Abstract
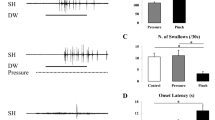
We designed an electrical stimulation system to safely and reliably evoke the swallowing reflex in awake humans, and then examined the neural control of reflex swallowing initiated by oropharyngeal stimulation. A custom-made electrode connected to a flexible stainless-steel coil spring tube was introduced into the pharyngeal region through the nasal cavity and placed against the posterior wall of the oropharynx. Surface electrodes placed over the suprahyoid muscles recorded the electromyogram during swallowing. Swallowing reflexes were induced several times by 30 s of repetitive electrical pulse stimulation (intensity: 0.2–1.2 mA, frequency: 10–70 Hz, pulse duration: 1.0 ms). The onset latency of the swallowing reflex was measured over the 10–70 Hz frequency range. In addition, the two time intervals between the first three swallows were measured. The onset latency of the swallowing reflex became shorter as the stimulus frequency increased up to ≤30 Hz. Once the frequency exceeded 30 Hz, there was no further reduction in the latency. This finding was consistent with those of previous studies in anesthetized animals. The time intervals between successive swallowing reflexes did not change with increased stimulus frequencies. Furthermore, prolonged stimulation often failed to elicit multiple swallowing reflexes. The frequency dependence of onset latency suggests that temporal summation of pharyngeal afferents is required to activate the medullary swallowing center. This reliable stimulation method may help in rehabilitation of dysphagic patients without causing aspiration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kitagawa J, Shingai T, Takahashi T, Yamada Y. Pharyngeal branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a major role in reflex swallowing from the pharynx. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2002;282:R1342–7.
Miller AJ. Deglutition. Physiol Rev. 1982;62:129–84.
Pommerenke WT. A study of the sensory areas eliciting the swallowing reflex. Am J Physiol. 1928;84:36–4.
Shingai T, Shimada K. Reflex swallowing elicited by water and chemical substances applied in the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx of the rabbit. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26:455–69.
Steele CM, Miller AJ. Sensory input pathways and mechanisms in swallowing: a review. Dysphagia. 2010;25:323–33.
Storey AT. Laryngeal initiation of swallowing. Exp Neurol. 1968;20:359–65.
Storey AT. A functional analysis of sensory units innervating epiglottis and larynx. Exp Neurol. 1968;20:366–83.
Travers JB, Norgren R. Electromyographic analysis of the ingestion and rejection of sapid stimuli in the rat. Behav Neurosci. 1986;100:544–5.
Chee C, Arshad S, Singh S, Mistry S, Hamdy S. The influence of chemical gustatory stimuli and oral anaesthesia on healthy human pharyngeal swallowing. Chem Senses. 2005;30:393–400.
Kaatzke-McDonald MN, Post E, Davis PJ. The effects of cold, touch, and chemical stimulation of the anterior faucial pillar on human swallowing. Dysphagia. 1996;11:198–206.
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Colangelo LA, Kahrilas PJ, Smith CH. Temporal and biomechanical characteristics of oropharyngeal swallowing in younger and older men. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2000;43:1264–74.
Sciortino KF, Liss JM, Case JL, Gerritsen KGM, Katz RC. Effects of mechanical, cold, gustatory, and combined stimulation to the human anterior faucial pillars. Dysphagia. 2003;18:16–26.
Shingai T, Miyaoka Y, Ikarashi R, Shimada K. Swallowing reflex elicited by water and taste solutions in humans. Am J Physiol. 1989;256:822–6.
Kajii Y, Shingai T, Kitagawa J, Takahashi Y, Taguchi Y, Noda T, Yamada Y. Sour taste stimulation facilitates reflex swallowing from the pharynx and larynx in the rat. Physiol Behav. 2002;77:321–5.
Logemann JA, Pauroski BR, Colangelo L, Lazarus C, Fujiu M, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of a sour bolus on oropharyngeal swallowing measures in patients with neurogenic dysphagia. J Speech Hear Res. 1995;38:556–63.
Palmer PM, McCulloch TM, Jaffe D, Neel AT. Effects of a sour bolus on the intramuscular electromyographic (EMG) activity of muscles in the submental region. Dysphagia. 2005;20:210–7.
Pelletier CA, Lawless HT. Effect of citric acid and citric acid-sucrose mixtures on swallowing in neurogenic oropharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2003;18:231–41.
Miura Y, Morita Y, Koizumi H, Shingai T. Effects of taste solutions, carbonation, and cold stimulus on the power frequency content of swallowing submental surface electromyography. Chem Senses. 2009;34:325–31.
Shaker R, Medda BK, Ren J, Jaradeh S, Pengyan X, Lang IM. Pharyngo glottal closure reflex: identification and characterization in a feline model. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:G521–5.
Doty RW. Influence of stimulus pattern on reflex deglutition. Am J Physiol. 1951;166:142–58.
Jean A. Brain stem control of swallowing: neuronal network and cellular mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:929–69.
Kitagawa J, Nakagawa K, Hasegawa M, Iwakami T, Shingai T, Yamada Y, Iwata K. Facilitation of reflex swallowing from the pharynx and larynx. J Oral Sci. 2009;51:167–71.
Miller AJ. Characteristics of the swallowing reflex induced by peripheral nerve and brain stem stimulation. Exp Neurol. 1972;34:210–22.
Sinclair WJ. Initiation of reflex swallowing from the naso- and oropharynx. Am J Physiol. 1970;218:956–60.
Sinclair WJ. Role of the pharyngeal plexus in initiation of swallowing. Am J Physiol. 1971;221:1260–3.
Hamdy S, Aziz Q, Rothwell JC, Hobson A, Thompson DG. Sensorimotor modulation of human cortical swallowing pathways. J Physiol. 1998;506:857–66.
Park CL, O’Neill PA, Martin DF. A pilot exploratory study of oral electrical stimulation on swallow function following stroke: an innovative technique. Dysphagia. 1997;12:161–6.
Power M, Fraser C, Hobson A, Rothwell JC, Mistry S, Nicholson DA, Thompson DG, Hamdy S. Changes in pharyngeal corticobulbar excitability and swallowing behavior after oral stimulation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;286:G45–50.
Yamamura K, Kitagawa J, Kurose M, Sugino S, Takatsuji H, Mostafeezur R, Zakir H, Yamada Y. Neural mechanisms of swallowing and effects of taste and other stimuli on swallowing initiation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33:1786–90.
Mu L, Sanders I. Sensory nerve supply of the human oro- and laryngo-pharynx: a preliminary study. Anat Rec. 2000;258:406–20.
Costa J, Guzmán J, Valldeoriola F, Rumià J, Tolosa E, Casanova-Molla J, Valls-Solé J. Modulation of the soleus H reflex by electrical subcortical stimuli in humans. Exp Brain Res. 2011;212:439–48.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported in part by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) Grants-in Aid for Scientific Research Kakenhi 20659289 and 23592730, and a Grant from Ajinomoto Co., Ltd. for collaborative research.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takatsuji, H., Zakir, H.M., Mostafeezur, R.M. et al. Induction of the Swallowing Reflex by Electrical Stimulation of the Posterior Oropharyngeal Region in Awake Humans. Dysphagia 27, 473–480 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-012-9393-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-012-9393-1