Abstract
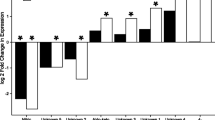
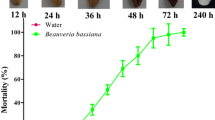
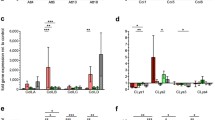
Metarhizium anisopliae is an important insect pathogenic fungus widely used in biological pest control. The aim of this study was to identify genes differentially expressed in vivo by M. anisopliae CQMa102 in the hemolymph of infected Locusta migratoria. Suppression-subtractive hybridization was performed using cDNA generated from hyphal bodies purified from hemolymph and the fungus germinating and differentiating on locust wings. A total of 350/1,600 random clones screened by cDNA array dot blotting were sequenced, resulting in 120 uniquely expressed sequence tags (ESTs) that were up-regulated during colonization of hemolymph. Among these 120 ESTs, 42 (35.0%) had matches in the NR protein database, and 29 (24.2%) were significantly similar to known proteins involved in various cellular processes, including general metabolism, cell wall remodeling, protein synthesis, signal transduction and stress responses. In contrast, the remaining 78 ESTs (65.0%) either had low similarity in the NR database or represented novel genes. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of five randomly selected genes revealed that all were highly expressed in the host hemolymph. These results provide new insight into the underlying molecular mechanisms of adaptation to host hemolymph and may increase understanding of host–pathogen interactions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altincicek B, Linder M, Linder D, Preissner KT, Vilcinskas A (2007) Microbial metalloproteinases mediate sensing of invading pathogens and activate innate immune responses in the lepidopteran model host Galleria mellonella. Infect Immun 75(1):175–183
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bai C, Xu XL, Chan FY, Lee RTH, Wang Y (2006) MNN5 encodes an iron-regulated alpha-1, 2-mannosyltransferase important for protein glycosylation, cell wall integrity, morphogenesis, and virulence in Candida albicans. Eukaryot Cell 5(2):238–247
Beyer K, Jimenez SJ, Randall TA, Lam S, Binder A, Boller T, Collinge MA (2002) Characterization of Phytophthora infestans genes regulated during the interaction with potato. Mol Plant Pathol 3(6):473–485
Borges-Walmsley MI, Walmsley AR (2000) cAMP signalling in pathogenic fungi: control of dimorphic switching and pathogenicity. Trends Microbiol 8:133–141
Brennan CA, Anderson KV (2004) Drosophila: the genetics of innate immune recognition and response. Annu Rev Immunol 22:457–483
Chapman RF (1998) The insects: structure and function. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Charnley AK (2003) Fungal pathogens of insects: cuticle degrading enzymes and toxins. Adv Bot Res 40:241–321
Cooper JA, Reiss NA, Schwartz RJ, Hunter T (1983) Three glycolytic enzymes are phosphorylated at tyrosine in cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Nature 302(5905):218–223
Die JV, Dita MA, Krajinski F, Gonzalez-Verdejo CI, Rubiales D, Moreno MT, Roman B (2007) Identification by suppression-subtractive hybridization and expression analysis of Medicago truncatula putative defence genes in response to Orobanche crenata parasitization. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 70(1–3):49–59
Doekel S, Gal MFCL, Gu JQ, Chu M, Baltz RH, Brian P (2008) Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase module fusions to produce derivatives of daptomycin in Streptomyces roseosporus. Microbiology 154:2872–2880
Gillespie JP, Bailey AM, Cobb B, Vilcinskas A (2000) Fungi as elicitors of insect immune responses. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 44:49–68
He M, Xia YX (2009) Construction and analysis of a normalized cDNA library from Metarhizium anisopliae var acridum germinating and differentiating on Locusta migratoria wings. FEMS Microbiol Lett 291(1):127–135
Hirschi K, VanEtten H (1996) Expression of the pisatin-detoxifying genes (PDA) of Nectria haematococca in vitro and in planta. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 9(6):483–491
Hoffmann JA (2003) The immune response of Drosophila. Nature 426:33–38
Hunter DM, Milner RJ, Spurginal PA (2001) Aerial treatment of the Australian plague locust, Chortoicetes terminifera (Orthoptera: crididae) with Metarhizium anisopliae Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes). Bull Entomol Res 91(2):93–99
Kleinkauf H, von Döhren H (1990) Nonribosomal biosynthesis of peptide antibiotics. Eur J Biochem 192(1):1–15
Marie G, Vanessa G, Alexey AM, Jean-Marc R, Chengshu W, Tariq MB, Marcia B, Jules AH, Dominique F (2006) Dual detection of fungal infections in Drosophila via recognition of glucans and sensing of virulence factors. Cell 127:1425–1437
Mewes HW, Dietmann S, Frishman D, Gregory R, Mannhaupt G, Mayer KFX, Munsterkotter M, Ruepp A, Spannagl M, Stuempflen V, Rattei T (2008) MIPS: analysis and annotation of genome information in 2007. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D196–D201
Pollard A, Wyn Jones RG (1979) Enzyme activities in concentrated solutions of glycine-betaine and other solutes. Planta 144:291–298
Roberts DW, Humber RA (1981) Entomogenous fungi. In: Cole GT, Kendrick B (eds) Biology of conidial fungi. Academic Press, New York, pp 201–236
Scholte EJ, Takken W, Knols BGJ (2007) Infection of adult Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus mosquitoes with the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Acta Trop 102(3):151–158
Sestak S, Hagen I, Tanner W, Strahl S (2004) Scw10p, a cell wall glucanase/transglucosidase important for cell wall stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiology 150:3197–3208
St Leger RJ (2007) Metarhizium anisopliae as a model for studying bioinsecticidal host–pathogen interactions. In: Maurizio V, Jonathan G (eds) Novel biotechnologies for biocontrol agent enhancement and management. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 179–204
St Leger RJ, Cooper RM, Charnley AK (1986a) Cuticle-degrading enzymes of entomopathogenic fungi: cuticle degradation in vitro by enzymes from entomopathogens. J Invertebr Pathol 47:167–177
St Leger RJ, Charnly AK, Cooper RM (1986b) Cuticle degrading enzymes of entomopathogenic fungi: synthesis in culture on cuticle. J Invertebr Pathol 48:85–95
St Leger RJ, Bidochka MJ, Roberts DW (1994) Isoforms of the cuticle-degrading proteinase and production of a metalloproteinase by Metarhizium anisopliae. Arch Biochem Biophys 313(1):1–7
St Leger RJ, Joshi L, Bidochka MJ, Roberts DW (1996) Construction of an improved mycoinsecticide overexpressing a toxic protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:6349–6354
Steenkamp ET, Wingfield BD, Coutinho TA, Wingfield MJ, Marasas WF (1999) Differentiation of Fusarium subglutinans f. sp. pini by histone gene sequence data. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(8):3401–3406
Takahashi H, Kumagai T, Kitani K, Mori M, Matoba Y, Sugiyama M (2007) Cloning and characterization of a Streptomyces single module type non-ribosomal peptide synthetase catalyzing a blue pigment synthesis. J Biol Chem 282(12):9073–9081
Vilcinskas A, Götz P (1999) Parasitic fungi and their interactions with the insect immune system. Adv Parasitol 43:267–313
Wang CS, St Leger RJ (2006) A collagenous protective coat enables Metarhizium anisopliae to evade insect immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(17):6647–6652
Wang CS, St Leger RJ (2007) A scorpion neurotoxin increases the potency of a fungal insecticide. Nature Biotechnology 25(12):1455–1456. doi:101038/nbt1357
Wang CT, Cao YQ, Wang ZK, Yin YP, Peng GX, Li ZL, Xia YX (2007) Differentially expressed glycoproteins in Locusta migratoria hemolymph infected with Metarhizium anisopliae. J Invertebr Pathol 96(3):230–236
Wang CS, Duan ZB, St Leger RJ (2008) MOS1 osmosensor of Metarhizium anisopliae is required for adaptation to insect host hemolymph. Eukaryot Cell 7(2):302–309
Wright MS, Raina AK, Lax AR (2005) A strain of the fungus Metarhizium anisopliae for controlling subterranean termites. J Econ Entomol 98(5):1451–1458
Xia YX, Clarkson JM, Charnley AK (2001) Acid phosphatases of Metarhizium anisopliae during infection of the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Arch Microbiol 176(6):427–434
Xia YX, Clarkson JM, Charnley AK (2002a) Trehalose-hydrolysing enzymes of Metarhizium anisopliae and their role in pathogenesis of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. J Invertebr Pathol 80(3):139–147
Xia YX, Gao MY, Clarkson JM, Charnley AK (2002b) Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression of a neutral trehalase from the insect pathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. J Invertebr Pathol 80:127–137
Zhang CS, Cao YQ, Wang ZK, Yin YP, Peng GX, Xia YX (2007) A method to construct cDNA library of the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae, in the hemolymph of the infected locust. Mol Biotechnol 36(1):23–31
Zhao H, Charnley AK, Wang ZK, Yin YP, Li ZL, Li YL, Cao YQ, Peng GX, Xia YX (2006) Identification of an extracellular acid trehalase and its gene involved in fungal pathogenesis of Metarizium anisopliae. J Biochem 140(3):319–327
Zhou H, Hu HY, Zhang LJ, Li RY, Ouyang HM, Ming J, Jin C (2007) O-Mannosyltransferase 1 in Aspergillus fumigatus (AfPmt1p) is crucial for cell wall integrity and conidium morphology, especially at an elevated temperature. Eukaryot Cell 6(12):2260–2268
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30771446) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2006AA10A212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Heitman.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Xia, Y. Identification of genes differentially expressed in vivo by Metarhizium anisopliae in the hemolymph of Locusta migratoria using suppression-subtractive hybridization. Curr Genet 55, 399–407 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-009-0254-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-009-0254-x