Abstract
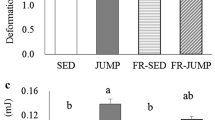
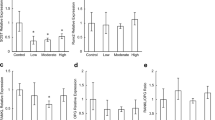
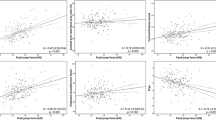
Jump training is a high-impact training regimen that increases bone volume in young bones. The aim of our study was to determine whether downregulation of adipogenesis that is associated with upregulation of osteogenesis is detected after jump training in growing rat tibiae. Four-week-old rats were jump trained for 1, 2, or 4 weeks for 5 days/week, and the height of jumping progressively increased to 35 cm. We performed morphometry to directly quantitate changes in bone volume and marrow adipocyte distribution in tibiae after the jump training. We also examined changes in the expression of osteogenic and adipogenic transcription factor proteins and mRNAs after the jump training. Four weeks of jump training induced an increase in trabecular bone volume, which was associated with the recruitment of runt-related transcription factor 2 expressing cells, as well as a decrease in marrow fat volume. However, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ2 protein and mRNA expression levels did not change after high-impact jump training. The mRNA expression levels of the adipocyte differentiation genes CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs)α, C/EBPβ, and C/EBPδ also showed no change during the training period in jump-trained rats. We suggest that the levels of osteogenic factors that were upregulated by mechanical loading from high-impact jumping suppress adipogenesis in marrow rather than adipogenic transcription factors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah BM, Haack-Sorensen M, Fink T, Kassem M (2006) Inhibition of osteoblast differentiation but not adipocyte differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by sera obtained from aged females. Bone 39:181–188
Adams M, Reginato MJ, Shao D, Lazar MA, Chatterjee VK (1997) Transcriptional activation by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is inhibited by phosphorylation at a consensus mitogen-activated protein kinase site. J Biol Chem 272:5128–5132
Ahdjoudj S, Lasmoles F, Holy X, Zerath E, Marie PJ (2002) Transforming growth factor beta2 inhibits adipocyte differentiation induced by skeletal unloading in rat bone marrow stroma. J Bone Miner Res 17:668–677
Ahdjoudj S, Kaabeche K, Holy X, Fromigue O, Modrowskia D, Zerath E, Marie PJ (2005) Transforming growth factor-h inhibits CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein expression and PPARg activity in unloaded bone marrow stromal cells. Exp Cell Res 303:138–147
Benayahu D, Shur I, Shamgar BE (2000) Hormonal changes affect the bone and bone marrow cells in a rat model. J Cell Biochem 79:407–415
Botolin S, Faugere MC, Malluche H, Orth M, Meyer R, McCabe LR (2005) Increased bone adiposity and peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-γ2 expression in type I diabetic mice. Endocrinology 146:3622–3631
Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B, Middleton J (2007) Mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells 25:2739–2749
Cherian PP, Aj Siller-Jackson, Gu S, Wang X, Bonewald LF, Sprague E, Jiang JX (2005) Mechanical strain opens connexin 43 hemichannels in osteocytes: a novel mechanism for the release of prostaglandin. Mol Biol Cells 16:3100–3106
David V, Martin A, Lafage-Proust MH, Malaval L, Peyroche S, Jones DB, Vico L, Guignandon A (2007) Mechanical loading down-regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in bone marrow stromal cells and favors osteoblastogenesis at the expense of adipogenesis. Endocrinology 148:2553–2562
Duncan RL, Turner CH (1995) Mechanotransduction and the functional response of bone to mechanical strain. Calcif Tissue Int 57:344–358
Enomoto H, Furuichi T, Zanma A, Yamana K, Yoshida C, Sumitani S, Yamamoto H, Enomoto-Iwamoto M, Iwamoto M, Komori T (2004) Runx2 deficiency in chondrocytes causes adipogenic changes in vitro. J Cell Sci 117:417–425
Gregoire FM, Smas CM, Sul HS (1998) Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physiol Rev 78:783–809
He S, Nakada D, Morrison SJ (2009) Mechanisms of stem cell self-renewal. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25:377–406
Heinrich CH, Going SB, Pamenter RW, Perry CD, Boyden TW, Lohman TG (1990) Bone mineral content of cyclically menstruating female resistance and endurance trained athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 22:558–563
Honda A, Umemura Y, Nagasawa S (2001) Effect of high-impact and low-repetition training on bones in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Res 16:1688–1693
Hu E, Kim JB, Sarraf P, Spiegelman BM (1996) Inhibition of adipogenesis through MAP kinase-mediated phosphorylation of PPAR gamma. Science 274:2100–2103
Ikegame M, Ishibashi O, Yoshizawa T, Shimomura J, Komori T, Ozawa H, Kawashima H (2001) Tensile stress induces bone morphogenetic protein 4 in preosteoblastic and fibroblastic cells, which later differentiate into osteoblasts leading to osteogenesis in the mouse calvariae in organ culture. J Bone Miner Res 16:24–32
Jiang JX, Cherian PP (2003) Hemichannels formed by connexin 43 play an important role in the release of prostaglandin E2 by osteocytes in response to mechanical strain. Cell Commun Adhes 10:259–264
Ju YI, Sone T, Okamoto T, Fukunaga M (2008) Jump exercise during remobilization restores integrity of the trabecular architecture after tail suspension in young rats. J Appl Physiol 104:1594–1600
Justesen J, Stenderup K, Ebbesen EN, Mosekilde L, Steiniche T, Kassem L (2001) Adipocyte tissue volume in bone marrow is increased with aging and in patients with osteoporosis. Biogerontology 2:165–171
Kawamoto T, Shimizu M (2000) A method for preparing 2- to 50-μm-thick fresh-frozen sections of large samples and undecalcified hard tissues. Histochem Cell Biol 113:331–339
Ke HZ, Jee WS, Mori S, Li XJ, Kimmel DB (1992) Effects of long-term daily administration of Prostaglandin-E2 on maintaining elevated proximal tibial metaphyseal cancellous bone mass in male rats. Calcif Tissue Int 50:245–252
Kobayashi H, Gao Y, Ueta C, Yamaguchi A, Komori T (2000) Multilineage differentiation of Cbfa1-deficient calvarial cells in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273:630–636
Komori T (2005) Regulation of skeletal development by the Runx family of transcription factors. J Cell Biochem 95:445–453
Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, Yamaguchi A, Sasaki K, Deguchi K, Shimizu Y, Bronson RT, Gao YH, Inada M, Sato M, Okamoto R, Kitamura Y, Yoshiki S, Kishimoto T (1997) Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell 89:755–764
Kondo Y, Irie K, Ikegame M, Ejiri S, Handa K, Ozawa H (2001) Role of stromal cells in osteoclast differentiation in bone marrow. J Bone Miner Metab 19:352–358
Luu YK, Capilla E, Rosen CJ, Gilsanz V, Pessin JE, Judex S, Rubin CT (2009) Mechanical stimulation of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation promotes osteogenesis while preventing dietary induced obesity. J Bone Miner Res 24:50–61
Mandrup S, Lane MD (1997) Regulating adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 272:5367–5370
Menuki K, Mori T, Sakai A, Sakuma M, Okimoto N, Shimizu Y, Kunugita N, Nakamura T (2008) Climbing exercise enhances osteoblast differentiation and inhibits adipogenic differentiation with high expression of PTH/PTHrP receptor in bone marrow cells. Bone 43:613–620
Moerman EJ, Teng K, Lipschitz DA, Lecka-Czernik B (2004) Aging activates adipogenic and suppresses osteogenic programs in mesenchymal marrow stroma/stem cells: the role of PPAR-γ2 transcription factor and TGF-β/BMP signaling pathways. Aging Cell 3:379–389
Morrie EK (1985) Red-yellow marrow conversion: its effect on the location of some solitary bone lesions. Skeletal Radiol 14:10–19
Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, Zhang Z, Deng JM, Behringer RR, Crombrugghe B (2002) The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor Osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell 108:17–29
Notomi T, Okazaki Y, Okimoto N, Saitoh S, Nakamura T, Suzuki M (2000) A comparison of resistance and aerobic training for mass, strength and turnover of bone in growing rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 83:469–474
Otto F, Thornell AP, Crompton T, Denzel A, Gilmour KC, Rosewell IR, Stamp GW, Beddington RS, Mundlos S, Olsen BR, Selby PB, Owen MJ (1997) Cbfa1, a candidate gene for cleidocranial dysplasia syndrome, is essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone development. Cell 89:765–771
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Risser WL, Lee EJ, LeBlanc A, Poindexter HB, Risser JM, Schneider V (1990) Bone density in eumenorrheic female college athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 22:570–574
Rosen ED (2005) The transcriptional basis of adipocyte development. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 73:31–34
Sen B, Xie Z, Case N, Ma M, Rubin C, Rubin J (2008) Mechanical strain inhibits adipogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells by stimulating a durable β-catenin signal. Endocrinology 149:6065–6075
Umemura Y, Ishiko T, Tshjimoto H, Miura H, Mokushi N, Suzuki H (1995) Effects of jump training on bone hypertrophy in young and old rats. Int J Sports Med 16:364–367
Umemura Y, Ishiko T, Yamauchi T, Kurono M, Mashiko S (1997) Five jumps per day increase bone mass and breaking force in rats. J Bone Miner Res 12:1480–1485
Wozney JM, Rosen V, Celeste AJ, Mitsock LM, Whitters MJ, Kriz RW, Hewick RM, Wang EA (1988) Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science 242:1528–1534
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Project No. 20300217 to H. Takekura and N. Kasuga) from the Japan society for the Promotion of Science, by a Grant-in-Aid for Science, and by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the National Institute of Fitness and Sports in Kanoya (President’s Discretionary Budget 2008 to H. Takekura).
Conflicts of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jacques Poortmans.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuki, A., Yotani, K., Tamaki, H. et al. Upregulation of osteogenic factors induced by high-impact jumping suppresses adipogenesis in marrow but not adipogenic transcription factors in rat tibiae. Eur J Appl Physiol 109, 641–650 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1383-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1383-0