Abstract
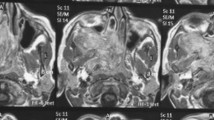
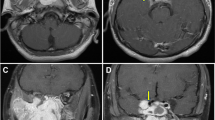
The endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma (JNA) emerges as an alternative approach to open procedures due to reduced morbidity and comparable recurrence rates. The purpose of this study was to present our experience with the endoscopic management of JNA using retrospective chart review of ten male patients (mean age 15.7 years) with JNA who were treated endoscopically at our institution between the years 2003 and 2010. According to the Radkowski’s system, one patient was at stage Ia, two at stage Ib, one at stage IIa, two at stage IIb, two at stage IIc (infratemporal fossa invasion) and two at stage IIIa (clivus erosion). Six patients underwent preoperative embolization. The endoscopic treatment involved total ethmoidectomy, middle meatal antrostomy, sphenoidotomy, clipping of the sphenopalatine artery and its branches and drilling of the pterygoid basis. All patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging 3 months postoperatively and then if indicated clinically. Mean follow-up was 23.7 months (range 3–70). All but one patient were free of macroscopic disease. A patient with stage IIb JNA developed a recurrence after 9 months. The residual tumor was resected endoscopically and the sphenopalatine foramen widened by drilling. The patient is free of disease 25 months postoperatively. The intra-operative blood loss was not excessive (200–800 ml, mean: 444 ml) and no patient required a blood transfusion. Patients were discharged after 4–8 days (mean 5 days). One patient developed postoperative infraorbital nerve hypoesthesia. Results showed that endoscopic treatment of stage I and IIa/b JNA is a valid alternative to external approaches. For select tumors with limited infratemporal fossa invasion and skull base erosion, the endoscopic approach may also be indicated. It is a safe and effective treatment modality due to the lack of external scars, minimal bone resection and blood loss and low recurrence rate.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glad H, Vainer B, Buchwald C, Petersen BL, Theilgaard SA, Bonvin P, Lajer C, Jakobsen J (2007) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas in Denmark 1981–2003: diagnosis, incidence, and treatment. Acta Otolaryngol 127:292–299
Wormald PJ, Van Hasselt A (2003) Endoscopic removal of juvenile angiofibromas. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:684–691
Sennes LU, Butugan O, Sanchez TG, Bento RF, Tsuji DH (2003) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: the routes of invasion. Rhinology 41:235–240
Spielmann PM, Adamson R, Cheng K, Sanderson RJ (2008) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: spontaneous resolution. Ear Nose Throat J 87:521–523
Herman P, Lot G, Chapot R, Salvan D, Huy PT (1999) Long-term follow-up of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas: analysis of recurrences. Laryngoscope 109:140–147
Karkos PD, Fyrmpas G, Carrie SC, Swift AC (2006) Endoscopic versus open surgical interventions for inverted nasal papilloma: a systematic review. Clin Otolaryngol 31:499–503
Banhiran W, Casiano RR (2005) Endoscopic sinus surgery for benign and malignant nasal and sinus neoplasm. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13:50–54
Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Vazquez AA, Pueyo J, Carbonell Casasus J (1998) Endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal fibromas. HNO 46:172–174
Eloy P, Watelet JB, Hatert AS, de Wispelaere J, Bertrand B (2007) Endonasal endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Rhinology 45:24–30
Hofmann T, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Koele W, Reittner P, Klein E, Stammberger H (2005) Endoscopic resection of juvenile angiofibromas—long term results. Rhinology 43:282–289
Nicolai P, Berlucchi M, Tomenzoli D, Cappiello J, Trimarchi M, Maroldi R, Battaglia G, Antonelli AR (2003) Endoscopic surgery for juvenile angiofibroma: when and how. Laryngoscope 113:775–782
Schick B, el Rahman el Tahan A, Brors D, Kahle G, Draf W (1999) Experiences with endonasal surgery in angiofibroma. Rhinology 37:80–85
Andrews JC, Fisch U, Valavanis A, Aeppli U, Makek MS (1989) The surgical management of extensive nasopharyngeal angiofibromas with the infratemporal fossa approach. Laryngoscope 99:429–437
Pryor SG, Moore EJ, Kasperbauer JL (2005) Endoscopic versus traditional approaches for excision of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Laryngoscope 115:1201–1207
Enepekides DJ (2004) Recent advances in the treatment of juvenile angiofibroma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 12:495–499
Radkowski D, McGill T, Healy GB, Ohlms L, Jones DT (1996) Angiofibroma. Changes in staging and treatment. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 122:122–129
Bothwell MR, Piccirillo JF, Lusk RP, Ridenour BD (2002) Long-term outcome of facial growth after functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:628–634
Robinson S, Patel N, Wormald PJ (2005) Endoscopic management of benign tumors extending into the infratemporal fossa: a two-surgeon transnasal approach. Laryngoscope 115:1818–1822
Andrade NA, Pinto JA, Nobrega Mde O, Aguiar JE, Aguiar TF, Vinhaes ES (2007) Exclusively endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:492–496
Borghei P, Baradaranfar MH, Borghei SH, Sokhandon F (2006) Transnasal endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma without preoperative embolization. Ear Nose Throat J 85:740–743, 746
Jorissen M, Eloy P, Rombaux P, Bachert C, Daele J (2000) Endoscopic sinus surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg 54:201–219
Scholtz AW, Appenroth E, Kammen-Jolly K, Scholtz LU, Thumfart WF (2001) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: management and therapy. Laryngoscope 111:681–687
Hackman T, Snyderman CH, Carrau R, Vescan A, Kassam A (2009) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: the expanded endonasal approach. Am J Rhinol Allergy 23:95–99
Danesi G, Panciera DT, Harvey RJ, Agostinis C (2008) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: evaluation and surgical management of advanced disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 138:581–586
Roger G, Tran Ba Huy P, Froehlich P, Van Den Abbeele T, Klossek JM, Serrano E, Garabedian EN, Herman P (2002) Exclusively endoscopic removal of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: trends and limits. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:928–935
Onerci TM, Yucel OT, Ogretmenoglu O (2003) Endoscopic surgery in treatment of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 67:1219–1225
El-Banhawy OA, Shehab El-Dien A, Amer T (2004) Endoscopic-assisted midfacial degloving approach for type III juvenile angiofibroma. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 68:21–28
Roche PH, Paris J, Regis J, Moulin G, Zanaret M, Thomassin JM, Pellet W (2007) Management of invasive juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas: the role of a multimodality approach. Neurosurgery 61:768–777 (discussion 777)
Budzynowska K, Pietniczka M, Dowzenko A, Borowska K, Czepiel W (2008) Safe extirpating of AFJ after preoperative tumor obliteration with tissue adhesive glue. Otolaryngol Pol 62:408–411
Mann WJ, Jecker P, Amedee RG (2004) Juvenile angiofibromas: changing surgical concept over the last 20 years. Laryngoscope 114:291–293
Naraghi M, Kashfi A (2003) Endoscopic resection of nasopharyngeal angiofibromas by combined transnasal and transoral routes. Am J Otolaryngol 24:149–154
Giavroglou C, Constantinidis J, Triaridis S, Daniilidis J, Dimitriadis A (2007) Angiographic evaluation and embolization of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. HNO 55:36–41
Lloyd G, Howard D, Phelps P, Cheesman A (1999) Juvenile angiofibroma: the lessons of 20 years of modern imaging. J Laryngol Otol 113:127–134
Liang Y, Wang D, Huang W, Ling F, Liu Y, Lu F (2003) Direct intratumoral embolization of hypervascular tumors of the head and neck. Chin Med J (Engl) 116:616–619
Howard DJ, Lloyd G, Lund V (2001) Recurrence and its avoidance in juvenile angiofibroma. Laryngoscope 111:1509–1511
Renkonen S, Hagstrom J, Vuola J, Niemela M, Porras M, Kivivuori SM, Leivo I, Makitie AA (2011) The changing surgical management of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268:599–607
Lund VJ, Lloyd GA, Howard DJ (1989) Juvenile angiofibroma—imaging techniques in diagnosis. Rhinology 27:179–185
Marshall AH, Bradley PJ (2006) Management dilemmas in the treatment and follow-up of advanced juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 68:273–278
El Sharkawy AA, Elmorsy SM (2011) Transnasal endoscopic management of recurrent juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol [Epub ahead of print]
Park CK, Kim DG, Paek SH, Chung HT, Jung HW (2006) Recurrent juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma treated with gamma knife surgery. J Korean Med Sci 21:773–777
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fyrmpas, G., Konstantinidis, I. & Constantinidis, J. Endoscopic treatment of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas: our experience and review of the literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269, 523–529 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-011-1708-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-011-1708-6