Abstract
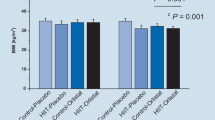
We assessed the major factors regulating adiponectin levels and the influence of exercise training on adiponectin levels in young obese men (19.2±1.1 yrs, BMI: 31.1±4.2, %fat: 27.2±3.9%). Subjects were separated into three groups (aerobic exercise group [AE: n=7], aerobic and resistance exercise group [AE+RE: n=7], control group [n=7]). AE underwent an 8-week training program (three times per week, more than 30 min endurance exercise at ventilatory threshold (VT) intensity). AE+RE went through resistance exercise two or three times per week together with the above endurance exercise for 5 months. Prior to intervention (n=21), adiponectin levels were significantly correlated with percentage of fat. Stepwise multiple regression analysis revealed that percent body fat was an independent predictor of basal adiponectin levels (r2=0.370; P<0.01). After intervention, fat mass, and VT were significantly improved in AE. AE+RE exhibited significant reduction in weight, BMI, percent body fat and fat mass, and had significantly increased VT, \(\ifmmode\expandafter\dot\else\expandafter\.\fi{V}{\text{O}}_{2} \max ,\) cycling power and torque. Insulin was not changed in both groups. The control group exhibited no significant change in any variables. Although adiponectin levels were unchanged in the three groups, a significant negative correlation between delta fat mass and delta adiponectin levels was observed (n=21, r=−0.461, P<0.05). In addition, delta percent body fat was an independent predictor of delta adiponectin levels (r2=0.327, P<0.05). These findings indicate that for increasing the adiponectin level, improvement of the body composition of young obese men is more important than the way training is performed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American college of sports medicine (2000) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, 6th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, 151 pp
American college of sports medicine (2001) ACSM’s resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, 362 pp
Adamczak M, Wiecek A, Funahashi T, Chudek J, Kokot F, Matsuzawa Y (2003) Decreased plasma adiponectin concentration in patients with essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 16:72–75
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (1999) Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257:79–83
Bartok C, Schoeller DA (2004) Estimation of segmental muscle volume by bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy. J Appl Physiol 96:161–166
Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ (1986) A new method for detecting the anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl Physiol 60:2020–2027
Boudou P, Sobngwi E, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Vexiau P, and Gautier J-F (2003) Absence of exercise-induced variations in adiponectin levels despite decreased abdominal adiposity and improved insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic men. Eur J Endocrinol 149:421–424
Bracco D, Daniel T, Rone LC, Michel L, Peter B, Yves S (1996) Segmental body composition assessed by bioelectrical impedance analysis and DEXA in humans. J Appl Phyisiol 81:2580–2587
Emoto M, Nishizawa Y, Maekawa K, Hiura Y, Kanda H, Kawagishi T, Shoji T, Okuno Y, Morii H (1999) Homeostasis model assessment as a clinical index of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients treated with sulfonylureas. Diabetes care 22:818–822
Esposito K, Pontillo A, Palo CD, Giugliano G, Masella M, Marfella R, Giugliano D (2003) Effect of weight loss and lifestyle changes on vascular inflammatory markers in obese women. JAMA 289:1799–1804
Franckowiak SC, Fontaine K, Andersen RE (2003) Comparison of proximal and distal placement of electrodes to assess body composition by bioelectrical impedance in obese adults. J Strength Cond Res 17:522–526
Haffner SM, Miettinen H, Stern MP (1997) The homeostasis model in the San Antonio Heart Study. Diabetes Care 20:1087–1092
Hara T, Fujiwara H, Shoji T, Mimura T, Nakao H, and Fijimoto S (2003) Decreased plasma adiponectin levels in young obese males. J Atheroscler Thromb 10:234–238
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakajima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y (2000) Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1595–1599
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Bodkin NL, Ortmeyer HK, Arita Y, Hansen BC, Matsuzawa Y (2001) Circulating concentrations of the adipocyte protein adiponectin are decreased in parallel with reduced insulin sensitivity during the progression to type 2 diabetes in rhesus monkeys. Diabetes 50:1126–1133
Hulver MW, Zheng D, Tanner CJ, Houmard J.A, Kraus WE, Slents CA, Sinha MK, Pories WJ, MAcDonald KG, Dohm GL (2002) Adiponectin is not altered with exercise training despite enhanced insulin action. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283:E861–E865
Kern PA, Di Gregorio GB, Lu T, Rassouli N, Ranganathan G (2003) Adiponectin expression from human adipose tissue: relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. Diabetes 52:1779–1785
Kraemer WJ, Ratamess NA, French DN (2002) Resistance training for health and performance. Curr Sports Med Rep 1:165–171
Kriketos AD, Gan SK, Poynten AM, Furler SM, Chisholm DJ, Campbell LV (2004) Exercise increases adiponectin levels and insulin sensitivity in humans. Diabetes Care 27:629–630
Kumada M, Kihara S, Sumitsuji S, Kawamoto T, Matsumoto S, Ouchi N, Arita Y, Okamoto Y, Shimomura I, Hiraoka H, Nakamura T, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2003) Association of hypoadinectinemia with coronary artery disease in men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:85–89
Lindsay RS, Funahashi T, Hanson RL, Matsuzawa Y, Tanaka S, Tataranni PA, Knowler WC, Krakoff J (2002) Adiponectin and development of type 2 diabetes in the Pima Indian population. Lancet 360:57–58
Lorenzo AD, Andreoli A (2003) Segmental bioelectrical impedance analysis. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 6:551–555
Lukaski HC (2000) Assessing regional muscle mass with segmental measurements of bioelectrical impedance in obese women during weight loss. Ann N Y Acad Sci 904:154–158
Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K (1996) cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript 1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 211:286–289
Maeda N, Shimomura I, Kishida K, Nishizawa H, Matsuda M, Nagaretani H, Furuyama N, Kondo H, Takahashi M, Arita Y, Komuro R, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Tochino Y, Okutomi K, Horie M, Takeda S, Aoyama T, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2002) Diet-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking adiponectin/ACRP30. Nat Med 8:731–737
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Musi N, Fujii N, Hirshman MF, Ekberg I, Froberg S, Ljungqvist O, Thorell A, Goodyear LJ (2001) AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is activated in muscle of subjects with type 2 diabetes during exercise. Diabetes 50:921–927
Nemet D, Wang P, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Tanaka S, Engelman L, Cooper DM (2003) Adipocytokines, body composition, and fitness in children. Pediatr Res 53:148–152
Okamoto Y, Arita Y, Nishida M, Muraguchi M, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Igura T, Inui Y, Kihara S, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Miyagawa J, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2000) An adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, adheres to injured vascular walls. Hormone Metab Res 32:47–50
Organ LW, Bradham GB, Gore DT, Lozier SL (1994) Segmental bioelectrical impedance analysis: theory and application of a new technique. J Appl Physiol 77:98–112
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (1999) Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 100:2473–2476
Poehlman ET, Dvorak RV, DeNino WF, Brochu M, Ades PA. (2000) Effects of resistance training and endurance training on insulin sensitivity in nonobese, young women: a controlled randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:2463–2468
Ryan AS, Nicklas BJ, Berman DM, Elahi D (2003) Adiponectin levels do not change with moderate dietary induced weight loss and exercise in obese postmenopausal women. Int J Obes 27:1066–1071
Segal KR, Gutin B, Presta E, Wang J, Van Itallie TB (1985) Estimation of human body composition by electrical impedance methods: a comparative study. J Appl Physiol 58:1565–1571
Spranger J, Kroke A, Mohlig M, Bergmann MM, Ristow M, Boeing H, Pfeiffer AF (2003) Adiponectin and protection against type 2 mellitus. Lancet 361:226–228
Stefan N, Bunt JC, Salbe AD, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Tataranni PA (2002) Plasma adiponectin concentrations in children: relationships with obesity and insulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4652–4656
Stewart SP, Bramley PN, Heighton R, Green JH, Horsman A, Losowsky MS, Smith MA (1993) Estimation of body composition from bioelectrical impedance of body segments: comparison with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Br J Nutr 69:645–55
Wasserman K, Whipp BJ, Koyal SN, Beaver WL (1973) Anaerobic threshold and respiratory gas exchange during exercise. J Appl Physiol 35:236–243
Weiss R, Dufour S, Groszmann A, Petersen K, Dziura J, Taksali SE, Shulman G, Caprio S (2003) Low adiponectin levels in adolescent obesity: a marker of increased intramyocellular lipid accumulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:2014–2018
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, Tataranni PA (2001) Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1930–1935
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Tsuchida A, Yokomizo T, Kita S, Sugiyama T, Miyagishi M, Hara K, Tsunoda M, Murakami K, Ohteki T, Uchida S, Takekawa S, Waki H, Tsuno NH, Shibata Y, Terauchi Y, Froguel P, Tobe K, Koyasu S, Taira K, Kitamura T, Shimizu T, Nagai R, Kadowaki T (2003) Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 423(6941):762–769
Yang WS, Lee WJ, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Matsuzawa Y, Chao CL, Chen CL, Tai TY, Chuang LM (2001) Weight reduction increases plasma levels of an adipose-derived anti-inflammatory protein, adiponectin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:3815–3819
Yatagai T, Nishida Y, Nagasaka S, Nakamura T, Tokuyama K, Shindo M, Tanaka H, Ishibashi S (2003) Relationship between exercise training-induced increase in insulin sensitivity and adiponectinemia in healthy men. Endocr J 50:233–238
Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Tripepi G, Benedetto FA, Cutrupi S, Parlongo S, Malatino LS, Bonanno G, Seminara G, Rapisarda F, Fatuzzo P, Buemi M, Nicocia G, Tanaka S, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2002) Adiponectin, metabolic risk factors, and cardiovascular events among patients with end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:134–141
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the subjects who participated in the present study, and are also grateful to Tokuko Katahira, Setsuko Senda and Kaori Nanba (Medical Center for Student Health, Osaka City University) for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, T., Fujiwara, H., Nakao, H. et al. Body composition is related to increase in plasma adiponectin levels rather than training in young obese men. Eur J Appl Physiol 94, 520–526 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-005-1374-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-005-1374-8