Abstract
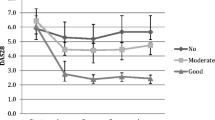
The objective of this study was to investigate the influence of TNF-α promoter alleles on clinical response to etanercept therapy in JIA. TNF-α promoter polymorphisms at positions −163, −238, −244, −308, −376 were determined in 137 JIA patients treated with etanercept for at least 3 months. A PCR fragment of about 500 bp of the TNF gene promoter was amplified. Polymorphisms were detected by a single sequencing procedure. Patients with the genotype −308GG achieved an ACR-JRA 30 response at month 6 more frequently than patients with the genotype −308GA or AA. This was already notable at month 3 of therapy. This difference in the total patient group is attributable to the JIA subgroup with rheumatoid factor negative polyarthritis. In this subgroup, patients with the −308GG genotype achieved an ACR-JRA 30 response more frequently than those with the −308GA or AA genotype (84 vs. 33% at months three, P < 0.01, 93 vs. 67% at months six, P < 0.05). There was no influence of the −238 TNF-α promoter alleles on clinical response. The rare alleles at position −376 or at positions −163 and −244 were too infrequent. There is an association between TNF gene promoter polymorphisms and response to etanercept in rheumatoid factor negative polyarticular JIA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lovell DJ, Giannini EH, Reiff A, Jones OY, Schneider R, Olson JC, Stein LD, Gedalia A, IIowite NT, Wallace CA, Lange M, Finck BK, Burge DJ, Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group (2003) Long-term efficacy and safety of etanercept in children with polyarticular-course juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: interim results from an ongoing multicenter, open-label, extended-treatment trial. Arthritis Rheum 48(1):218–226
Wilson AG, Symons JA, McDowell TL, McDevitt HO, Duff GW (1997) Effects of a polymorphism in the human TNF alpha promoter on transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3195–3199
Zeggini E, Thomson W, Kwiatkowski D, Richardson A, Ollier W, Donn R, British Paediatric Rheumatology Study Group (2002) Linkage and association studies of single-nucleotide polymorphism-tagged tumor necrosis factor haplotypes in juvenile oligoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46(12):3304–3311
Schmeling H, Wagner U, Peterson A, Horneff G (2006) Tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter polymorphisms in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 24(1):103–108
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, Baum J, Glass DN, Goldenberg J, He X, Maldonado-Cocco J, Orozco-Alcala J, Prieur AM, Suarez-Almazor ME, Woo P, International League of Associations for Rheumatology (2001) International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (second revision 2004, Edmonton). J Rheumatol 31(2):390–392
Giannini EH, Ruperto N, Ravevelli A, Lovell DJ, Felson DT, Martini A (1997) Preliminary definition of improvement in juvenile arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 40:1202–1209
Padyukov L, Lampa J, Heimbürger M, Ernestam S, Cederholm T, Lundkvist I, Andersson P, Hermansson Y, Harju A, Klareskog L, Bratt J (2003) Genetic markers for the efficacy of tumour necrosis factor blocking therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62:526–529
Kang CP, Lee KW, Yoo DH, Kang C, Bae SC (2005) The influence of a polymorphism at position −857 of the tumour necrosis factor α gene on clinical response to etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 44:547–552
Balog A, Klausz G, Gál J, Molnár T, Nagy F, Ocsovszky I, Gyulai Z, Mándi Y (2004) Investigation of the prognostic value of TNF-α gene polymorphism among patients treated with infliximab, and the effects of infliximab therapy on TNF-α production and apoptosis. Pathobiology 71:274–280
Louis E, Vermeire S, Rutgeerts P, De Vos M, Van Gossum A, Pescatore P, Fiasse R, Pelckmans P, Reynaert H, D’Haens G, Malaise M, Belaiche J (2002) A positive response to infliximab in Crohn disease: association with higher systemic inflammation before treatment but not with −308 TNF gene polymorphism. Scand J Gastroenterol 37:818–824
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the following contributors for including their patients to the study: R. Berner, M. Borte, I. Feddersen, I. Földvari, D. Föll, H. Girschick, G. Heubner, C. Huemer, S. Kastner, M. Kirschstein, H. Kössel, H. Michels, D. Möbius, S. Müller, T. Niehues, A. Nimtz-Talaska, J. Quietsch, J. Roth, A. Thon, R. Trauzeddel, A. Urban, and E. Weissbarth-Riedel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmeling, H., Horneff, G. Tumour necrosis factor alpha promoter polymorphisms and etanercept therapy in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatol Int 27, 383–386 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-006-0208-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-006-0208-2