola V, Martin A, Clavé P. Natural capsaicinoids improve swallow response in older patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. Gut. 2013;62(9):1280–7.
Rofes L, Arreola V, Martin A, Clavé P. Effect of oral piperine on the swallow response of patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. J Gastroenterol. 2014;49(12):1517–23.
Nakayama K, Sekizawa K, Sasaki H. ACE inhibitor and swallowing reflex. Chest. 1998;113(5):1425.
Sekizawa K, Matsui T, Nakagawa T, Nakayama K, Sasaki H. ACE inhibitors and pneumonia. Lancet. 1998;352:1069.
Cabré M, Serra-Prat M, Palomera E, Almirall J, Pallares R, Clavé P. Prevalence and prognostic implications of dysphagia in elderly patients with pneumonia. Age Ageing. 2010;39:39–45.
Charlson M, Pompei P, Ales K, Mackenzie C. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40:373–83.
Mahoney FI, Barthel DW. Functional evaluation: the Barthel Index. Md State Med J. 1965;14:61–5.
WHO (2015) The anatomical therapeutic chemical classification system with defined daily doses (ATC/DDD). World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/classifications/atcddd/en/. Accessed 01 Oct 2015
Clavé P, Arreola V, Romea M, Medina L, Palomera E, Serra-Prat M. Accuracy of the volume-viscosity swallow test for clinical screening of oropharyngeal dysphagia and aspiration. Clin Nutr. 2008;27:806.
Stewart JT. Reversible dysphagia associated with neuroleptic treatment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001;49:1260–1.
Bashford G, Bradd P. Drug-induced Parkinsonism associated with dysphagia and aspiration: a brief report. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 1996;9(3):133–5.
Gonzalez F. Extrapyramidal syndrome presenting as dysphagia: a case report. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2008;25:398–400.
Brandt N. Medications and dysphagia: How do they impact each other? Nutr Clin Pract. 1999;14:S27–30.
Korsten M, Rosman A, Fishbein S, Shlein R, Goldberg H, Biener A. Chronic xerostomia increases esophageal acid exposure and is associated with esophageal injury. Am J Med. 1991;90(6):701–6.
Sukys-Claudino L, Moraes W, Guilleminault C, Tufik S, Poyares D. Beneficial effect of donepezil on obstructive sleep apnea: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Sleep Med. 2012;13(3):290–6.
Dantas R, Souza R. Dysphagia induced by chronic ingestion of benzodiazepine. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(7):1194–6.
Almirall J, Rofes L, Serra-Prat M, et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a risk factor for community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(4):923–8.
Gaillard JM Benzodiazepines and GABA-ergic transmisión. In: Kryger MH, Roth T. Dement WC. (eds.) Principles and practie of sleep Medicine. Philadelphia. P. WB Saunders, 1989. pp. 213–218.
Almirall J, Serra-Prat M, Baron F, Palomera E, Bolíbar I. The use of benzodiazepines could be a protective factor for community-acquired pneumonia in <60-year-old subjects. Thorax. 2013;68:965–6.
Almirall J, Bolíbar I, Serra-Prat M, et al. New evidence of risk factors for community-acquired pneumonia: a population-based study. Eur Respir J. 2008;31:1274–84.
Burks TN, Andres-Mateos E, Marx R, Mejias R, Van Erp C, Simmers JL, et al. Losartan restores skeletal muscle remodeling and protects against disuse atrophy in sarcopenia. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:82ra37.
Murphy R, Gardiner P, Rousseau G, Bouvier M, Béliveau L. Chronic β-blockade increases skeletal muscle β-adrenergicreceptor density and enhances contractile force. J Appl Physiol. 1997;83(2):459–65.
Bradley W, Daroff R, Fenichel G, Jankovic J. Neurology in clinical practice, the neurological disorders. JAMA. 2001;285(4):172.
Shimizu T, Fujioka S, Otonashi H, Kondo M, Sekizawa K. ACE inhibitor and swallowing difficulties in stroke. A preliminary study. J Neurol. 2008;255(2):288–9.
Arai T, Yasuda Y, Toshima S, Yoshimi N, Kashiki Y. ACE inhibitors and pneumonia in elderly people. Lancet. 1998;352:1937–8.
Nakayama K, Sekizawa K, Sasaki H. ACE inhibitor and swallowing reflex. Chest. 1998;113:1425.
Perez I, Smithard DG, Davies H, et al. Pharmacological treatment of dysphagia in stroke. Dysphagia. 1998;13:12–6.
Ohkubo T, Chapman N, Neal B, Woodward M, Omae T, Chalmers J. Effects of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-based regimen on pneumonia risk. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;169(9):1041–5.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jane Lewis for reviewing the English of the manuscript. This work has been conducted within the framework of a doctoral thesis in medicine from the Autonomous University of Barcelona.
Author Contributions
MM and LR: designed and coordinated the study and drafted the manuscript; LC: critical input and revision of the manuscript; EP and MSP: statistical analysis and revision of the manuscript; MC: collected the data. All authors approved the final version of the article.
Financial Support
None of the authors have any conflict of interest nor have received any funding related to the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miarons, M., Campins, L., Palomera, E. et al. Drugs Related to Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Older People. Dysphagia 31, 697–705 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9735-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9735-5