Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the feasibility and efficacy of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) unsuitable for standard loco-regional therapies.
Materials and methods
Patients with 1–3 inoperable HCC lesions with diameter ≤6 cm were treated by SBRT. According to lesions size and liver function, two prescription regimens were adopted: 48–75 Gy in three fractions or 36–60 Gy in six fractions. SBRT was delivered using the volumetric modulated arc therapy technique with flattening filter-free photon beams. The primary end points of this study were in-field local control (LC) and toxicity. Secondary end points were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS).
Results
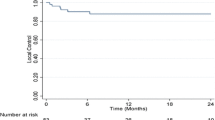
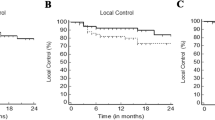
Forty-three patients with 63 HCC lesions were irradiated. All patients had Child–Turcotte–Pugh class A or B disease. Thirty lesions (48 %) were treated with 48–75 Gy in three consecutive fractions, and 33 (52 %) received 36–60 Gy in six fractions. Median follow-up was 8 months (range 3–43 months). Actuarial LC at 6, 12 and 24 months was 94.2 ± 3.3, 85.8 ± 5.5 and 64.4 ± 11.5 %, respectively. A biological equivalent dose (BED) >100 Gy and GTV size were significant prognostic factors for LC in univariate analysis (p < 0.001 and p < 0.02). Median OS was 18.0 ± 5.8 months. Actuarial OS at 6, 12 and 24 months was 91.1 ± 4.9, 77.9 ± 8.2 and 45.3 ± 14.0 %, respectively. Univariate analysis showed that OS is correlated with LC (p < 0.04), BED >100 (p < 0.05) and cumulative gross tumor volume GTV <5 cm (p < 0.04). Median PFS was 8 months, with a 1-year PFS rate of 41 %. A significant (≥grade 3) toxicity was observed in seven patients (16 %) 2–6 months after the completion of the treatment. No classic radiation-induced liver disease was observed.
Conclusion
Stereotactic body radiation therapy is a safe and effective therapeutic option for HCC lesions unsuitable to standard loco-regional therapies, with acceptable local control rates and low treatment-related toxicity. The significant correlation between LC and higher doses and between LC and OS supports the clinical value of SBRT in these patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andolino DL, Johnson CS, Maluccio M et al (2011) Stereotactic body radio-therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:e447–e453
Bibault JE, Dewas S, Vautravers-Dewas C et al (2013) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic factors of local control, overall survival, and toxicity. PLoS One 8:e77472
Bujold A, Massey CA, Kim JJ et al (2012) Sequential phase I and II trials of stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 44:1659
Cardenes HR, Price TR, Perkins SM et al (2010) Phase I feasibility trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol 12:218–225
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z et al (2009) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:25–34
Choi BO, Choi IB, Jang HS et al (2008) Stereotactic body radiation therapy with or without transarterial chemoembolization for patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma: preliminary analysis. BMC Cancer 8:351
Culleton S, Jiang H, Haddad CR et al (2014) Outcomes following definitive stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with Child–Turcotte–Pugh B or C hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 111:412–417
Dawson LA, Normolle D, Balter JM, McGinn C, Lawrence T, Ten Haken R (2002) Analysis of radiation induced liver disease using the Lyman NTCP model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:810–821
Dewas S, Bibault JE, Mirabel X et al (2012) Prognostic factors affecting local control of hepatic tumors treated by stereotactic body radiation therapy. Radiat Oncol 7:166
Eisenhauer E, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumors: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Eriguchi T, Takeda A, Sanuki N et al (2013) Acceptable toxicity after stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver tumors adjacent to the central biliary system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:1006–1011
European Association for the Study of the Liver and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (2012) EASL–EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 56:908–943
Ferlay J, Shin H, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin D (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127:2893–2917
Goodman KA, Wiegner EA, Maturen KE et al (2010) Dose-escalation study of single-fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78:486–493
Herfarth KK, Debus J, Lohr F et al (2001) Stereotactic single-dose radiation therapy of liver tumors: results of a phase I/II trial. J Clin Oncol 19:164–170
Huang WY, Jen YM, Lee MS et al (2012) Stereotactic body radiation therapy in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:355–361
Jacob R, Turley F, Redden D et al (2014) Adjuvant stereotactic body radiotherapy following transarterial chemoembolization in patients with non-resectable hepatocellular carcinoma tumours of ≥3 cm. HPB, Oxford
Kang JK, Kim MS, Cho CK et al (2012) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma as a local salvage treatment after incomplete transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer 118:5424–5431
Klein J, Dawson LA (2013) Hepatocellular carcinoma radiation therapy: review of evidence and future opportunities. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87:22–32
Kwon JH, Bae SH, Kim JY et al (2010) Long-term effect of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma ineligible for local ablation therapy or surgical resection. Stereotactic radiotherapy for liver cancer. BMC Cancer 10:475
Lawrence TS, Robertson JM, Anscher MS, Jirtle R, Ensminger W, Fajardo L (1995) Hepatic toxicity resulting from cancer treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31:1237–1248
Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J (1999) Intention-to treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation. Hepatology 30:1434–1440
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V et al (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:378–390
Llower JM, Bruix J (2003) Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 37:429–442
Mendez Romero A, Wunderink W, Hussain SM et al (2006) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary and metastatic liver tumors: a single institution phase I–II study. Acta Oncol 45:831–837
Oliveri RS, Wetterslev J, Gluud C (2011) Transarterial (chemo)embolisation for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:CD004787
Park JH, Yoon SM, Lim YS et al (2013) Two-week schedule of hypofractionated radiotherapy as a local salvage treatment for small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 28:1638–1642
Que JY, Lin LC, Lin KL, Lin CH, Lin YW, Yang CC (2014) The efficacy of stereotactic body radiation therapy on huge hepatocellular carcinoma unsuitable for other local modalities. Radiat Oncol 9:120
Sanuki N, Takeda A, Oku Y et al (2014a) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective outcome analysis in 185 patients. Acta Oncol 53:399–404
Sanuki N, Takeda A, Kunieda E et al (2014b) Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 20:3100–3111
Scorsetti M, Arcangeli S, Tozzi A, Comito T, Alongi F, Navarria P (2013) Is stereotactic body radiation therapy an attractive option for unresectable liver metastases? A preliminary report from a phase 2 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86:336–342
Seo YS, Kim MS, Yoo SY et al (2010) Preliminary result of stereotactic body radiotherapy as a local salvage treatment for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol 102:209–214
Tse RV, Hawkins M, Lockwood G et al (2008) Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26:657–664
Xi M, Zhang L, Zhao L et al (2013) Effectiveness of stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein and/or inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis. PLoS One 8:e63864
Zhong NB, Lv GM, Chen ZH (2014) Stereotactic body radiotherapy combined with transarterial chemoembolization for huge (≥10 cm) hepatocellular carcinomas: a clinical study. Mol Clin Oncol 2:839–844
Conflict of interest
L. Cozzi acts as Scientific Advisor to Varian Medical Systems and is Clinical Research Scientist at Humanitas cancer center. All other co-authors have no conflicts of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scorsetti, M., Comito, T., Cozzi, L. et al. The challenge of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): results of a single-institutional experience on stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 1301–1309 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-1929-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-1929-y