Abstract
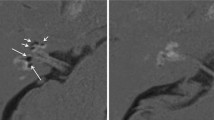
Vertigo patients exhibiting features of vestibular migraine (VM) and Menière’s disease (MD) present a difficult diagnostic challenge to the clinician, and the two entities are likely to overlap. The aim of the present study was to investigate the occurrence of endolymphatic hydrops in patients with VM and auditory symptoms. This was an observatory diagnostic study. At an academic interdisciplinary dizziness centre, nineteen consecutive patients with definite or probable VM and auditory symptoms were examined by locally enhanced inner ear MR imaging. MR images were evaluated for the presence of endolymphatic hydrops. Of the 19 included patients, four patients (21 %) demonstrated evidence of cochlear and vestibular endolymphatic hydrops on locally enhanced inner ear MR imaging (three with “definite VM”, one with “probable VM”). Locally enhanced inner ear MR imaging may be useful in the diagnostic evaluation of patients with VM and auditory symptoms, as some of these patients have signs of endolymphatic hydrops. Whether these patients suffer from MD only and are misdiagnosed as VM or suffer from both, VM and MD or whether endolymphatic hydrops is a consequence of inner ear damage due to VM are clinically relevant questions that can be evaluated by application of this technique.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neuhauser H, Leopold M, von Brevern M, Arnold G, Lempert T (2001) The interrelations of migraine, vertigo, and migrainous vertigo. Neurology 56:436–441
Neuhauser H, Lempert T (2009) Vestibular migraine. Neurol Clin 27:379–391
Lempert T, Olesen J, Furman J et al (2012) Vestibular migraine: diagnostic criteria. J Vestib Res 22:167–172
Dieterich M, Brandt T (1999) Episodic vertigo related to migraine (90 cases): vestibular migraine? J Neurol 246:883–892
Neuhauser HK, von Brevern M, Radtke A et al (2005) Epidemiology of vestibular vertigo: a neurotologic survey of the general population. Neurology 65:898–904
Cutrer FM, Baloh RW (1992) Migraine-associated dizziness. Headache 32:300–304
Cha YH, Lee H, Santell LS, Baloh RW (2009) Association of benign recurrent vertigo and migraine in 208 patients. Cephalalgia 29:550–555
Brantberg K, Baloh RW (2011) Similarity of vertigo attacks due to Meniere’s disease and benign recurrent vertigo, both with and without migraine. Acta Otolaryngol 131:722–727
Radtke A, Lempert T, Gresty MA, Brookes GB, Bronstein AM, Neuhauser H (2002) Migraine and Meniere’s disease: is there a link? Neurology 59:1700–1704
Radtke A, von Brevern M, Neuhauser H, Hottenrott T, Lempert T (2012) Vestibular migraine: long-term follow-up of clinical symptoms and vestibulo-cochlear findings. Neurology 79:1607–1614
Kayan A, Hood JD (1984) Neuro-otological manifestations of migraine. Brain 107(Pt 4):1123–1142
Battista RA (2004) Audiometric findings of patients with migraine-associated dizziness. Otol Neurotol 25:987–992
Neff BA, Staab JP, Eggers SD et al (2012) Auditory and vestibular symptoms and chronic subjective dizziness in patients with Meniere’s disease, vestibular migraine, and Meniere’s disease with concomitant vestibular migraine. Otol Neurotol 33:1235–1244
AAO-HNS (1995) Committee on hearing and equilibrium guidelines for the diagnosis and evaluation of therapy in Meniere’s disease. American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Foundation, Inc. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113:181–185
Nakashima T, Naganawa S, Pyykko I et al (2009) Grading of endolymphatic hydrops using magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Otolaryngol 129(s560):5–8
Gurkov R, Flatz W, Louza J, Strupp M, Ertl-Wagner B, Krause E (2012) In vivo visualized endolymphatic hydrops and inner ear functions in patients with electrocochleographically confirmed Meniere’s disease. Otol Neurotol 33:1040–1045
Grieve SM, Obholzer R, Malitz N, Gibson WP, Parker GD (2012) Imaging of endolymphatic hydrops in Meniere’s disease at 1.5 T using phase-sensitive inversion recovery: (1) demonstration of feasibility and (2) overcoming the limitations of variable gadolinium absorption. Eur J Radiol 81:331–338
Hallpike CS (1956) The caloric tests. J Laryngol Otol 70:15–28
Jongkees LB, Maas JP, Philipszoon AJ (1962) Clinical nystagmography. A detailed study of electro-nystagmography in 341 patients with vertigo. Pract Otorhinolaryngol (Basel) 24:65–93
Ferraro JA, Durrant JD (2006) Electrocochleography in the evaluation of patients with Meniere’s disease/endolymphatic hydrops. J Am Acad Audiol 17:45–68
Naganawa S, Satake H, Kawamura M, Fukatsu H, Sone M, Nakashima T (2008) Separate visualization of endolymphatic space, perilymphatic space and bone by a single pulse sequence; 3D-inversion recovery imaging utilizing real reconstruction after intratympanic Gd-DTPA administration at 3 Tesla. Eur Radiol 18:920–924
Menière P. Mémoire sur des lésions de l’oreille interne donnant lieu à des symptômes de congestion cérébrale apoplectiforme. Gazette médicale de Paris 1861; 16:88–89, 239–240, 379–380, 597–601
Strupp M, Versino M, Brandt T (2010) Vestibular migraine. Handb Clin Neurol 97:755–771
Kim HH, Kumar A, Battista RA, Wiet RJ (2005) Electrocochleography in patients with Meniere’s disease. Am J Otolaryngol 26:128–131
Louza JP, Flatz W, Krause E, Gurkov R (2012) Short-term audiologic effect of intratympanic gadolinium contrast agent application in patients with Meniere’s disease. Am J Otolaryngol 33:533–537
Louza J, Krause E, Gürkov R (2013) Audiologic evaluation of Menière’s disease patients one day and one week after intratympanic application of Gadolinium contrast agent: our experience in sixty-five patients. Clin Otolaryngol 38(3):262–266
Kahmke R, Kaylie D (2012) What are the diagnostic criteria for migraine-associated vertigo? Laryngoscope 122:1885–1886
Arenberg IK, Ackley RS, Ferraro J, Muchnik C (1988) ECoG results in perilymphatic fistula: clinical and experimental studies. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 99:435–443
Arts HA, Adams ME, Telian SA, El-Kashlan H, Kileny PR (2009) Reversible electrocochleographic abnormalities in superior canal dehiscence. Otol Neurotol 30:79–86
Radtke A, Neuhauser H, von Brevern M, Hottenrott T, Lempert T (2011) Vestibular migraine–validity of clinical diagnostic criteria. Cephalalgia 31:906–913
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Federal German Ministry of Education and Research (grant no. 01EO0901). The corresponding author had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has a conflict of interest to declare. None of the authors has any financial conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the Federal German Ministry of Education and Research (grant No. 01EO0901).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gürkov, R., Kantner, C., Strupp, M. et al. Endolymphatic hydrops in patients with vestibular migraine and auditory symptoms. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271, 2661–2667 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2751-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2751-2