Abstract
Introduction
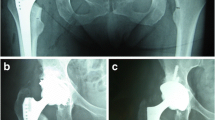
Thrust plate prosthesis (TPP) is a relatively new concept in total hip arthroplasty and advocated to be used in young patients. We retrospectively evaluated the results of 67 patients (71 hips) who were older than 65 years of age and underwent hip arthroplasty using the TPP.
Patients and methods
There were 50 female and 17 male patients with a mean age 71 (range 65–89) years. All patients received accelerated rehabilitation program either with full weight bearing in the second postoperative day or at 6 weeks. All patients were followed-up for at least 2 years (range 28–87 months).
Results
The average Harris hip score improved from 43 (range 8–72) to 93 (range 64–100) at the latest follow-up (p < 0.001). The overall revision rate was 8.4%. However, when the patients with definitive history of trauma were excluded the rate for loosening and technical errors decreased to 4.2%. There was no significant difference between the Harris hip score of patients with full weight bearing in the second postoperative day or 6 weeks (p = 0.57).
Conclusion
We conclude that the TPP could be indicated for older patients without age limit and that an accelerated rehabilitation program with early weight bearing can be applied to these patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beretier H, Burgi M, Schenk R (1997) Finite element investigations of the proximal femur after implantation of the thrust plate prosthesis compared with findings in a post-mortem histological specimen and in radiological follow-up examinations. In: Huggler AH, Jacob HAC (eds) The thrust plate prosthesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 48–62
Buergi ML, Stoffel KK, Jacob HAC, Bereiter HH (2005) Radiological findings and clinical results of 102 thrust-plate femoral hip prostheses. A follow-up of 2 to 8 years. J Arthroplasty 20:108–117
Dorr LD, Wan Z, Gruen T (1997) Functional results in total hip replacement in patients 65 years and older. Clin Orthop 336:143–151
Engh CA, Glassman AH, Bobyn JD (1986) Surgical principles in cementless total hip arthroplasty. Tech Orthop 1:35–53
Fink B, Siegmüller C, Shneider T, Conrad S, Schmielau G, Ruther W (2000) Short-and medium-term results of the thrust plate prosthesis in patients with polyarthritis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 120:294–298
Furnes O, Espehaug B, Lie SA, Engesaeter LB, Vollset SE, Hallan G, Fenstad AM, Havelin L (2005) Prospective studies of hip and knee prostheses. The Norwegian Arthroplasty Register 1987–2004. In: 72nd annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 23–27 February, Washington
Gocen Z, Sen A, Unver B, Karatosun V, Gunal I (2004) The effect of preoperative physiotherapy and education on the outcome of total hip replacement. Prospective randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil 18:353–358
Goldstein TS (1999) Geriatric orthopaedics. Rehabilitative management of common problems. Aspen Publishers, Maryland
Goto T, Yasunaga Y, Takahashi K, Ochi M (2004) Biomechanical analysis and quantitative analysis of bone scintigraphy on thrust plate hip prosthesis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124:357–362
Gursoy Y, Gunal I, Aksoy S, Sarioglu T, Kose N (1996) Strain distribution in the proximal femora. Comparison of intra and extramedullary type prostheses with intact bone. Arthroplasty Arthroscopic Surg 7:24–28, [In Turkish]
Healy WL (2002) Hip implant selection for total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients. Clin Orthop 405:54–64
Herberts P, Malchau H (1997) How outcome studies have changed total hip arthroplasty practices in Sweden. Clin Orthop 344:44–60
Huggler AH, Jacob HAC (1980) A new approach towards hip-prosthesis design. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 97:141–144
Huggler AH, Jacob HAC, Beretier H, Haferkom M, Ryf C, Schenk R (1993) Long-term results with the uncemented thrust plate prosthesis (TPP). Acta Orthop Belg 59(Suppl 1):215–223
Huggler AH (1997) The thrust plate prosthesis: a new experience in hip surgery. In: Huggler AH, Jacob HAC (eds) The thrust plate prosthesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–24
Jacob HAC (1997) Biomechanical principles and design details of the thrust plate prosthesis. In: Huggler AH, Jacob HAC (eds) The thrust plate prosthesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 25–47
Jacob HAC, Huggler AH (1980) An investigation into biomechanical causes of prosthesis stem loosening within the proximal end of the human femur. J Biomech 13:159–173
Karatosun V, Gunal I, Unver B (2001) Thrust plate prosthesis: early results of a new concept in the femoral component of total hip arthroplasty [In Turkish]. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 35:35–40
McAuley JP, Moore KD, Culpepper MJ 2nd, Engh CA (1998) Total hip arthroplasty with porous-coated prostheses fixed without cement in patients who are sixty-five years of age or older. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80:1648–1655
Meek RM, Michos J, Grigoris P, Hamblen DL (2002) Mid-term results and migration behaviour of a ti-alloy cemented stem. Int Orthop 26:356–360
Munin MC, Hockenberry PS, Flynn PG, Toplak W (1998) Rehabilitation. In: Callaghan JJ, Rosenberg AG, Rubash HE (eds) The adult hip. Lippincott Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, pp 1571–1579
Ranawat CS, Rasquinha VJ, Ranawat AS (2003) Cementless stems in patients aged >60 years: just say no. Orthopedics 26:920–922
Rao RR, Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Eng K, Rothman RH (1998) Immediate weight bearing after cementless total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 349:156–162
Rasquinha VJ, Ranawat CS (2004) Durability of the cemented femoral stem in patients 60 to 80 years old. Clin Orthop 419:115–123
Rothman RH, Cohn JC (1990) Cemented versus cementless total hip arthroplasty. A critical review. Clin Orthop 254:153–169
Sharma S, Verma G, Draviraj KP, Bhamra M (2005) Early results with the thrust plate prosthesis in young patients with osteoarthritis of the hip. Acta Orthop Belg 71:182–188
Söderman P (2000) On the validity of the results from the Swedish national total hip arthroplasty register. Acta Orthop Scand 71(Suppl 296):1–33
Steens W, Rosenbaum D, Goetze C, Gosheger G, van den Daele R, Steinbeck J (2003) Clinical and functional outcome of the thrust plate prosthesis: short-and medium-term results. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 18: 647–654
Unver B, Karatosun V, Gunal I, Angin S (2004) Comparison of two different rehabilitation programmes for thrust plate prosthesis: a randomized controlled study. Clin Rehabil 18:84–91
Woolson ST, Adler NS (2002) The effect of partial or full weight bearing ambulation after cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 17:820–825
Yasunaga Y, Goto T, Hisatome T, Tanaka R, Yamasaki T, Ochi M (2003) Bone-preserving prosthesis with a single axis for treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head: midterm results for the thrust plate hip prosthesis. J Orthop Sci 8:818–822
Zelle BA, Gerich TG, Bastian L, Shuler FD, Pape HC, Krettek C (2004) Total hip arthroplasty in young patients using the thrust plate prosthesis: clinical and radiological results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124:310–316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karatosun, V., Unver, B. & Gunal, I. Hip arthroplasty with the thrust plate prosthesis in patients of 65 years of age or older: 67 patients followed 2–7 years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128, 377–381 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-007-0487-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-007-0487-4