Abstract
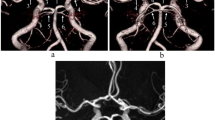
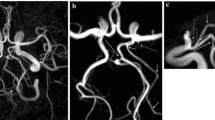
The accessory middle cerebral artery (MCA) is a common variation of the MCA that arises from the anterior cerebral artery. We report a patient with anastomosis of the accessory MCA with the main MCA, an extremely rare variant that we diagnosed by magnetic resonance (MR) angiography. Both partial maximum-intensity-projection and partial volume-rendering MR angiographic images obtained at 3 T are useful to identify such rare vascular variation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abanou A, Lasjaunias P, Manelfe C, Lopez-Ibor L (1984) The accessory middle cerebral artery (AMCA). Diagnostic and therapeutic consequences. Anat Clin 6:305–309
Elsharkawy A, Ishii K, Niemelä M, Kivisaari R, Lehto H, Hernesniemi J (2013) Management of aneurysms at the origin of duplicated middle cerebral artery: series of four patients with review of the literature. World Neurosurg 80:e313–e318
Kai Y, Hamada J, Morioka M, Yano S, Kudo M, Kuratsu J (2006) Treatment of unruptured duplicated middle cerebral artery aneurysm: case report. Surg Neurol 65:190–193
Komiyama M, Nakajima H, Nishikawa M, Yasui T (1998) Middle cerebral artery variations: duplicated and accessory arteries. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:45–49
Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A, ter Brugge KG (2001) The cranial internal carotid artery division. In: Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A, ter Brugge KG (eds) Surgical neuro-angiography, vol 1. Clinical vascular anatomy and variations, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 575–629
Padget DH (1948) The development of the cranial arteries in the human embryo. Contrib Embryol Carneg Inst 32:205–261
Teal JS, Rumbaugh CL, Bergeron RT, Segall HD (1973) Anomalies of the middle cerebral artery: accessory artery, duplication, and early bifurcation. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 118:567–575
Uchino A, Kato A, Takase Y, Kudo S (2000) Middle cerebral artery variations detected by magnetic resonance angiography. Eur Radiol 10:560–563
Uchino A, Saito N, Okada Y, Nakajima R (2012) Duplicate origin and fenestration of the middle cerebral artery on MR angiography. Surg Radiol Anat 34:401–404
Vuillier F, Medeiros E, Moulin T, Cattin F, Bonneville JF, Tatu L (2008) Main anatomical features of the M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery: a 3D time-of flight magnetic resonance angiography at 3 T study. Surg Radiol Anat 30:509–514
Acknowledgments
We thank Rosalyn Uhrig, M.A., for editorial assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, M., Uchino, A. & Suzuki, C. Anastomosis between accessory middle cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery diagnosed by magnetic resonance angiography. Surg Radiol Anat 39, 685–687 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1763-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1763-1