Abstract
Objective
To clarify the oriented classification, relationships, and variations of the abducens nerve and provide a detailed description of its microsurgical anatomic features.
Methods
A microsurgical anatomic dissection of the abducens nerve was performed in 100 specimens obtained from 50 adult cadaveric heads fixed in formalin and two adult cadaveric heads stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological examination. Important neurovascular and structural relationships of the abducens nerve were observed.
Results
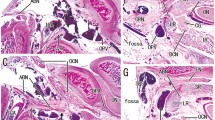
The abducens nerve was divided into five segments (cisternal, petroclival, internal carotid artery, fissural, and intraconal). It coursed in the petroclival venous confluence and there was a complex anatomic relationship. Two new types of abducens nerve variations were found. In one type, the duplicated nerve is split into two branches for a limited length in the cavernous sinus (CS). The other is a complex type, which has a complex course and pattern. This type of duplicated abducens nerve has a communicating branch in the cistern and numerous fasciculi in the CS. In addition, the two branches do not accompany each other for the entire course in the CS.
Conclusion
The vulnerability of the abducens nerve results from diverse factors. The inferolateral trunk, which arises from the intracavernous segment of carotid artery (also called the artery of the inferior CS), is an important landmark for finding the abducens nerve and sympathetic nerve. Variations of the abducens nerve are not rare. Keeping variations of the nerve in mind is important during skull base operations and transvenous endovascular interventions. Understanding the relationship of the abducens nerve with adjacent structures will help us in preparing for safe surgery.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bremond-Gignac D, Copin H, Cussenot O, Lassau JP, Henin D (2004) Anatomical histological and mesoscopic study of the adipose tissue of the orbit. Surg Radiol Anat 26:297–302
d’Avella E, Tschabitscher M, Santoro A, Delfini R (2008) Blood supply to the intracavernous cranial nerves: comparison of the endoscopic and microsurgical perspectives. Neurosurgery 62:305–311
Destrieux C, Velut S, Kakou MK, Lefrancq T, Arbeille B, Santini JJ (1997) A new concept in Dorello’s canal microanatomy: the petroclival venous confluence. J Neurosurg 87:67–72
Dorello P (1905) Considerazioni sopra la causa della paralisi transitoria dell’abducente nelle flogosi dell’orecchio medio. Atti Clin Otorinolaringoiatrica. Univ Roma 3:209–217
Harris FS, Rhoton AL (1976) Anatomy of the cavernous sinus: a microsurgical study. J Neurosurg 45:169–180
Iaconetta G, Fusco M, Cavallo LM, Cappabianca P, Samii Mm, Tschabitscher M (2007) The abducens nerve: microanatomic and endoscopic study. Neurosurgery 61:7–14
Iaconetta G, Tessitore E, Samii M (2001) Duplicated abducent nerve and its course: microanatomical study and surgery-related considerations. J Neurosurg 95:853–858
Jain KK (1964) Aberrant roots of the abducent nerve. J Neurosurg 21:349–351
Lang J (1995) Nervus abducent. In: Lang J (ed) Skull base and related structures: atlas of clinical anatomy. Schattauer, Stuttgart, pp 85–86
Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A, Ter Brugge KG (2001) Clinical vascular anatomy and variations, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 389–414
Lazow SK, Izzo SR, Feinberg ME, Berger JR (1995) Bilateral abducens nerve palsy secondary to maxillofacial trauma: report of case with proposed mechanism of injury. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 53:1197–1199
Nathan H, Ouaknine G, Kosary IZ (1974) The abducens nerve: anatomical variations in its course. J Neurosurg 41:561–566
Ono K, Arai H, Endo T, Tsunoda A, Sato K, Sakai T, Makita J (2004) Detailed MR imaging anatomy of the abducent nerve: evagination of CSF into Dorello canal. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:623–626
Ozveren MF, Erol FS, Alkan A, Kocak A, Onal C, Türe U (2007) Microanatomical architecture of Dorello’s canal and its clinical implications. Neurosurgery 60:1–8
Ozveren MF, Sam B, Akdemir I, Alkan A, Tekdemir I, Deda H (2003) Duplication of the abducens nerve at the petroclival region: an anatomic study. Neurosurgery 52:645–652
Takagi H, Miyasaka Y, Kuramae T, Ohwada T, Tsunoda M (1976) Bilateral traumatic abducens nerve palsy without skull fracture or intracranial hematoma—a report of 3 cases and consideration of the mechanism of injury. No Shinkei Geka 4:963–969
Tillack TW, Winer JA (1962) Anomaly of the abducens nerve. Yale J Biol Med 34:620–624
Tsitsopoulos PD, Tsonidis CA, Petsas GP, Hadjiioannou PN, Njau SN, Anagnostopoulos IV (1996) Microsurgical study of the Dorello’s canal. Skull Base Surg 6:181–185
Umansky F, Elidan J, Valarezo A (1991) Dorello’s canal: a microanatomical study. J Neurosurg 75:294–298
Umansky F, Valarezo A, Elidan J (1992) The microsurgical anatomy of the abducens nerve in its intracranial course. Laryngoscope 102:1285–1292
Willinsky R, Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A (1987) Intracavernous branches of the internal carotid artery (ICA). Comprehensive review of their variations. Surg Radiol Anat 9:201–215
Zhang Y, Liu H, Liu E-Z, Lin Y-Z, Zhao S-G, Jing G-H (2010) Microsurgical anatomy of the ocular motor nerves. Surg Radiol Anat 32:623–628
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yu, H., Shen, BY. et al. Microsurgical anatomy of the abducens nerve. Surg Radiol Anat 34, 3–14 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-011-0850-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-011-0850-6