Abstract
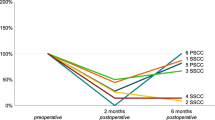
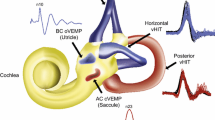
The aim of this paper was to evaluate prospectively, in a group of patients affected by VN, a diagnostic protocol employing C-VEMPs, O-VEMPs and vHIT together. The diagnosis of vestibular neurolabyrinthitis was based on the clinical history, absence of associated auditory or neurological symptoms, and a neuro-otological examination with an evaluation of lateral semicircular canal function using the Fitzgerald–Hallpike caloric vestibular test and ice test. Our series revealed an incidence of 55 % of superior and inferior vestibular neurolabyrinthitis, 40 % of superior vestibular neurolabyrinthitis and 5 % of inferior vestibular neurolabyrinthitis. These data, however, comprised different degrees of vestibular involvement considering the evaluation of each single vestibular end-organ with potential different prognosis. Four patients had only deficits of the horizontal and superior semicircular canals or their ampullary nerves. The implementation of C-VEMPs, O-VEMPs and vHIT in a vestibular diagnostic protocol has made possible to observe patients with ampullary VN, unidentifiable with other types of vestibular exams. The effect of age seems to have some impact on the recovery. When recovery firstly involves the utricular and saccular nerves and subsequently the ampullary nerves, it may be reasonable to expect a more favorable and successful outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Magliulo G, Gagliardi M, Appiani GC, D’Amico R (2003) Preservation of the saccular nerve and of the vestibular evoked myogenic potential during vestibular schwannoma surgery. Otol Neurotol 24:308–311
Aw ST, Fetter M, Cremer PD, Karlberg M, Halmagyi GM (2001) Individual semicircular canal function in superior and inferior vestibular neuritis. Neurology 11(57):768–774
Ulmer E, Bernard-Demanze L, Lacour M (2011) Statistical study of normal canal deficit variation range. Measurement using the head impulse video system. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 128:278–282
Govender S, Rosengren SM, Colebatch JG (2011) Vestibular neuritis has selective effects on air- and bone-conducted cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials. Clin Neurophysiol 122:1246–1255
Shin BS, Oh SY, Kim JS, Kim TW, Seo MW, Lee H, Park YA (2012) Cervical and ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in acute vestibular neuritis. Clin Neurophysiol 123:369–375 Epub 19 Jul 2011
Magliulo G, Gagliardi S, Appiani MC, Iannella G, Gagliardi M (2012) Selective vestibular neurolabyrinthitis of the lateral and superior semicircular canals and ampullary nerves. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 121:640–644
Walther LE, Blödow A (2013) Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential to air conducted sound stimulation and video head impulse test in acute vestibular neuritis. Otol Neurotol 34:1084–1089
Magliulo G, Gagliardi S, Appiani MC, Iannella G, Re M (2014) Vestibular Neurolabyrinthitis: a follow-up study with cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials and the video head impulse test. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 123:162–173
Kim HA, Hong JH, Lee H, Yi HA, Lee SR, Jang BC, Ahn BH, Baloh RW (2008) Otolith dysfunction in vestibular neuritis. Neurology 70:449–453
Ulmer E, Chays A (2005) Curthoys and Halmagyi head impulse test: an analytical device. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac 122:84–90
Leveque M, Seiderman L, Tran H, Langagne T, Ulmer E, Chays A (2010) Vestibular function outcomes after vestibular neurectomy in Meniere disease:can vestibular neurectomy provide complete vestibular deafferentation? Auris Nasus Larynx 37:308–313
Magliulo G, Cuiuli G, Gagliardi M, Ciniglio-Appiani G, D’Amico R (2004) Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials and glycerol testing. Laryngoscope 114:338–343
Magliulo G, Cianfrone G, Gagliardi M, Cuiuli G, D’Amico R (2004) Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials and distortion-product otoacoustic emissions combined with glycerol testing in endolymphatic hydrops: their value in early diagnosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 113:1000–1005
Magliulo G, Parrotto D, Cuiuli G, Alla FR, Gagliardi M (2007) Preservation of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials with modified translabyrinthine approach. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:720–723
Welgampola MS, Carey JP (2010) Waiting for the evidence: VEMP testing and the ability to differentiate utricular versus saccular function. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143:281–283
Zellhuber S, Mahringer A, Rambold HA (2014) Relation of video-head-impulse test and caloric irrigation: a study on the recovery in unilateral vestibular neuritis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271:2375–2383
Murofushi T, Iwasaki S, Ushio M (2006) Recovery of vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials after vertigo attack due to vestibular neuritis. Acta Otolaryngol 126:364–367
Halmagyi GM, Karlberg M, Curthoys IS, Todd MJ (2002) Inferior vestibular neuritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 956:306–313
Schmid-Priscoveanu A, Bohmer A, Obzim H, Straumann D (2001) Caloric and search-coil head-impulse testing in patients after vestibular neuritis. JARO 2:72–78
D’Onofrio F (2013) Vertical eye movements during horizontal head impulse test: a new clinical sign of superior vestibular neuritis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 33:418–424
Manzari L, Burgess AM, MacDougall HG, Curthoys IS (2013) Vestibular function after vestibular neuritis. Int J Audiol. 52:713–718
Bartolomeo M, Biboulet R, Pierre G, Mondain M, Uziel A, Venail F (2014) Value of the video head impulse test in assessing vestibular deficits following vestibular neuritis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271:681–688
Eleftheriadou A, Skalidi N, Velegrakis GA (2012) Vestibular rehabilitation strategies and factors that affect the outcome. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:2309–2316
Han BI, Song HS, Kim JS (2011) Vestibular rehabilitation therapy: review of indications mechanisms, and key exercises. J Clin Neurol 7:184–196
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magliulo, G., Iannella, G., Gagliardi, S. et al. A 1-year follow-up study with C-VEMPs, O-VEMPs and video head impulse testing in vestibular neuritis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 3277–3281 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3404-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3404-9