Abstract.
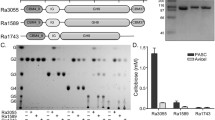
Ruminococcus albus is an important fibrolytic bacterium in the rumen. Cellobiose is metabolized by this organism via hydrolytic and well as phosphorylytic enzymes, but the relative contributions of each pathway were not clear. The cellobiose consumption rate by exponentially growing cells was less than that of crude extracts (75 versus 243 nmol/min/mg protein). Cellobiose phosphorolytic cleavage was much greater than hydrolytic activity (179 versus 19 nmol/min/mg protein) indicating that phosphorylases were key enzymes in the initial metabolism of the soluble products of cellulose degradation. Cellodextrin phosphorylase appeared to be active against substrates as large as cellohexaose. Phosphorylase activities were cytoplasmic, but hydrolytic activities were associated with both the membrane and cytoplasmic fractions. Free glucose was phosphorylated with a GTP-dependent glucokinase, and this enzyme showed 20-fold higher activity with GTP or ITP (>324 nmol/min/mg protein) than with ATP, UTP, CTP, GDP, or PEP. The activity was decreased at least 57% when mannose, 2-deoxyglucose, or fructose was used as substrate compared with glucose. The K m s for glucose and GTP were 321 and 247 μM, respectively. Since phosphorolytic cleavage conserves more metabolic energy than simple hydrolysis, it is likely that such pathways provide for more efficient growth of R. albus in substrate-limiting conditions like those found in the rumen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 February 1997 / Accepted: 31 March 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, J., Dawson, K. & Strobel, H. Cellobiose and Cellodextrin Metabolism by the Ruminal Bacterium Ruminococcus albus . Curr Microbiol 35, 221–227 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900242
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900242