Abstract
Purpose
To explore the potential correlation and prognostic value of Livin, Survivin and Caspase 3 expression in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).
Methods
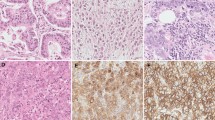
We prospectively examined the simultaneous expression of Livin, Survivin and Caspase 3 with immunohistochemistry in the paraffin blocks of 138 patients who underwent transurethral resection, and ten cases of normal bladder specimens were studied as the control group. During a 48-month follow-up, clinical pathologic factors including gender, age, pathology stage, histology grade, adjuvant therapy and recurrence time were recorded. The curves for recurrence-free survival (RFS) were estimated by the Kaplan–Meier method, and the relationship between these proteins’ expression and clinical pathologic factors was analyzed with the Cox regression model.
Results
Livin and Survivin showed a high expression (H-exp) level of 65.22 and 71.01 % in NMIBC, respectively, whereas Caspase 3 expression level was 50.72 %, and H-exp level of Livin and Survivin were 72.7 and 80.0 % in pT1 stage, respectively, which were proved to be higher than that in pTa/Tis ratio (P < 0.05). The relation between the H-exp and low-expression (L-exp) groups of Livin and Survivin and RFS were found statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conversely, there was better RFS in H-exp Caspase 3 group than in L-exp group (P < 0.05). A risk score was developed on the basis of all three biomarkers to estimate the prognosis of NMIBC patients, and those expressing high Survivin and Livin and low Caspase 3 had a significant shorter RFS time (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Livin, Survivin and Caspase 3 may be valuable as promising indicators of early recurrence in NMIBC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29
Parkin MD, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Shariat SF, Casella R, Khoddami SM et al (2004) Urine detection of survivin is a sensitive marker for the noninvasive diagnosis of bladder cancer. J Urol 171:626–630
Ashhab Y, Alian A, Polliack A et al (2001) Two splicing variants of a new inhibitor of apoptosis gene with different biological properties and tissue distribution pattern. FEBS Lett 495:56–60
Karam JA, Lotan Y, Ashfaq R et al (2007) Survivin expression in patients with non-muscle-invasive urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology 70:482–486
Alnemri ES, Livingston DJ, Nicholson DW et al (1996) Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell 87:171–172
Dai CH, Li J, Shi SB et al (2010) Survivin and Smac gene expressions but not livin are predictors of prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy following surgery. Jpn J Clin Oncol 40:327–335
Gazzaniga P, Gradilone A, Giuliani L et al (2003) Expression and prognostic significance of LIVIN, SURVIVIN and other apoptosis-related genes in the progression of superficial bladder cancer. Ann Oncol 14:85–90
Smolewski P, Robak T (2011) Inhibitors of apoptosis protein (IAPs) as potential molecular targets for therapy of hematological malignancies. Curr Mol Med 11:633–649
Chen N, Gong J, Chen X et al (2009) Caspases and inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in cutaneous and mucosal melanoma: expression profile and clinic pathologic significance. Hum Pathol 40:950–956
Sobin LH, Wittekind C (2002) TNM classification of malignant tumors, 6th edn. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 199–202
Ebele JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI et al (2004) World Health Organization classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of tumors of the urinary system and male genital organs. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 90–91
Yin W, Chen N, Zhang Y et al (2006) Survivin nuclear labeling index: a superior biomarker in superficial urothelial carcinoma of human urinary bladder. Mod Pathol 19:1487–1497
Atlasi Y, Mowla SJ, Ziaee SA (2009) Differential expression of survivin and its splice variants, survivin-DEx3 and survivin-2B, in bladder cancer. Cancer Detect Prev 32:308–313
Weikert S, Christoph F, Schrader M et al (2005) Quantitative analysis of survivin mRNA expression in urine and tumor tissue of bladder cancer patients and its potential relevance for disease detection and prognosis. Int J Cancer 116:100–104
Schultz I, Kiemeney L, Witjes JA et al (2003) Survivin mRNA expression is elevated in malignant urothelial cell carcinomas and predicts time to recurrence. Anticancer Res 23:3327–3331
Birkhahn M, Mitra AP, Williams AJ et al (2010) Predicting recurrence and progression of noninvasive papillary bladder cancer at initial presentation based on quantitative gene expression profiles. Eur Urol 57:12–20
Chen DJ, Huerta S (2009) Smac mimetics as new cancer therapeutics. Anticancer Drugs 20:646–658
Yang D, Song X, Zhang J et al (2010) Therapeutic potential of siRNA-mediated combined knockdown of the IAP genes (Livin, XIAP, and Survivin) on human bladder cancer T24 cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 42:137–144
Liu HB, Kong CZ, Zeng Y et al (2009) Livin may serve as a marker for prognosis of bladder cancer relapse and a target of bladder cancer treatment. Urol Oncol 27:271–283
Xi RC, Sheng YR, Chen WH et al (2013) Expression of survivin and livin predicts early recurrence in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. J Surg Oncol 107:550–554
Caldas H, Honsey LE, Altura RA (2005) Survivin 2alpha: a novel Survivin splice variant expressed in human malignancies. Mol Cancer 4:11–15
Ceballos-Cancino G, Espinosa M, Maldonado V et al (2007) Regulation of mitochondrial Smac/DIABLO-selective release by survivin. Oncogene 26:7969–7975
Giodini A, Kallio MJ, Wall NR et al (2002) Regulation of micro- tubule stability and mitotic progression by survivin. Cancer Res 62:2462–2467
Tu SP, Jiang XH, Lin MC et al (2003) Suppression of survivin expression inhibits in vivo tumorigenicity and angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Cancer Res 63:7724–7732
Margulis V, Lotan Y, Shariat SF (2008) Survivin: a promising biomarker for detection and prognosis of bladder cancer. World J Urol 26:59–65
Wang H, Xi X, Kong X et al (2004) The expression and significance of survivin mRNA in urinary bladder carcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130:487–490
Salvesen GS (2002) Caspases: opening the boxes and interpreting the arrow. Cell Death Differ 9:3–5
Liu C, Wu X, Luo C et al (2010) Antisense oligonucleotide targeting Livin induces apoptosis of human bladder cancer cell via a mechanism involving caspase 3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:63–68
Karam JA, Lotan Y, Karakiewicz PI et al (2007) Use of combined apoptosis biomarkers for prediction of bladder cancer recurrence and mortality after radical cystectomy. Lancet Oncol 8:128–136
Acknowledgments
We thank the technicians at Beijing ChaoYang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, for their excellent technical support.
Conflict of interest
We declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, X., Wei, P. et al. Livin, Survivin and Caspase 3 as early recurrence markers in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. World J Urol 32, 1477–1484 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1246-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1246-0