Abstract
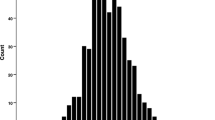
In the present study, dissection of genetic bases of testis weight in mice was performed. Autosomes and the X chromosome were searched using traditional quantitative trait locus (QTL) scans, and the Y chromosome was searched by association studies of Y-consomic strains. QTL analysis was performed in ♀DDD × ♂CBA F2 mice; the inbred mouse DDD has the heaviest testes, whereas the inbred mouse CBA has the lightest testes. Two significant testis weight QTLs were identified on chromosomes 1 and X. A DDD allele was associated with increased and decreased testis weight at the locus on chromosomes 1 and X, respectively. In the reciprocal cross ♀CBA × ♂DDD F2 mice, QTL on chromosome 1, and not on chromosome X, had a significant effect on testis weight. The DDD allele at the X-linked locus could not sustain testis weight in combination with the Y chromosome of the CBA strain. The Y chromosome per se had a significant effect on testis weight, i.e., DH-Chr YDDD had significantly heavier testes than DH-Chr YCBA. On the basis of the results of Y-chromosome-wide association studies using 17 Y-consomic strains, variations in Uty, Usp9y, and Sry were significantly associated with testis weight. Thus, testis weight is a complex quantitative phenotype controlled by multiple genes on autosomes and sex chromosomes and their interactions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolor H, Wakasugi N, Zhao WD, Ishikawa A (2006) Detection of quantitative trait loci causing abnormal spermatogenesis and reduced testis weight in the small testis (Smt) mutant mouse. Exp Anim 55:97–108
Broman KW, Sen Ś (2009) A guide to QTL mapping with R/qtl. Springer, New York
Broman KW, Wu H, Sen Ś, Churchill GA (2003) R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19:889–890
Carlisle C, Winking H, Weichenhan D, Nagamine CM (1996) Absence of correlation between Sry polymorphisms and XY sex reversal caused by the M. m. domesticus Y chromosome. Genomics 33:32–45
Cervino AC, Li G, Edwards S, Zhu J, Laurie C, Tokiwa G, Lum PY, Wang S, Castellani LW, Lusis AJ, Carison S, Sachs AB, Schadt EE (2005) Integrating QTL and high-density SNP analyses in mice to identify Insig2 as a susceptibility gene for plasma cholesterol levels. Genomics 86:505–517
Chubb C (1992) Genes regulating testis size. Biol Reprod 47:29–36
Coward P, Nagai K, Chen D, Thomas HD, Nagamine CM, Lau YFC (1994) Polymorphism of a CAG trinucleotide repeat within Sry correlates with B6.YDom sex reversal. Nat Genet 6:245–250
Darvasi A (2001) In silico mapping of mouse quantitative trait loci. Science 294:2423
DiPetrillo K, Tsaih SW, Sheehan S, Johns C, Kelmenson P, Gavras H, Churchill GA, Paigen B (2004) Genetic analysis of blood pressure in C3H/HeJ and SWR/J mice. Physiol Genomics 17:215–220
Eicher EM (1994) Sex and trinucleotide repeats. Nat Genet 6:221–223
Eicher EM, Washburn LL, Whiteney JB, Morrow KE (1983) Mus poschiavinus Y chromosome in the C57BL/6J murine genome causes sex reversal. Science 217:535–537
Elliott RW, Poslinski D, Tabaczynski D, Hohman C, Pazik J (2004) Loci affecting male fertility in hybrids between Mus macedonicus and C57BL/6. Mamm Genome 15:704–710
Good JM, Dean MD, Nachman MW (2008) A complex genetic basis to X-linked hybrid male sterility between two species of house mouse. Genetics 179:2213–2228
Graves JAM (2010) Sex chromosome evolution and the expression of sex-specific genes in the placenta. Placenta 24:S27–S32
Greenfield A, Scott D, Pennisi D, Ehrmann I, Ellis P, Cooper L, Simpson E, Koopman P (1996) An H-YDb epitope is encoded by a novel mouse Y chromosome gene. Nat Genet 14:474–478
Grupe A, Germer S, Usuka J, Aud D, Belknap JK, Klein RF, Ahluwalia MK, Higuchi R, Peltz G (2001) In silico mapping of complex disease-related traits in mice. Science 292:1915–1918
Guo Y, Lu P, Farrell E, Zhang X, Weller P, Monshouwer M, Wang J, Liao G, Zhang Z, Hu S, Allard J, Shafer S, Usuka J, Peltz G (2007) In silico and in vitro pharmacogenetic analysis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:17735–17740
Harcourt AH, Harvey PH, Larson SG, Short RV (1981) Testis weight, body weight and breeding system in primates. Nature 293:55–57
Hayward P, Shire JGM (1974) Y chromosome effect on adult testis size. Nature 250:499–500
Herrick CS, Wolfe HG (1977) Effect of the Y-chromosome on testis size in the mouse (Mus musculus). Genetics 86:s27
Hunt SE, Mittwoch U (1987) Y-chromosomal and other factors in the development of testis size in mice. Genet Res 50:205–211
Krausz C, Degl’lnnocenti S, Nuti F, Morelli A, Felici F, Morelli A, Felici F, Sansone M, Varriale G, Forti G (2006) Natural transmission of USP9Y gene mutations: a new perspective on the role of AZFa genes in male fertility. Hum Mol Genet 15:2673–2681
Kunieda T, Toyoda Y (1992) Nucleotide sequence of mouse Sry gene is different between Y chromosome originating from Mus musculus musculus and Mus musculus domesticus. Genomics 13:236–237
L’Hôte D, Serres C, Laissue P, Oulmouden A, Rogel-Gaillard C, Montagutelli X, Vaiman D (2007) Centimorgan-range one-step mapping of fertility traits using interspecific recombinant congenic mice. Genetics 176:1907–1921
Le Roy I, Tordjman S, Migliore-Samour D, Degrelle H, Roubertoux PL (2001) Genetic architecture of testis and seminal vesicle weights in mice. Genetics 158:333–340
Leader-Williams N (1979) Age-related changes in the testicular and antler cycles of reindeer, Rangifer tarandus. J Reprod Fertil 57:117–126
Liu P, Wang Y, Vikis H, Maciag A, Wang D, Lu Y, Liu Y, You M (2006) Candidate lung tumor susceptibility genes identified through whole-genome association analyses in inbred mice. Nat Genet 38:888–895
Luddi A, Margollicci M, Gambera L, Serafini F, Cioni M, De Leo V, Balestri P, Piomboni P (2009) Spermatogenesis in a man with complete deletion of USP9Y. New Engl J Med 360:881–885
Marquis G, Montplaisir S, Pelletier M, Mousseau S, Auger P (1985) Genetic resistance to murine cryptococcosis: Increased susceptibility in the CBA/N XID mutant strain of mice. Infect Immun 47:282–287
Massett MP, Fan R, Berk BC (2009) Quantitative trait loci for exercise training responses in FVB/NJ and C57BL/6J mice. Physiol Genomics 40:15–22
Matsuda Y, Hirobe T, Chapman VM (1991) Genetic basis of X-Y chromosome dissociation and male sterility in interspecific hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4850–4854
Miller KE, Lundrigan BL, Tucker PK (1995) Length variation of CAG repeats in Sry across populations of Mus domesticus. Mamm Genome 6:206–208
Oka A, Mita A, Sakurai-Yamatani N, Yamamoto H, Takagi N, Takano-Shimizu T, Toshimori K, Moriwaki K, Shiroishi T (2004) Hybrid breakdown caused by substitution of the X chromosome between two mouse subspecies. Genetics 166:913–924
Otsuka S, Namiki Y, Ichii O, Hashimoto Y, Sasaki N, Endoh D, Kon Y (2010) Analysis of factors decreasing testis weight in MRL mice. Mamm Genome 21:153–161
Park YG, Clifford R, Buetow KH, Hunter KW (2003) Multiple cross and inbred strain haplotype mapping of complex-trait candidate genes. Genome Res 13:118–121
Rawlings DJ, Saffran DC, Tsukada S, Largaespada DA, Grimaldi JC, Cohen L, Mohr RN, Bazan JF, Howard M, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Witte ON (1993) Mutation of unique region of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in immunodeficient XID mice. Science 261:358–361
Scher I, Ahmed A, Strong DM, Steinberg AD, Paul WE (1975) X-linked B-lymphocyte immune defect in CBA/N mice. I. Studies of the function and composition of spleen cells. J Exp Med 141:788–803
Scott DM, Ehrmann IE, Ellis PS, Bishop CE, Agulnik AI, Simpson E, Mitchell MJ (1995) Identification of a mouse male-specific transplantation antigen, H-Y. Nature 376:695–698
Shire JGM, Bartke A (1972) Strain differences in testicular weight and spermatogenesis with special reference to C57BL/10J and DBA/2J mice. J Endocrinol 55:163–171
Storchová R, Gregorová S, Buckiová D, Kyselová V, Divina P, Forejt J (2004) Genetic analysis of X-linked hybrid sterility in the house mouse. Mamm Genome 15:515–524
Su WL, Sieberts SK, Kleinhanz RR, Lux K, Millstein J, Molony C, Schadt EE (2010) Assessing the prospects of genome-wide association studies performed in inbred mice. Mamm Genome 21:143–152
Sun C, Skaletsky H, Birren B, Devon K, Tang Z, Silber S, Oates R, Page DC (1999) An azoospermic man with a de novo point mutation in the Y-chromosomal gene USP9Y. Nat Genet 23:429–432
Suto J (2008) Genetic dissection of testis weight in a mouse strain having an extremely large testis: major testis weight determinants are autosomal rather than Y-linked on the basis of comprehensive analyses in Y-chromosome consomic strains. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B 84:393–406
Suto J (2009) The A y allele at the agouti locus reduces the size and alters the shape of the mandible in mice. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B 85:248–257
Thomas JD, Sideras P, Smith CI, Vorechovsky I, Chapman V, Paul WE (1993) Colocalization of X-linked agammaglobulinemia and X-linked immunodeficiency genes. Science 261:355–358
Vogt MHJ, Goulmy E, Kloosterboer FM, Blokland E, de Paus RA, Willemze R, Falkenburg JH (2000a) UTY gene codes for an HLA-B60-restricted human male-specific minor histocompatibility antigen involved in stem cell graft rejection: characterization of the critical polymorphic amino acid residues for T-cell recognition. Blood 96:3126–3132
Vogt MHJ, de Paus RA, Voogt PJ, Willemze R, Falkenburg JH (2000b) DFFRY codes for a new human male-specific minor transplantation antigen involved in bone marrow graft rejection. Blood 95:1100–1105
Vyskočilová M, Pražanová Z, Piálek J (2009) Polymorphism in hybrid male sterility in wild-derived Mus musculus musculus strains on proximal chromosome 17. Mamm Genome 20:83–91
Wang W, Meadows LR, den Haan JM, Sherman NE, Chen Y, Blokland E, Shabanowitz J, Agulnik AI, Hendrickson RC, Bishop CE (1995) Human H-Y: a male-specific histocompatibility antigen derived from the SMCY protein. Science 269:1588–1590
Zídek V, Musilová A, Pintíř P, Šimáková M, Pravenec M (1998) Genetic dissection of testicular weight in the mouse with the BXD recombinant inbred strains. Mamm Genome 9:503–505
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Nos. 15500305 and 19500373).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suto, Ji. Genetic dissection of testis weight in mice: quantitative trait locus analysis using F2 intercrosses between strains with extreme testis weight, and association study using Y-consomic strains. Mamm Genome 22, 648–660 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-011-9353-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-011-9353-3