Abstract
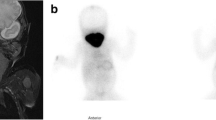
Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) due to thyroglobulin (TG) deficit is an autosomal recessive disease (OMIM #274700) characterized by hypothyroidism, goiter, low serum TG, and a negative perchlorate discharge test. The aim of this study was to perform the genetic analysis of the TG gene in two sisters born from consanguineus parents and affected by CH and low serum TG levels. The index patient and her sister were identified at neonatal screening for CH and treated with L-thyroxine (L-T4). After discontinuation of L-T4 therapy, hypothyroidism was confirmed, serum TG was undetectable, and no organification defect after 123I scintigraphy and perchlorate test was shown; thyroid ultrasound showed a eutopic gland of normal size. DNA was extracted from peripheral white blood cells of the two sisters and the father. All 48 exons of TG gene were amplified by polymerase chain reaction and subjected to direct sequencing. A novel homozygous point mutation in exon 10 of TG gene was identified in the patient and her sister. The mutation determined a stop codon at position 768 (R768X) resulting in an early truncated protein or in the complete absence of the protein. The father (euthyroid) was heterozygous carrier of the mutation. Conclusion: Genetic analysis of TG gene was performed in two sisters affected by CH. A novel point mutation of the TG gene determining a stop codon at position 768 of the protein was identified. The early truncated nonfunctioning protein or the absence of the protein due to the premature degradation of abnormal mRNA may be responsible of the observed phenotype.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowicz MJ, Targovnik HM, Varela V, Cochaux P, Krawiec L, Pisarev MA, Propato FV, Juvenal G, Chester HA, Vassart G (1992) Identification of a mutation in the coding sequence of the human thyroid peroxidase gene causing congenital goiter. J Clin Invest 90:1200–1204
Afink G, Kulik W, Overmars H, de Randamie J, Veenboer T, van Cruchten A, Craen M, Ris-Stalpers C (2008) Molecular characterization of iodotyrosine dehalogenase deficiency in patients with hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:4894–4901
Bizhanova A, Kopp P (2010) Genetics and phenomics of Pendred syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol 322:83–90
Caputo M, Rivolta CM, Gutnisky VJ, Gruñeiro-Papendieck L, Chiesa A, Medeiros-Neto G, González-Sarmiento R, Targovnik HM (2007) Recurrence of the p.R277X/p.R1511X compound heterozygous mutation in the thyroglobulin gene in unrelated families with congenital goiter and hypothyroidism: haplotype analysis using intragenic thyroglobulin polymorphisms. J Endocrinol 195:167–177
Citterio CE, Coutant R, Rouleau S, Miralles García JM, Gonzalez-Sarmiento R, Rivolta CM, Targovnik HM (2011) A new compound heterozygous for c.886C > T/c.2206C > T [p.R277X/p.Q717X] mutations in the thyroglobulin gene as a cause of foetal goitrous hypothyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 74:533–535
Dohán O, De la Vieja A, Paroder V, Riedel C, Artani M, Reed M, Ginter CS, Carrasco N (2003) The sodium/iodide Symporter (NIS): characterization, regulation, and medical significance. Endocr Rev 24:48–77
Gutnisky VJ, Moya CM, Rivolta CM, Domené S, Varela V, Toniolo JV, Medeiros-Neto G, Targovnik HM (2004) Two distinct compound heterozygous constellations (R277X/IVS34-1 G > C and R277X/R1511X) in the thyroglobulin (TG) gene in affected individuals of a Brazilian kindred with congenital goiter and defective TG synthesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:646–657
Hishinuma A, Fukata S, Nishiyama S, Nishi Y, Oh-Ishi M, Murata Y, Ohyama Y, Matsuura N, Kasai K, Harada S, Kitanaka S, Takamatsu J, Kiwaki K, Ohye H, Uruno T, Tomoda C, Tajima T, Kuma K, Miyauchi A, Ieiri T (2006) Haplotype analysis reveals founder effects of thyroglobulin gene mutations C1058R and C1977S in Japan. J Clin Endocrino Metab 91:3100–3104
Kim PS, Kwon OY, Arvan P (1996) An endoplasmic reticulum storage disease causing congenital goiter with hypothyroidism. J Cell Biol 133:517–527
Kim PS, Lee J, Jongsamak P, Menon S, Li B, Hossain SA, Bae JH, Panijpan B, Arvan P (2008) Defective protein folding and intracellular retention of thyroglobulin-R19K mutant as a cause of human congenital goiter. Mol Endocrinol 22:477–484
Lee J, Wang X, Di Jeso B, Arvan P (2009) The cholinesterase-like domain, essential in thyroglobulin trafficking for thyroid hormone synthesis, is required for protein dimerization. J Biol Chem 284:12752–12761
Medeiros-Neto G, Targovnik HM, Vassart G (1993) Defective thyroglobulin synthesis and secretion causing goiter and hypothyroidism. Endoc Rev 14:165–183
Medeiros-Neto G, Kim PS, Yoo SE, Vono J, Targovnik HM, Camargo R, Hossain SA, Arvan P (1996) Congenital hypothyroid goiter with deficient thyroglobulin. Identification of an endoplasmic reticulum storage disease with induction of molecular chaperones. J Clin Invest 98:2838–2844
Medeiros-Neto G, Knobel M, DeGroot LJ (2002) Genetic disorders of the thyroid hormone synthesis. In: Baxter JD (ed) Genetics in Endocrinology. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 375–402
Mendive FM, Rivolta CM, Moya CM, Vassart G, Targovnik HM (2001) Genomic organization of the human thyroglobulin gene: the complete intron-exon structure. Eur J Endocrinol 145:485–496
Moreno JC, Bikker H, Kempers MJ, van Trotsenburg AS, Baas F, de Vijlder JJ, Vulsma T, Ris-Stalpers C (2002) Inactivating mutations in the gene for thyroid oxidase 2 (THOX2) and congenital hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 347:95–102
Moreno JC, Klootwijk W, van Toor H, Pinto G, D'Alessandro M, Lèger A, Goudie D, Polak M, Grüters A, Visser TJ (2008) Mutations in the iodotyrosine deiodinase gene and hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 358:1811–1818
Park SM, Chatterjee VK (2005) Genetics of congenital hypothyroidism. J Med Genet 42:379–389
Rawitch AB, Litwer MR, Gregg J, Turner CD, Rouse JB, Hamilton JW (1984) The isolation of identical thyroxine containing amino acid sequences from bovine, ovine and porcine thyroglobulins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 118:423–429
Ricketts MH, Simons MJ, Parma J, Mercken L, Dong Q, Vassart G (1987) A nonsense mutation causes hereditary goitre in the Afrikander cattle and unmasks alternative splicing of thyroglobulin transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3181–3184
Rivolta CM, Targovnik HM (2006) Molecular advances in thyroglobulin disorders. Clin Chim Acta 374:8–24
Targovnik HM, Medeiros-Neto G, Varela V, Cochaux P, Wajchenberg BL, Vassart G (1993) A nonsense mutation causes human hereditary congenital goiter with preferential production of a 171-nucleotide-deleted thyroglobulin ribonucleic acid messenger. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 77:210–215
Targovnik HM, Esperante SA, Rivolta CM (2010) Genetics and phenomics of hypothyroidism and goiter due to thyroglobulin mutations. Mol Cell Endocrinol 322:44–55
Targovnik HM, Citterio CE, Rivolta CM (2011) Thyroglobulin gene mutations in congenital hypothyroidism. Horm Res Paediatr 75:311–321
Targovnik HM, Edouard T, Varela V, Tauber M, Citterio CE, González-Sarmiento R, Rivolta CM (2012) Two novel mutations in the thyroglobulin gene as cause of congenital hypothyroidism: identification a cryptic donor splice site in the exon 19. Mol Cell Endocrinol 348:313–321
Tonacchera M, Banco M, Lapi P, Di Cosmo C, Perri A, Montanelli L, Moschini L, Gatti G, Gandini D, Massei A, Agretti P, De Marco G, Vitti P, Chiovato L, Pinchera A (2004) Genetic analysis of TTF-2 gene in children with congenital hypothyroidism and cleft palate, congenital hypothyroidism, or isolated cleft palate. Thyroid 14:584–588
van de Graaf SA, Ris-Stalpers C, Pauws E, Mendive FM, Targovnik HM, de Vijlder JJ (2001) Up to date with human thyroglobulin. J Endocrinol 170:307–321
van de Graaf SA, Ris-Stalpers C, Veenboer GJ, Cammenga M, Santos C, Targovnik HM, de Vijlder JJ, Medeiros-Neto G (1999) A premature stop codon in thyroglobulin messenger RNA results in familial goiter and moderate hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:2537–2542
Vono-Toniolo J, Rivolta CM, Targovnik HM, Medeiros-Neto G, Kopp P (2005) Naturally occurring mutations in the thyroglobulin gene. Thyroid 15:1021–1033
Zamproni I, Grasberger H, Cortinovis F, Vigone MC, Chiumello G, Mora S, Onigata K, Fugazzola L, Refetoff S, Persani L, Weber G (2008) Biallelic inactivation of the dual oxidase maturation factor 2 (DUOXA2) gene as a novel cause of congenital hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:605–610
Acknowledgments
In memory of our mentor Professor Aldo Pinchera.
This work was supported by the following grants: Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica (MURST) and Ministero della Sanità, Ricerca Finalizzata. We are grateful to MURST and Ministero della Sanità for funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Patrizia Agretti and Giuseppina De Marco contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agretti, P., De Marco, G., Di Cosmo, C. et al. Congenital hypothyroidism caused by a novel homozygous mutation in the thyroglobulin gene. Eur J Pediatr 172, 959–964 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-1976-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-1976-9