Abstract
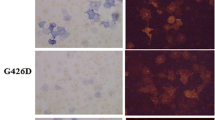
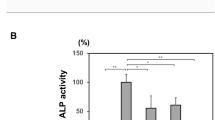
A total of 22 Japanese patients with hypophosphatasia were included in a study analysing the relationship between mutations in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) gene and the severity of the phenotype in Japanese patients with hypophosphatasia. The enzymatic activity of some of the identified mutant TNSALP proteins was also examined using corresponding expression vectors. Eighteen mutations, including 6 novel ones, were identified in the patients. Among them, the common mutations were F310L and T1559del. Of note, five patients with F310L mutation in one of the alleles exhibited a relatively mild phenotype without respiratory complications despite its perinatal onset. In contrast, the T1559del mutation is associated with perinatal lethal and infantile forms when not found in patients with the F310L mutation. The genotype-phenotype relationship was, to some extent, consistent with the enzymatic activity of the mutant ALP proteins; mutations K207E and G409C found in a surviving case of infantile hypophosphatasia, as well as F310L, retained some residual activities, whereas T1559del caused a complete loss of activity. Conclusion:In Japanese patients, the common mutations F310L and T1559del are associated with the relatively mild and lethal forms of hypophosphatasia, respectively. Our results may enhance the importance of genotyping patients with hypophosphatasia to predict their prognosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TNSALP :
-
tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase
References
Antonarakis SE, the Nomenclature Working Group (1998) Recommendations for a nomenclature system for human gene mutations. Hum Mutat 11: 1–3
Barcia JP, Strife CF, Langman CB (1997) Infantile hypophosphatasia: treatment options to control hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and chronic bone demineralization. J Pediatr 130: 825–828
Cai G, Michigami T, Yamamoto T, Yasui N, Satomura K, Yamagata M, Shima M, Nakajima S, Mushiake S, Okada S, Ozono K (1998) Analysis of localization of mutated tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase proteins associated with neonatal hypophosphatasia using green fluorescent protein chimeras. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83: 3936–3942
Henthorn PS, Whyte MP (1992) Missense mutations of the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene in hypophosphatasia. Clin Chem 38: 2501–2505
Henthorn PS, Raducha M, Fedde KN, Lafferty MA, Whyte MP (1992) Different missense mutations at the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene locus in autosomal recessively inherited forms of mild and severe hypophosphatasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 9924–9928
Herasse M, Spentchian M, Taillandier A, Mornet E (2002) Evidence of a founder effect for the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) gene E174K mutation in hypophosphatasia patients. Eur J Hum Genet 10: 666–668
Lia-Baldini AS, Muller F, Taillandier A, Gibrat JF, Mouchard M, Robin B, Simon-Bouy B, Serre JL, Aylsworth AS, Bieth E, Delanote S, Freisinger P, Hu JC, Krohn HP, Nunes ME, Mornet E (2001) A molecular approach to dominance in hypophosphatasia. Hum Genet 109: 99–108
Lowry OH, Roberts NR, Wu ML, Hixon WS, Crawford EJ (1954) The quantitative histochemistry of brain. II. Enzyme measurements. J Biol Chem 207: 19–37
Mochizuki H, Saito M, Michigami T, Ohashi H, Koda N, Yamaguchi S, Ozono K (2000) Severe hypercalcemia and respiratory insufficiency associated with infantile hypophosphatasia caused by two novel mutations of the TNSALP gene. Eur J Pediatr 159: 375–379
Moore CA, Curry CJR, Henthorn PS, Smith JA, Smith JC, O’Lague P, Coburn SP, Weaver DD, Whyte MP(1999) Mild autosomal dominant hypophosphatasia: in utero presentation in two families. Am J Med Genet 86: 410–415
Mornet E (2000) Hypophosphatasia: the mutations in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene. Hum Mutat 15: 309–315
Mornet E, Taillandier A, Peyramaure S, Kaper F, Muller F, Brenner R, Bussiere P, Freisinger P, Godard J, Le Merrer M, Oury JF, Plauchu H, Puddu R, Rival JM, Superti-Furga A, Touraine RL, Serre JL, Simon-Bouy B (1998) Identification of fifteen novel mutations in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) gene in European patients with severe hypophosphatasia. Eur J Hum Genet 6: 308–314
Müller HL, Yamazaki M, Michigami T, Kageyama T, Schönau E, Schneider P, Ozono K (2000) Asp361Val mutant of alkaline phosphatase found in patients with dominantly inherited hypophosphatasia inhibits the activity of the wild-type enzyme. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85: 743–747
Oestreich AE, Bofinger MK (1989) Prominent transverse (Bowdler) bone spurs as a diagnostic clue in a case of neonatal hypophosphatasia without metaphyseal irregularity. Pediatr Radiol 19: 341–342
Orimo H, Hayashi Z, Watanabe A, Hirayama T, Hirayama T, Shimada T (1994) Novel missense and frameshift mutations in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene in a Japanese patient with hypophosphatasia. Hum Mol Genet 3: 1683–1684
Orimo H, Goseki-Sone M, Inoue M, Tsubakio Y, Sakiyama T, Shimada T (2002) Importance of deletion of T at nucleotide 1559 in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene in Japanese patients with hypophosphatasia. J Bone Miner Metab 20: 28–33
Ozono K, Yamagata M, Michigami T, Nakajima S, Sakai N, Cai G, Satomura K, Yasui N, Okada S, Nakayama M (1996) Identification of novel missense mutations (Phe310Leu and Gly439Arg) in a neonatal case of hypophosphatasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81: 4458–4461
Pauli RM, Modaff P Sipes SL, Whyte MP(1999) Mild hypophosphatasia mimicking severe osteogenesis imperfecta in utero: bent but not broken. Am J Med Genet 86: 434–438
Sergi C, Mornet E, Troeger J, Voigtlaender T (2001) Perinatal hypophosphatasia: radiology, pathology and molecular biology studies in a family harboring a splicing mutation (648+1A) and a novel missense mutation (N400S) in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) gene. Am J Med Genet 103: 235–240
Spentchian M, Merrien Y, Herasse M, Dobbie Z, Glaser D, Holder SE, Ivarsson SA, Kostiner D, Mansour S, Norman A, Roth J, Stipoljev F, Taillemite JL, van der Smagt JJ, Serre JL, Simon-Bouy B, Taillandier A, Mornet E (2003) Severe hypophosphatasia: characterization of fifteen novel mutations in the ALPL gene. Hum Mutat 22: 105–106
Taillandier A, Zurutuza L, Muller F, Simon-Bouy B, Serre JL, Bird L, Brenner R, Boute O, Cousin J, Gaillard D, Heidemann PH, Steinmann B, Wallot M, Mornet E (1999) Characterization of eleven novel mutations (M45L, R119H, 544delG, G145V, H154Y, C184Y, D289V, 862+5A, 1172delC, R411X, E459K) in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) gene in patients with severe hypophosphatasia. Hum Mutat 13: 171–172
Unger S, Mornet E, Mundlos S, Blaser S, Cole DE (2002) Severe cleidocranial dysplasia can mimic hypophosphatasia. Eur J Pediatr 161: 623–626
Weiss MJ, Henthorn PS, Lafferty MA, Slaughter C, Raducha M, Harris H (1986) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a human liver/bone/kidney-type alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 7182–7186
Whyte MP (1994) Hypophosphatasia and the role of alkaline phosphatase in skeletal mineralization. Endocr Rev 15: 439–461
Whyte MP, Kurtzberg J, McAlister WH, Mumm S, Podgornik MN, Coburn SP, Ryan LM, Miller CR, Gottesman GS, Smith AK, Douville J, Waters-Pick B, Armstrong RD, Martin PL (2003) Marrow cell transplantation for infantile hypophosphatasia. J Bone Miner Res 18: 624–636
Zurutuza L, Muller F, Gibrat JF, Taillandier A, Simon-Bouy B, Serre JL, Mornet E (1999) Correlations of genotype and phenotype in hypophosphatasia. Hum Mol Genet 8: 1039–1046
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. P. S. Henthorn of the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine for generously providing the TNSALP expression vector. We also thank the physicians listed below for referring patients with hypophosphatasia for TNSALP gene analysis: Drs. Kennichi Satomura and Hidehiko Kawabata, Osaka Medical Centre and Research Institute for Maternal and Child Health; Dr. Norio Miharu, Hiroshima University; Dr. Tsuyoshi Oikawa, Jikei Medical University; Dr. Yu Ikeda, Shiga Medical University; Dr. Yasushi Uchida, Nagahama Municipal Hospital; Dr. Go Hasegawa, Nikko Memorial Hospital; Drs. Hiroyuki Tanaka, Masaru Inoue, Okayama University School of Medicine; Dr. Toru Ogiwara, Osaka Medical School; Drs. Katshuhiko Tachibana, Masayuki Adachi, Tetshusi Ueno, Hiroshima Municipal Hospital; Dr. Hiroshi Mochizuki, Saitama Medical Centre; Dr. Oguchi, Hata Hospital; Dr. Shuichiro Akagi, Chifune Hospital; Dr. Yuka Sasamoto, St. Marianna University; Dr. Kusuki, Osaka Medical Centre; Dr. Ichiba, Osaka City University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michigami, T., Uchihashi, T., Suzuki, A. et al. Common mutations F310L and T1559del in the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene are related to distinct phenotypes in Japanese patients with hypophosphatasia. Eur J Pediatr 164, 277–282 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-004-1612-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-004-1612-9