Abstract
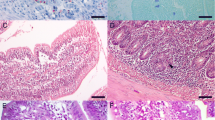
Secretory immunoglobulin A (SIgA), as a vital actor involving in the mucosal immunity, plays a key role in defending a variety of pathogenic infections, such as bacteria, viruses and parasites. Eimeria tenella is an obligate intracellular apicomplexan parasite contacting with the digestive tract mucosa and specially parasitizes chicken caecum, causing a severe form of coccidiosis. Coccidiosis is currently mainly controlled using chemotherapeutic agents. Diclazuril, a classic coccidiostat, was used widely in the poultry industry. Because of the rising problem of drug resistance, it is therefore crucial to understand the pattern of the SIgA expression in the action of diclazuril against E. tenella. In this study, the intestinal morphology in the caecum was analyzed by haematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, and the SIgA expression was examined by immunohistochemical technique. At the same time, the duodenum, jejunum and ileum tissues have also been evaluated. HE staining results showed that E. tenella infection caused severe damage characterized by structural disorder, haemorrhage, inflammatory cell infiltration, serous and fibrinous exudation in chicken caecum and invisible damage in the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. With the treatment of diclazuril, the damage in the caecum was alleviated obviously. Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated that the SIgA level in the infected group was increased in the duodenum (p < 0.05), jejunum and ileum, respectively, but decreased (p < 0.01) in the caecum, compared with the control group. Interestingly, the SIgA level was decreased in the duodenum (p < 0.05), jejunum and ileum but increased (p < 0.05) in the caecum in the infected/diclazuril group in comparison to the infected group. The results showed that diclazuril effectively alleviated the damage in the caecum induced by E. tenella and provided a cure for coccidiosis by improving the immune function in chickens.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellussi L, Cambi J, Passali D (2013) Functional maturation of nasal mucosa: role of secretory immunoglobulin a (SIgA). Multidiscip Respir Med 8(1):46–48
Bodammer P, Zirzow E, Klammt S, Maletzki C, Kerkhoff C (2013) Alteration of DSS-mediated immune cell redistribution in murine colitis by oral colostral immunoglobulin. BMC Immunol 14:10–18
Brandtzaeg P (2009) Mucosal immunity: induction, dissemination, and effector functions. Scand J Immunol 70(6):505–515
Chapman HD, Thomas K (2012) Jeffers: pioneer of coccidiosis research. Avian Pathol 41(2):123–131
Chapman HD, Jeffers TK, Williams RB (2010) Forty years of monensin for the control of coccidiosis in poultry. Poult Sci 89(9):1788–1801
Chaudhari AA, Jawale CV, Kim SW, Lee JH (2012) Construction of a Salmonella gallinarum ghost as a novel inactivated vaccine candidate and its protective efficacy against fowl typhoid in chickens. Vet Res 43(1):44–54
Chawda JG, Chaduvula N, Patel HR, Jain SS, Lala AK (2011) Salivary SIgA and dental caries activity. Indian Pediatr 48(9):719–721
Cheng K, Wu Z, Gao B, Xu J (2014) Analysis of influence of Baicalin joint resveratrol retention enema on the TNF-alpha, SIgA, IL-2 IFN-gamma of rats with respiratory syncytial virus infection. Cell Biochem Biophys. doi:10.1007/s12013-014-0055-9
Conway DP, Mathis GF, Johnson J, Schwartz M, Baldwin C (2001) Efficacy of diclazuril in comparison with chemical and ionophorous anticoccidials against Eimeria spp. in broiler chickens in floor pens. Poult Sci 80(4):426–430
Dalloul RA, Lillehoj HS (2006) Poultry coccidiosis: recent advancements in control measures and vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 5(1):143–163
Davids BJ, Palm JE, Housley MP, Smith JR, Andersen YS, Martin MG, Hendrickson BA, Johansen FE, Svärd SG, Gillin FD, Eckmann L (2006) Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor in intestinal immune defense against the lumen-dwelling protozoan parasite Giardia. J Immunol 177(9):6281–6290
De Pablos LM, dos Santos MF, Montero E, Garcia-Granados A, Parra A, Osuna A (2010) Anticoccidial activity of maslinic acid against infection with Eimeria tenella in chickens. Parasitol Res 107(3):601–604
El-Gebaly NS, Halawa EF, Moussa HM, Rabia I, Abu-Zekry M (2012) Saliva and sera IgA and IgG in Egyptian Giardia-infected children. Parasitol Res 111(2):571–575
Gonzalez-Hernandez MB, Liu T, Payne HC, Stencel-Baerenwald JE, Ikizler M, Yagita H, Dermody TS, Williams IR, Wobus CE (2014) Efficient Norovirus and Reovirus replication in the mouse intestine requires microfold (M) cells. J Virol 88(12):6934–6943
Hefferon KL (2010) The mucosal immune response to plant-derived vaccines. Pharm Res 27(10):2040–2042
Jiang L, Lin J, Han H, Zhao Q, Dong H, Zhu S, Huang B (2012) Identification and partial characterization of a serine protease inhibitor (serpin) of Eimeria tenella. Parasitol Res 110(2):865–874
Jonker MA, Hermsen JL, Sano Y, Heneghan AF, Lan J, Kudsk KA (2012) Small intestine mucosal immune system response to injury and the impact of parenteral nutrition. Surgery 151(2):278–286
Kaboutari J, Arab HA, Ebrahimi K, Rahbari S (2014) Prophylactic and therapeutic effects of a novel granulated formulation of Artemisia extract on broiler coccidiosis. Trop Anim Health Prod 46(1):43–48
Liu DY, Li JJ (2010) Effect of hyperoxia on the intestinal IgA secretory component in neonatal rats and on intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Braz J Med Biol Res 43(11):1034–1041
Liu DY, Jiang W, Liu P (2011) Reduction of the amount of intestinal secretory IgA in fulminant hepatic failure. Braz J Med Biol Res 44(5):477–482
Liu DY, Jiang T, Wang S, Cao X (2013) Effect of hyperoxia on pulmonary SIgA and its components, IgA and SC. J Clin Immunol 33(5):1009–1017
Lu H, Wu Z, Xu W, Yang J, Chen Y, Li L (2011) Intestinal microbiota was assessed in cirrhotic patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Intestinal microbiota of HBV cirrhotic patients. Microb Ecol 61(3):693–703
Mabbott NA, Donaldson DS, Ohno H, Williams IR, Mahajan A (2013) Microfold (M) cells: important immunosurveillance posts in the intestinal epithelium. Mucosal Immunol 6(4):666–677
Macpherson AJ, McCoy KD, Johansen FE, Brandtzaeg P (2008) The immune geography of IgA induction and function. Mucosal Immunol 1(1):11–22
Maes L, Coussement W, Vanparijs O, Marsboom R (1988) In vivo action of the anticoccidial diclazuril (Clinacox) on the developmental stages of Eimeria tenella: a histological study. J Parasitol 74(6):931–938
McDonald V, Shirley MW (2009) Past and future: vaccination against Eimeria. Parasitology 136(12):1477–1489
Morris GM, Woods WG, Richards DG, Gasser RB (2007) Investigating a persistent coccidiosis problem on a commercial broiler-breeder farm utilising PCR-coupled capillary electrophoresis. Parasitol Res 101(3):583–589
Nodeh H, Mansoori B, Rahbari S, Modirsanei M, Aparnak P (2008) Assessing the effect of diclazuril on the intestinal absorptive capacity of broilers infected with experimental coccidiosis, using d-xylose absorption test. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 31(3):265–267
Otsuki T, Shimizu K, Iemitsu M, Kono I (2011) Salivary secretory immunoglobulin a secretion increases after 4-weeks ingestion of chlorella-derived multicomponent supplement in humans: a randomized cross over study. Nutr J 10(1):91–95
Otsuki T, Shimizu K, Iemitsu M, Kono I (2012) Chlorella intake attenuates reduced salivary SIgA secretion in kendo training camp participants. Nutr J 11(1):103–110
Peek HW, Landman WJ (2011) Coccidiosis in poultry: anticoccidial products, vaccines and other prevention strategies. Vet Q 31(3):143–161
Reyna-Garfias H, Miliar A, Jarillo-Luna A, Rivera-Aguilar V, Pacheco-Yepez J, Baeza I, Campos-Rodríguez R (2010) Repeated restraint stress increases IgA concentration in rat small intestine. Brain Behav Immun 24(1):110–118
Shima H, Watanabe T, Fukuda S, Fukuoka SI, Ohara O, Ohno H (2014) A novel mucosal vaccine targeting Peyer’s patch M cells induces protective antigen-specific IgA responses. Int Immunol. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxu061
Shirley MW, Lillehoj HS (2012) The long view: a selective review of 40 years of coccidiosis research. Avian Pathol 41(2):111–121
Stockinger S, Hornef MW, Chassin C (2011) Establishment of intestinal homeostasis during the neonatal period. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(22):3699–3712
Vega-López MA, Arenas-Contreras G, Bailey M, González-Pozos S, Stokes CR, Ortega MG, Mondragón-Flores R (2001) Development of intraepithelial cells in the porcine small intestine. Dev Immunol 8(2):147–158
Wang C, Han C, Li T, Yang D, Shen X, Fan Y, Xu Y, Zheng W, Fei C, Zhang L, Xue F (2013) Nuclear translocation and accumulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase involved in diclazuril-induced apoptosis in Eimeria tenella (E. tenella). Vet Res 44(1):29–37
Williams RB (2002) Anticoccidial vaccines for broiler chickens: pathways to success. Avian Pathol 31(4):317–353
Zhang DF, Sun BB, Yue YY, Yu HJ, Zhang HL, Zhou QJ, Du AF (2012) Anticoccidial effect of halofuginone hydrobromide against Eimeria tenella with associated histology. Parasitol Res 111(2):695–701
Zhou B, Wang H, Xue F, Wang X, Fei C, Wang M, Zhang T, Yao X, He P (2010a) Effects of diclazuril on apoptosis and mitochondrial transmembrane potential in second-generation merozoites of Eimeria tenella. Vet Parasitol 168(3–4):217–222
Zhou BH, Wang HW, Wang XY, Zhang LF, Zhang KY, Xue FQ (2010b) Eimeria tenella: effects of diclazuril treatment on microneme genes expression in second-generation merozoites and pathological changes of caeca in parasitized chickens. Exp Parasitol 125(3):264–270
Zhou BH, Wang HW, Xue FQ, Wang XY, Yang FK, Ban MM, Xin RX, Wang CC (2010c) Actin-depolymerizing factor of second-generation merozoite in Eimeria tenella: clone, prokaryotic expression, and diclazuril-induced mRNA expression. Parasitol Res 106(3):571–576
Zhou BH, Shen XJ, Wang HW, Li T, Xue FQ (2012) Receptor for activated C kinase ortholog of second-generation merozoite in Eimeria tenella: clone, characterization, and diclazuril-induced mRNA expression. Parasitol Res 111(4):1447–1455
Zhou BH, Wang HW, Zhao ZS, Liu M, Yan WC, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Xue FQ (2013) A novel serine/threonine protein phosphatase type 5 from second-generation merozoite of Eimeria tenella is associated with diclazuril-induced apoptosis. Parasitol Res 112(4):1771–1780
Acknowledgments
This research was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31472238 and 31101855) and Student Research Training Program (No. 2011046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Ej., Zhou, Bh., Wang, Xy. et al. Effect of diclazuril on intestinal morphology and SIgA expression in chicken infected with Eimeria tenella . Parasitol Res 113, 4057–4064 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4074-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4074-7