Abstract
Background
Accounting for tumor heterogeneity, cancer stem cells (CSC) are involved in tumor metastasis, relapse, and drug resistance. Genes regulating CSC characteristics in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) were explored and validated in this study.
Methods
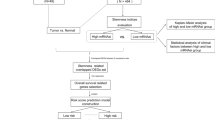
The mRNA stemness index (mRNAsi) of more than 500 LUAD cases from The Cancer Genome Atlas database were calculated using a one-class logistic regression machine learning algorithm based on the mRNA expression of pluripotent stem cells and their differentiated progeny. mRNAsi-related key genes were identified by weighted correlation network analysis. The expression levels and prognostic roles of key genes were analyzed in Oncomine, PrognoScan, and Kaplan–Meier plotter databases, and validated using data from our center.
Results
The mRNAsi was significantly higher in LUAD compared with normal lung tissues. LUAD patients of advanced stage exhibited a higher mRNAsi and worse overall survival (OS). Eight key genes were identified: heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 (HSPA4), cell division cycle associated 7 (CDCA7), cell division cycle 20 (CDC20), cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), CAP-GLY domain containing linker protein 1 (CLIP1), cyclin B1 (CCNB1), H2A histone family, member X (H2AFX), and Bloom syndrome, RecQ helicase-like (BLM). These genes were differentially expressed in various types of malignancies and validated in the LUAD cases. LUAD patients with low expression of CDC20, CDK1, CCNB1, H2AFX, or BLM had a significantly better OS, whereas OS was reduced for patients with low expression of CLIP1. In addition, the expression of CDCA7 did not significantly impact the OS of LUAD patients. The protein–protein interaction networks evaluated by STRING demonstrated strong relationships between these key genes, which were validated in our cases.
Conclusions
The mRNAsi was significantly higher in LUAD compared with normal samples. Eight mRNAsi-related key genes were associated with prognosis and the cell cycle, and were strongly correlated with each other and differentially expressed in tumor and normal samples. We provide a new strategy for exploring stemness-related genes in LUAD cases.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LUAD:
-
Lung adenocarcinoma
- CSC:
-
Cancer stem cells
- mRNAsi:
-
MRNA expression-based-stemness index
- OCLR:
-
One-class logistic regression
- WGCNA:
-
Weighted correlation network analysis
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas database
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- GS:
-
Gene significance
- MM:
-
Module membership
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology analysis
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis
- CDCA7:
-
Heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 (HSPA4), cell division cycle associated 7
- CDC20:
-
Cell division cycle 20
- CDK1:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1
- CLIP1:
-
CAP-GLY domain containing linker protein 1
- CCNB1:
-
Cyclin B1
- H2AFX:
-
H2A histone family, member X
- BLM:
-
Bloom syndrome, RecQ helicase-like
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- NSCLC:
-
Resistance of non-small cell lung cancer
References
Bonner WM, Redon CE, Dickey JS, Nakamura AJ, Sedelnikova OA, Solier S, Pommier Y (2008) GammaH2AX and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8:957–967
Bonnet D, Dick JE (1997) Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med 3:730–737
Colaprico A, Silva TC, Olsen C, Garofano L, Cava C, Garolini D, Sabedot TS, Malta TM, Pagnotta SM, Castiglioni I, Ceccarelli M, Bontempi G, Noushmehr H (2016) TCGAbiolinks: an R/bioconductor package for integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res 44:e71
Croteau DL, Popuri V, Opresko PL, Bohr VA (2014) Human RecQ helicases in DNA repair, recombination, and replication. Annu Rev Biochem 83:519–552
D'Alessandro M, Hnia K, Gache V, Koch C, Gavriilidis C, Rodriguez D, Nicot AS, Romero NB, Schwab Y, Gomes E, Labouesse M, Laporte J (2015) Amphiphysin 2 orchestrates nucleus positioning and shape by linking the nuclear envelope to the actin and microtubule cytoskeleton. Dev Cell 35:186–198
Desai TJ, Brownfield DG, Krasnow MA (2014) Alveolar progenitor and stem cells in lung development, renewal and cancer. Nature 507:190–194
Ferone G, Song JY, Sutherland KD, Bhaskaran R, Monkhorst K, Lambooij JP, Proost N, Gargiulo G, Berns A (2016) SOX2 is the determining oncogenic switch in promoting lung squamous cell carcinoma from different cells of origin. Cancer Cell 30:519–532
Gavet O, Pines J (2010) Progressive activation of CyclinB1-Cdk1 coordinates entry to mitosis. Dev Cell 18:533–543
GBD Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators (2016) Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388:1459–1544
German J (1997) Bloom’s syndrome. XX. The first 100 cancers. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 93:100–106
Guiu J, Bergen DJ, De Pater E, Islam AB, Ayllon V, Gama-Norton L, Ruiz-Herguido C, Gonzalez J, Lopez-Bigas N, Menendez P, Dzierzak E, Espinosa L, Bigas A (2014) Identification of Cdca7 as a novel Notch transcriptional target involved in hematopoietic stem cell emergence. J Exp Med 211:2411–2423
Held T, Barakat AZ, Mohamed BA, Paprotta I, Meinhardt A, Engel W, Adham IM (2011) Heat-shock protein HSPA4 is required for progression of spermatogenesis. Reproduction 142:133–144
Heng WS, Gosens R, Kruyt F (2019) Lung cancer stem cells: origin, features, maintenance mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. Biochem Pharmacol 160:121–133
Kapanidou M, Curtis NL, Bolanos-Garcia VM (2017) Cdc20: at the crossroads between chromosome segregation and mitotic exit. Trends Biochem Sci 42:193–205
Kato T, Daigo Y, Aragaki M, Ishikawa K, Sato M, Kaji M (2012) Overexpression of CDC20 predicts poor prognosis in primary non-small cell lung cancer patients. J Surg Oncol 106:423–430
Lanczky A, Nagy A, Bottai G, Munkacsy G, Szabo A, Santarpia L, Gyorffy B (2016) miRpower: a web-tool to validate survival-associated miRNAs utilizing expression data from 2178 breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 160:439–446
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform 9:559
Li M, Yang J, Zhou W, Ren Y, Wang X, Chen H, Zhang J, Chen J, Sun Y, Cui L, Liu X, Wang L, Wu C (2017) Activation of an AKT/FOXM1/STMN1 pathway drives resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Br J Cancer 117:974–983
Liu WT, Wang Y, Zhang J, Ye F, Huang XH, Li B, He QY (2018) A novel strategy of integrated microarray analysis identifies CENPA, CDK1 and CDC20 as a cluster of diagnostic biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett 425:43–53
Malta TM, Sokolov A, Gentles AJ, Burzykowski T, Poisson L, Weinstein JN, Kaminska B, Huelsken J, Omberg L, Gevaert O, Colaprico A, Czerwinska P, Mazurek S, Mishra L, Heyn H, Krasnitz A, Godwin AK, Lazar AJ, Stuart JM, Hoadley KA, Laird PW, Noushmehr H, Wiznerowicz M (2018) Machine learning identifies stemness features associated with oncogenic dedifferentiation. Cell 173:338–354
Malumbres M (2014) Cyclin-dependent kinases. Genome Biol 15:122
Martín-Cortázar C, Chiodo Y, Jiménez RP et al (2019) CDCA7 finely tunes cytoskeleton dynamics to promote lymphoma migration and invasion. Haematologica 105:730–740
Mizuno H, Kitada K, Nakai K, Sarai A (2009) PrognoScan: a new database for meta-analysis of the prognostic value of genes. Bmc Med Genom 2:18
Mounir M, Lucchetta M, Silva TC, Olsen C, Bontempi G, Chen X, Noushmehr H, Colaprico A, Papaleo E (2019) New functionalities in the TCGAbiolinks package for the study and integration of cancer data from GDC and GTEx. Plos Comput Biol 15:e1006701
Ochieng JK, Schilders K, Kool H, Boerema-De MA, Buscop-Van KM, Gontan C, Smits R, Grosveld FG, Wijnen RM, Tibboel D, Rottier RJ (2014) Sox2 regulates the emergence of lung basal cells by directly activating the transcription of Trp63. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 51:311–322
Osthus RC, Karim B, Prescott JE, Smith BD, McDevitt M, Huso DL, Danq CV (2005) The Myc target gene JPO1/CDCA7 is frequently overexpressed in human tumors and has limited transforming activity in vivo. Cancer Res 65:5620–5627
Pan S, Zhan Y, Chen X, Wu B, Liu B (2019) Identification of biomarkers for controlling cancer stem cell characteristics in bladder cancer by network analysis of transcriptome data stemness indices. Front Oncol 9:613
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ, Kincead-Beal C, Kulkarni P, Varambally S, Ghosh D, Chinnaiyan AM (2007) Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression profiles. Neoplasia 9:166–180
Saito M, Shiraishi K, Kunitoh H, Takenoshita S, Yokota J, Kohno T (2016) Gene aberrations for precision medicine against lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci 107:713–720
Singh S, Chellappan S (2014) Lung cancer stem cells: molecular features and therapeutic targets. Mol Aspects Med 39:50–60
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A, Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork P, Jensen LJ, Mering CV (2019) STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D607–D613
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ, Van Schil PE, Garg K, Austin JHM, Asamura H, Rusch VW, Hirsch FR, Scagliotti G, Mitsudomi T, Huber RM, Ishikawa Y, Jett J, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Sculier J, Takahashi T, Tsuboi M, Vansteenkiste J, Wistuba I, Yang P, Aberle D, Brambilla C, Flieder D, Franklin W, Gazdar A, Gould M, Hasleton P, Henderson D, Johnson B, Johnson D, Kerr K, Kuriyama K, Lee JS, Miller VA, Petersen I, Roggli V, Rosell R, Saijo N, Thunnissen E, Tsao M, Yankelewitz D (2011) International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 6:244–285
Wu CY, Lin CT, Wu MZ, Wu KJ (2011) Induction of HSPA4 and HSPA14 by NBS1 overexpression contributes to NBS1-induced in vitro metastatic and transformation activity. J Biomed Sci 18:1
Xu X, Rock JR, Lu Y, Futtner C, Schwab B, Guinney J, Hogan BL, Onaitis MW (2012) Evidence for type II cells as cells of origin of K-Ras-induced distal lung adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:4910–4915
Zhao M, Lu T, Huang Y, Yin J, Jiang T, Li M, Yang X, Zhan C, Feng M, Wang Q (2019) Survival and long-term cause-specific mortality associated with stage ia lung adenocarcinoma after wedge resection vs. segmentectomy: a population-based propensity score matching and competing risk analysis. Front Oncol 9:593
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank International Science Editing Co. for the language editing service.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.: 81672268).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethics approval
This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China (Approval No. B2017-042).
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
The RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) profiles and corresponding clinical phenotypes of human LUAD and normal lung samples were identified from the TCGA database (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov).
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, M., Chen, Z., Zheng, Y. et al. Identification of cancer stem cell-related biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma by stemness index and weighted correlation network analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146, 1463–1472 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03194-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03194-x