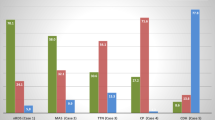
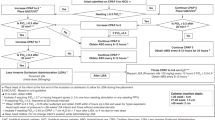
Abstract
Less invasive surfactant administration or minimally invasive surfactant therapy (LISA/MIST) has been proposed for the administration of surfactant in preterm infants without intubation. The aim of our survey was to assess the rate of utilization, premedication as well as technique and equipment used for LISA/MIST. Furthermore, attitudes and experiences in regard to indications, side effects, and efficacy should be assessed. An online-based survey was sent to 324 neonatologists from different centers within 37 European countries between December 2015 and March 2016. Of those 165 who responded (response rate 51%), 86 (52%) were using LISA/MIST. It is regarded the standard procedure for surfactant administration by 41%, with a wide variation in personal views on patient selection in terms of indication, appropriate gestational and postnatal age. Policies concerning premedication, devices, and technique of LISA/MIST differed widely. Side effects like surfactant reflux, bradycardia, and hypoxia were observed by 77% of neonatologists. Of neonatologists inexperienced in LISA/MIST, 89% would consider utilizing it in the future. Perceived efficacy of LISA/MIST was high (52%) to medium (33%).
Conclusion: The use of LISA/MIST within Europe is widespread. There is a wide variation concerning all aspects of LISA in daily clinical routine and different views on when and how LISA should be performed.
What is Known: • Noninvasive surfactant administration has been the subject of randomized controlled trials and has found its way into clinical routine. |
What is New: • Noninvasive surfactant administration techniques are widely applied in European neonatal units. • There is a wide variety of equipment used and techniques applied for less invasive surfactant delivery as well as different views on the indications and perceived efficacy of this intervention. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- INSURE:
-
Intubation, surfactant, extubation
- LISA:
-
Less invasive surfactant administration
- MIST:
-
Minimally invasive surfactant administration
- NICU:
-
Neonatal intensive care unit
- RDS:
-
Respiratory distress syndrome
- SWI:
-
Surfactant without intubation
References
Ali E, Abdel WM, Alsalami Z, Abouseif H, Gottschalk T, Rabbani R, Zarychanski R, Abou-Setta AM (2016) New modalities to deliver surfactant in premature infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 29:3519–3524
Anand KJ (2001) International Evidence-Based Group for Neonatal Pain: consensus statement for the prevention and management of pain in the newborn. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 155:173–180
Borszewska-Kornacka MK, Kostuch M, Korbal P, Krajewski P, Polish RDS Study Group (2015) Strategies of using surfactant results of the first polish national survey of daily practice. Dev Period Med 19:271–276
Chaudhary R, Chonat S, Gowda H, Clarke P, Curley A (2009) Use of premedication for intubation in tertiary neonatal units in the United Kingdom. Paediatr Anaesth 19:653–658
Committee on Fetus and Newborn and Section on Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine (2016) Prevention and management of procedural pain in the neonate: an update. Pediatrics 137:e20154271
Dargaville PA, Aiyappan A, Cornelius A, Williams C, De Paoli AG (2011) Preliminary evaluation of a new technique of minimally invasive surfactant therapy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 96:F243–F248
Dargaville PA, Aiyappan A, De Paoli AG, Kuschel CA, Kamlin CO, Carlin JB, Davis PG (2013) Minimally-invasive surfactant therapy in preterm infants on continuous positive airway pressure. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 98:F122–F126
De Luca D, Minucci A, Gentile L, Capoluongo ED (2014) Surfactant inadvertent loss using feeding catheters or endotracheal tubes. Am J Perinatol 31:209–212
Dekker J, Lopriore E, Rijken M, Rijntjes-Jacobs E, Smits-Wintjens V, Te Pas A (2016) Sedation during minimal invasive surfactant therapy in preterm infants. Neonatology 109:308–313
Göpel W, Kribs A, Hartel C, Avenarius S, Teig N, Groneck P, Olbertz D, Roll C, Vochem M, Weller U, von der WA, Wieg C, Wintgens J, Preuss M, Ziegler A, Roth B, Herting E (2015) Less invasive surfactant administration is associated with improved pulmonary outcomes in spontaneously breathing preterm infants. Acta Paediatr 104:241–246
Göpel W, Kribs A, Ziegler A, Laux R, Hoehn T, Wieg C, Siegel J, Avenarius S, von der WA, Vochem M, Groneck P, Weller U, Moller J, Hartel C, Haller S, Roth B, Herting E (2011) Avoidance of mechanical ventilation by surfactant treatment of spontaneously breathing preterm infants (AMV): an open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 378:1627–1634
Isayama T, Iwami H, McDonald S, Beyene J (2016) Association of noninvasive ventilation strategies with mortality and bronchopulmonary dysplasia among preterm infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 316:611–624
Kanmaz HG, Erdeve O, Canpolat FE, Mutlu B, Dilmen U (2013) Surfactant administration via thin catheter during spontaneous breathing: randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics 131:e502–e509
Kribs A, Hartel C, Kattner E, Vochem M, Kuster H, Moller J, Muller D, Segerer H, Wieg C, Gebauer C, Nikischin W, Wense A, Herting E, Roth B, Gopel W (2010) Surfactant without intubation in preterm infants with respiratory distress: first multi-center data. Klin Padiatr 222:13–17
Kribs A, Pillekamp F, Hunseler C, Vierzig A, Roth B (2007) Early administration of surfactant in spontaneous breathing with nCPAP: feasibility and outcome in extremely premature infants (postmenstrual age </=27 weeks). Paediatr Anaesth 17:364–369
Kribs A, Roll C, Gopel W, Wieg C, Groneck P, Laux R, Teig N, Hoehn T, Bohm W, Welzing L, Vochem M, Hoppenz M, Buhrer C, Mehler K, Stutzer H, Franklin J, Stohr A, Herting E, Roth B (2015) Nonintubated surfactant application vs conventional therapy in extremely preterm infants: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr 169:723–730
Kribs A, Vierzig A, Hunseler C, Eifinger F, Welzing L, Stutzer H, Roth B (2008) Early surfactant in spontaneously breathing with nCPAP in ELBW infants--a single centre four year experience. Acta Paediatr 97:293–298
Niemarkt HJ, Kuypers E, Jellema R, Ophelders D, Hutten M, Nikiforou M, Kribs A, Kramer BW (2014) Effects of less-invasive surfactant administration on oxygenation, pulmonary surfactant distribution, and lung compliance in spontaneously breathing preterm lambs. Pediatr Res 76:166–170
Oncel MY, Arayici S, Uras N, Alyamac-Dizdar E, Sari FN, Karahan S, Canpolat FE, Oguz SS, Dilmen U (2016) Nasal continuous positive airway pressure versus nasal intermittent positive-pressure ventilation within the minimally invasive surfactant therapy approach in preterm infants: a randomised controlled trial. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 101:F323–F328
Rojas-Reyes MX, Morley CJ, Soll R (2012) Prophylactic versus selective use of surfactant in preventing morbidity and mortality in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000510.pub2
Simon L, Trifa M, Mokhtari M, Hamza J, Treluyer JM (2004) Premedication for tracheal intubation: a prospective survey in 75 neonatal and pediatric intensive care units. Crit Care Med 32:565–568
Speer CP, Sweet DG, Halliday HL (2013) Surfactant therapy: past, present and future. Early Hum Dev 89(Suppl 1):S22–S24
Sweet DG, Carnielli V, Greisen G, Hallman M, Ozek E, Plavka R, Saugstad OD, Simeoni U, Speer CP, Vento M, Visser GH, Halliday HL (2016) European consensus guidelines on the management of respiratory distress syndrome - 2016 update. Neonatology 111:107–125
Verder H, Agertoft L, Albertsen P, Christensen NC, Curstedt T, Ebbesen F, Greisen G, Hobolth N, Holm V, Jacobsen T (1992) Surfactant treatment of newborn infants with respiratory distress syndrome primarily treated with nasal continuous positive air pressure. A pilot study. Ugeskr Laeger 154:2136–2139
Verder H, Robertson B, Greisen G, Ebbesen F, Albertsen P, Lundstrom K, Jacobsen T (1994) Surfactant therapy and nasal continuous positive airway pressure for newborns with respiratory distress syndrome. Danish-Swedish Multicenter Study Group. N Engl J Med 331:1051–1055
Welzing L, Kribs A, Eifinger F, Huenseler C, Oberthuer A, Roth B (2010) Propofol as an induction agent for endotracheal intubation can cause significant arterial hypotension in preterm neonates. Paediatr Anaesth 20:605–611
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Elena Neumann, Ruth Creutzfeldt, Dimitra Stavropoulou for linguistic advice, and Prof. Ewa Helwich, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, Institute of Mother and Child, Warsaw, Poland, for providing additional information on the use of LISA in Poland, and all participants of this survey—Austria: Universitätsklinik für Kinder-und Jugendheilkunde, Salzburg: M. Wald; Innsbruck Medical University: U. Kiechl-Kohlendorfer; Medical University Graz: B. Urlesberger. Belgium: Centre Hospitalier Régional de la Citadelle, Liège: V. Rigo; C.H.U. Saint-Pierre, Bruxelles: M. Tackoen; Antwerp University Hospital: P. van Reempts; Universitair Ziekenhuis Bruxelles: F. Cools; Ziekenhuis Oost-Limburg, Genk: C. Theyskens; CHC-Site St Vincent, Liege-Rocourt: P. Maton; Ghent University Hospital: K. Smets. Bulgaria: University Hospital “St. Anna”, Varna: M. Marinova-Achkar; University Hospital “Prof. St. Kirkovich”, Stara Zagora: H. Mumdzhiev; UMHAT “St George” Neonatology Clinic, Plovdiv: M. Krasteva. Bosnia and Herzegovina: University Clinical Center Sarajevo: S. Heljic. Cyprus: Hospital Archbishop Makarios III, Nicosia: P. Yiallouros. Croatia: University Hospital Osijek: V. Milas; University Hospital Center Rijeka: I. Čače; University Hospital Center “Sisters of Mercy”, Zagreb: R. Ribičić. Czech Republic: General University Hospital Prague: R. Plavka; The Institute for the Care of Mother and Child, Prague-Podoli: Z. Straňák. Denmark: Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet: G. Greisen; Hans Christian Andersen Children’s Hospital: G. Zachariassen. Estonia: Tartu University Hospital: H. Varendi. Finland: Tampere University Hospital: O. Tammela; Oulu University Hospital: M. Hallmann/T. Saarela. France: Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Limoges: A. Bedu; Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire de Strasbourg: D. Astruc; Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire de Tours: E. Saliba; Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Caen: B. Guillois/C. Alexandre; Hôpital de la Croix-Rousse, Lyon: J. Picaud; Groupe Hospitalier Cochin-Broca-Hôtel Dieu, Paris: P. Jarreau; Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Montpellier: C. Milesi; University Children’s Hospital, Bordeaux: O. Brissaud; CHU Estaing: M. Lang; CHRU Rennes: C. Lallemant; CHU Amiens-Picardie: P. Tourneux; Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nice: M. Saint-Faust; CHU de Nîmes: M. Di Maio; Groupe Hospitalier du Havre: J. Mourdie; Centre Hospitalier de la Côte Basque: P. Jouvencel; Centre Hospitalier Félix Guyon, Réunion: D. Ramful; North University Hospital, Marseille: C. Grosse. Germany: Universitätsklinikum Würzburg: E. Frieauff; Universitätsklinikum Schleswig-Holstein, Campus Lübeck: W. Göpel/C. Härtel; Universitätsklinikum Tübingen: A. Franz; Universitätsklinikum Ulm: R. Hopfner; Universitätsklinikum des Saarlandes, Homburg: S. Meyer; Schwarzwald-Baar Klinikum Villingen: M. Henschen; Hegau-Bodensee-Klinikum Singen: A. Trotter; Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg: D. Frommhold; Universitätsklinikum Dresden: D. Konstantelos; Universitätsklinikum Leipzig: C. Gebauer; Olgahospital Stuttgart: M. Vochem; Universitätsmedizin Göttingen: H. Küster; Universitätsmedizin Mannheim: T. Schaible; LMU, Klinikum der Universität München: A. Flemmer; Universitätsklinikum Bonn: A. Müller; Vestische Kinder- und Jugendklinik Datteln: C. Roll; Universitätsklinikum Düsseldorf: T. Höhn; Universitätsklinikum Essen: U. Felderhoff-Müser; Universitätsklinikum Frankfurt am Main: R. Schlösser; Universitätsklinikum Hamburg-Eppendorf: D. Singer; Medizinische Hochschule Hannover: B. Bohnhorst; Universitätsmedizin Mainz: A. Kidszun; Klinikum Saarbrücken: J. Möller; Universitätsklinikum Greifswald: M. Heckmann; Klinik für Kinder- und Jugendmedizin Speyer: A. Bosk; Kinderklinik Uniklinik Köln: A. Kribs; Universitätsklinikum Freiburg: R. Hentschel. Greece: Aristotle University - General Hospital Papageorgiou, Thessaloniki: P. Karagianni/K. Serafidis; “Mitera” General Maternity and Pediatric Clinic, Athens: M. Saklamaki-kontou; “Lito” Maternity Hospital, Athens: V. Delivoria; Helena Venizelou Perinatal Center, Athens: H. Salvanos; Alexandras Hospital General, Athens: G. Baroutis. Hungary: Semmelweis University, Budapest: M. Szabo; Medical University of Pécs: T. Erlt; Dél-pesti Kórház és Rendelőintézet, Budapest: M. C. László. Ireland: National University of Ireland, Galway: D. O′ Donovan; University College Cork: E. Dempsey; Coombe Women & Infants University Hospital, Dublin: J. Miletin; Rotunda Hospital, Dublin: N. McCallion. Italy: Azienda Ospedaliera di Padova: D. Trevisanuto; Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Pisana: A. Boldrini; Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico-Università degli Studi di Milano: F. Mosca; Ospedale dei Bambini ´V. Buzzi’, Milan: G. Lista; Ospedale Evangelico Villa Betania, Naples: F. Messina; Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Federico II, Naples: F. Raimondi; Careggi University Hospital of Florence: C. Dani; University La Sapienza, Rome: M. De Curtis; Ospedale San Giovanni Calibita FBF Isola Tiberina, Rome: L. Orfeo; Ospedale San Gerardo, Monza: P. Tagliabue; P.O. SS Annunziata, Naples: T. Vacchiano; Azienda Ospedaliera di Venere e Giovanni XXIII, Bari: A. del Vecchio. Latvia: Pauls Stradins Clinical University Hospital, Riga: V. Urtans. Lithuania: Hospital of Kaunas University of Medicine: R. Tamelienė; Vilnius University Childrens’ Hospital: A. Liubšys. Malta: Mater Dei Hospital: P. Soler. Moldavia: Institute for Mother and Child Health Care, Chisinau: V. Iesanu. Netherlands: Emma Children’s Hospital, Amsterdam: A. von Kaam; University Hospital Utrecht - Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital: F. Van Bel; Leiden University Medical Centre: A. te Pas; Beatrix Children’s Hospital, University of Groningen: A. Bos; Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen: W. de Boode. Norway: Oslo Rikshospitalet University Hospital: O. Saugstad; Barneklinikken Haukeland Sykehus, Bergen: H. Reigstad; University of Tromsø-Arctic, Tromsø: C. Klingenberg; Ålesund Hospital: W. Sivertsen; Vestre Viken Hospital, Drammen: K. Hochnowski; Sykehuset Østfold Hospital, Fredrikstad: S.H. Anderssen; Akershus University Hospital, Lørenskog: B. Nakstad. Poland: Olsztyn Hospital: J. Meller. Portugal: Centro Hospitalar de São João, Porto: H. Guimaraes; Maternidade Bissaya Barreto, Coimbra: C. Resende; Maternidade Daniel Matos, Coimbra: M. Afonso. Romania: “Polizu” Clinical Hospital, Bucharest: S. Stoicescu; Panait Sarbu Hospital, Bucharest: A. Toma; “Cuza Voda” Clinical Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Lasi: M. Stamatin. Slovakia: Jessenius Medical Faculty Martin/Comenius University Bratislava: M. Zibolen, K. Matasova; Klinika Neonatológie, Kosice: V. Chovanova. Slovenia: University Medical Centre Ljubljana: D. Paro-Panjan; University Medical Center Maribor: M. Treiber. Spain: Hospital General Universitario de Alicante: C. Tapia Collados; Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias: M. Jesus Ripalda; Hospital Clínic de Barcelona: F. Botet; Hospital de Navarra: A. Ocon; Complejo Hospitalario de Pontevedra: P. Suarez; Hospital Universitario de Salamanca: L. San Feliciano; Hospital Universitario Severo Ochoa, Madrid: E. Carrasco; Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Vigo: A. Guisan; Hospital Virgen de la Salud, Toledo: M. Redondo; University & Polytechnic Hospital La Fe, Valencia: M. Vento; Gregorio Marañon University Hospital, Madrid: M. Sanchez-Luna; Hospital Infantil La Paz, Madrid: F. Omeñaca; Complexo Hospitalario Universitario A Coruña: A. Avila-Alvarez; Hospital Sant Joan de Déu , Barcelona: M. Iriondo-Sanz; Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid: G. Carillo. Sweden: University Hospital, Umeå: S. Håkansson; Uppsala University: L. Hellström-Westas; Karolinska Institutet and University Hospital, Stockholm: K. Bohlin. Switzerland: University of Basel Children’s Hospital: S. Schulzke; Bern University Hospital: M. Nelle; Children’s Hospital Lucerne: M. Stocker; Geneva University Hospital: P. Rimensberger; University Hospital Zurich: C. Hagmann; Ostschweizer Kinderspital, St Gallen: D. Bailey. Turkey: Zekai Tahir Burak Maternity Teaching Hospital, Ankara: G. Kanmaz; Gazi University Hospital, Ankara: E. Ergenekon; Marmara University School of Medicine, Istanbul: E. Ozek; Firat University School of Medicine, Elazig: M. Aydin; Ataturk University Medical Faculty, Erzurum: K. Tekgündüz. Ukraine: Lviv National Medical University: K. Stepanovich. United Kingdom: Royal Maternity Hospital, Queen’s University, Belfast: D. Sweet; Imperial College London: P. Montaldo; Brighton and Sussex Medical School: H. Rabe; University Hospital of North Tees and University of Durham, Stockton-on-Tees: S. Gupta; Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals: P. Clarke; Northampton General Hospital: F. Thompson; Warrington Hospital: D. Webb; Blackpool Teaching Hospital: C. Rawlingson; Evelina London Children’s Hospital St Thomas: T. Watts; Great Ormond Street Hospital, London: Q. Mok; University Hospital of North Staffordshire, Stoke-on-Trent: K. Palmer; Oxford University Hospitals: C. Roehr.
Authors’ Contributions
Daniel Klotz conceived the study, designed the survey, contributed to data collection, analyzed data, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Ugo Porcaro designed the survey, collected data, analyzed data, and edited the manuscript. Thilo Fleck analyzed data, helped with translation, and edited the manuscript. Hans Fuchs contributed in study design, edited the survey, contributed in data collection and analysis, and edited the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No external funding was received for this study.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics committee of the University of Freiburg.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Patrick Van Reempts
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klotz, D., Porcaro, U., Fleck, T. et al. European perspective on less invasive surfactant administration—a survey. Eur J Pediatr 176, 147–154 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-016-2812-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-016-2812-9