Abstract
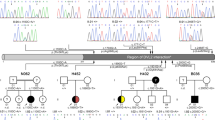
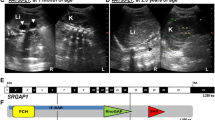
Megacystis–microcolon–intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome (MMIHS) is characterized by prenatal-onset distended urinary bladder with functional intestinal obstruction, requiring extensive surgical intervention for survival. While it is believed to be an autosomal recessive disorder, most cases are sporadic. Through whole-exome sequencing in a child with MMIHS, we identified a de novo mutation, p.R178L, in the gene encoding the smooth muscle gamma-2 actin, ACTG2. We subsequently detected another de novo ACTG2 mutation, p.R178C, in an additional child with MMIHS. Actg2 transcripts were primarily found in murine urinary bladder and intestinal tissues. Structural analysis and functional experiments suggested that both ACTG2 mutants interfere with proper polymerization of ACTG2 into thin filaments, leading to impaired contractility of the smooth muscle. In conclusion, our study suggests a pathogenic mechanism for MMIHS by identifying causative ACTG2 mutations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berdon WE, Baker DH, Blanc WA, Gay B, Santulli TV, Donovan C (1976) Megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome: a new cause of intestinal obstruction in the newborn. Report of radiologic findings in five newborn girls. AJR 126(5):957–964. doi:10.2214/ajr.126.5.957
Campeau E, Ruhl VE, Rodier F, Smith CL, Rahmberg BL, Fuss JO, Campisi J, Yaswen P, Cooper PK, Kaufman PD (2009) A versatile viral system for expression and depletion of proteins in mammalian cells. PLoS One 4(8):e6529. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006529
Carson M (1991) Ribbons 2 0. J Appl Crystallogr 24:958–961. doi:10.1107/S0021889891007240
Ciftci AO, Cook RC, van Velzen D (1996) Megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome: evidence of a primary myocellular defect of contractile fiber synthesis. J Pediatr Surg 31(12):1706–1711
Diaz-Horta O, Duman D, Foster J 2nd, Sirmaci A, Gonzalez M, Mahdieh N, Fotouhi N, Bonyadi M, Cengiz FB, Menendez I, Ulloa RH, Edwards YJ, Zuchner S, Blanton S, Tekin M (2012) Whole-exome sequencing efficiently detects rare mutations in autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss. PLoS One 7(11):e50628. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050628
Dominguez R, Holmes KC (2011) Actin structure and function. Ann Rev Biophys 40:169–186. doi:10.1146/annurev-biophys-042910-155359
Freedman AL, Johnson MP, Gonzalez R (2000) Fetal therapy for obstructive uropathy: past, present, future? Pediatr Nephrol 14(2):167–176
Garrett Q, Khaw PT, Blalock TD, Schultz GS, Grotendorst GR, Daniels JT (2004) Involvement of CTGF in TGF-beta1-stimulation of myofibroblast differentiation and collagen matrix contraction in the presence of mechanical stress. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(4):1109–1116
Gonzalez MA, Lebrigio RF, Van Booven D, Ulloa RH, Powell E, Speziani F, Tekin M, Schule R, Zuchner S (2013) GEnomes Management Application (GEM.app): a new software tool for large-scale collaborative genome analysis. Hum Mutat 34(6):842–846. doi:10.1002/humu.22305
Grinnell F, Ho CH (2002) Transforming growth factor beta stimulates fibroblast-collagen matrix contraction by different mechanisms in mechanically loaded and unloaded matrices. Exp Cell Res 273(2):248–255. doi:10.1006/excr.2001.5445
Lehtonen HJ, Sipponen T, Tojkander S, Karikoski R, Jarvinen H, Laing NG, Lappalainen P, Aaltonen LA, Tuupanen S (2012) Segregation of a missense variant in enteric smooth muscle actin gamma-2 with autosomal dominant familial visceral myopathy. Gastroenterology 143 (6):1482–1491 e1483. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.08.045
Marti-Renom MA, Stuart AC, Fiser A, Sanchez R, Melo F, Sali A (2000) Comparative protein structure modeling of genes and genomes. Ann Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 29:291–325. doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.29.1.291
Mc Laughlin D, Puri P (2013) Familial megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome: a systematic review. Pediatr Surg Int. doi:10.1007/s00383-013-3357-x
Meuwissen ME, Lequin MH, Bindels-de Heus K, Bruggenwirth HT, Knapen MF, Dalinghaus M, de Coo R, van Bever Y, Winkelman BH, Mancini GM (2013) ACTA2 mutation with childhood cardiovascular, autonomic and brain anomalies and severe outcome. Am J Med Genet Part A 161(6):1376–1380. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.35858
Milewicz DM, Ostergaard JR, Ala-Kokko LM, Khan N, Grange DK, Mendoza-Londono R, Bradley TJ, Olney AH, Ades L, Maher JF, Guo D, Buja LM, Kim D, Hyland JC, Regalado ES (2010) De novo ACTA2 mutation causes a novel syndrome of multi-systemic smooth muscle dysfunction. Am J Med Genet Part A 152A(10):2437–2443. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33657
Otterbein LR, Graceffa P, Dominguez R (2001) The crystal structure of uncomplexed actin in the ADP state. Science 293(5530):708–711. doi:10.1126/science.1059700
Piotrowska AP, Rolle U, Chertin B, De Caluwe D, Bianchi A, Puri P (2003) Alterations in smooth muscle contractile and cytoskeleton proteins and interstitial cells of Cajal in megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome. J Pediatr Surg 38(5):749–755. doi:10.1016/jpsu.2003.50159
Puri P, Shinkai M (2005) Megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome. Semin Pediatr Surg 14(1):58–63
Steiner RD, Adsit J, Basel D (1993) COL1A1/2-Related Osteogenesis Imperfecta. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT, Stephens K (eds) GeneReviews. Seattle
Yiee J, Wilcox D (2008) Abnormalities of the fetal bladder. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 13(3):164–170. doi:10.1016/j.siny.2007.10.002
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Derek M. Dykxhoorn for his assistance on recombinant lentivirus generation. This study was supported by the Hayward Foundation (to M.T.) and the National Institutes of Health Grant R01-GM083897 (to A.F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
W. Thorson and O. Diaz-Horta contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thorson, W., Diaz-Horta, O., Foster, J. et al. De novo ACTG2 mutations cause congenital distended bladder, microcolon, and intestinal hypoperistalsis. Hum Genet 133, 737–742 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1406-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1406-0