Abstract
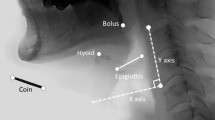
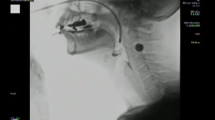
The purpose of this study was to identify the videofluoroscopic prognostic factors that affect the recovery of swallowing function at an early stage after stroke and to make a tool for predicting the long-term prognosis. Eighty-three poststroke patients were selected prospectively. These patients had all undergone videofluoroscopic swallowing studies at an average of 40 days after stroke onset and were followed up for over six months. Prognostic factors were determined by logistic regression analysis between the baseline videofluoroscopic findings and aspiration over six months (p < 0.05). A videofluoroscopic dysphagia scale (VDS) with a sum of 100 was made according to the odds ratios of prognostic factors. The validity of the scale was evaluated by using a receiver operating characteristic curve. The VDS was compiled using the following 14 items: lip closure, bolus formation, mastication, apraxia, tongue-to-palate contact, premature bolus loss, oral transit time, triggering of pharyngeal swallow, vallecular residue, laryngeal elevation, pyriform sinus residue, coating of pharyngeal wall, pharyngeal transit time, and aspiration. At a scale cutoff value of 47, the sensitivity was 0.91 and the specificity was 0.92. The VDS was developed to be used as an objective and quantifiable predictor of long-term persistent dysphagia after stroke.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gordon C, Langton-Hewer R, Wade DT: Dysphagia in acute stroke. BMJ 295:411–414, 1987
Smithard DG, O’Neill PA, England RE, Park CL, Wyatt R, Martin DF, Morris J: The natural history of dysphagia following a stroke. Dysphagia 12:188–193, 1997
Teasell RW, Bach D, McRae M: Prevalence and recovery of aspiration poststroke: a retrospective analysis. Dysphagia 9:35–39, 1994
Kidd D, Lawson J, Nesbitt R, MacMahon J: The natural history and clinical consequences of aspiration in acute stroke. QJM 88:409–413, 1995
Barer DH: The natural history and functional consequences of dysphagia after hemispheric stroke J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:236–241, 1989
Mann G, Grad-Dip P, Hankey GJ, Cameron D: Swallowing function after stroke: prognosis and prognostic factors at 6 months. Stroke 30:744–748, 1999
Horner J, Massey E: Silent aspiration following stroke. Neurology 38:317–319, 1988
Linden P, Siebens A: Dysphagia: predicting laryngeal penetration. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 64:281–283, 1983
DePippo KL, Holas MA, Reding MJ: Validation of the 3-oz water swallowing test for aspiration following stroke. Arch Neurol 49:1259–1261, 1992
Mann G, Hankey GJ: Initial clinical and demographic predictors of swallowing impairment following acute stroke. Dysphagia 16:208–215, 2001
Broadley S, Croser D, Cottrell J, Creevy M, Teo E, Yiu D, Pathi R, Taylor J, Thompson PD: Predictors of prolonged dysphagia following acute stroke. J Clin Neurosci 10:300–305, 2003
Logemann JA: Manual for the videofluorographic study of swallowing, 2nd ed. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed, 1993, pp 1–170
Schulzer M: Diagnostic tests: a statistical review. Muscle Nerve 17:815–819, 1994
Depippo KL, Holas MA, Reding MJ: The Burke dysphagia screening test: validation of its use in patients with stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 75:1284–1286, 1994
Mari F, Matei M, Ceravolo MG, Pisani A, Montesi A, Provinciali L: Predictive value of clinical indices in detecting aspiration in patients with neurological disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63:456–460, 1997
Smith HA, Lee SH, O’Nell PA, Connolly MJ: The combination of bedside swallowing assessment and oxygen saturation monitoring of swallowing in acute stroke: a safe and humane screening tool. Age Ageing 29:495–499, 2000
Addington WR, Stephens RE, Gilliland K, Rodriquez M: Assessing the laryngeal cough reflex and the risk of developing pneumonia after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 80:150–154, 1999
Broadley S, Cheek A, Salonikis S, Whitham E, Chong V, Cardone D, Alexander B, Taylor J, Thompson PD: Predicting prolonged dysphagia in acute stroke: the Royal Adelaide Prognostic Index for Dysphagic Stroke (RAPIDS). Dysphagia 20:303–310, 2005
Holas MA, DePippo KL, Reding MJ: Aspiration and relative risk of medical complications following stroke. Arch Neurol 51:1051–1053, 1994
Aslanyan S, Weir CJ, Diener HC, Kaste M, Lees KR: Pneumonia and urinary tract infection after acute ischaemic stroke: a tertiary analysis of the GAIN International trial. Eur J Neurol 11:49–53, 2004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, T.R., Paik, NJ., Park, JW. et al. The Prediction of Persistent Dysphagia Beyond Six Months After Stroke. Dysphagia 23, 59–64 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9097-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9097-0