Abstract
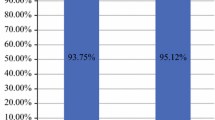
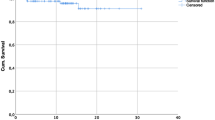
This study compares the incidence of local and regional recurrence of breast cancer between two contiguous time windows in a homogeneous population of 137 patients who underwent fat tissue transplant after modified radical mastectomy. Median follow-up time was 7.6 years and the follow-up period was divided into two contiguous time windows, the first starting at the date of the radical mastectomy and ending at the first lipoaspirate grafting session and the second beginning at the time of the first lipoaspirate grafting session and ending at the end of the total follow-up time. Although this study did not employ an independent control group, the incidence of local recurrence of breast cancer was found to be comparable between the two periods and in line with data from similar patient populations enrolled in large multicenter clinical trials and who did not undergo postsurgical fat tissue grafting. Statistical comparison of disease-free survival curves revealed no significant differences in relapse rate between the two patient subgroups before fat grafting and after fat grafting. Although further confirmation is needed from multicenter randomized clinical trials, our results support the hypothesis that autologous lipoaspirate transplant combines striking regenerative properties with no or marginal effects on the probability of post-mastectomy locoregional recurrence of breast cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman M (2000) Rejuvenation of the upper eyelid complex with autologous fat transplantation. Dermatol Surg 26:1113–1116
Coleman SR (2002) Hand rejuvenation with structural fat grafting. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:1731–1744
Trepsat F (2003) Periorbital rejuvenation combining fat grafting and blepharoplasties. Aesthetic Plast Surg 27:243–253
Tzikas TL (2004) Lipografting: autologous fat grafting for total facial rejuvenation. Facial Plast Surg 20:135–143
Coleman SR (2006) Structural fat grafting: more than a permanent filler. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(3 Suppl):108S–120S
Rigotti G, Marchi A, Galiè M, Baroni G, Benati D, Krampera M, Pasini A, Sbarbati A (2007) Clinical treatment of radiotherapy tissue damages by lipoaspirates transplant: a healing process mediated by adipose derived adult stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg 119(5):1409–1422
Delay E, Garson S, Tousson G, Sinna R (2009) Fat injection to the breast: technique, results, and indications based on 880 procedures over 10 years. Aesthet Surg J 29(5):360–376
Chan CW, McCulley SJ, Macmillan RD (2008) Autologous fat transfer—a review of the literature with a focus on breast cancer surgery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61(12):1438–1448
Mojallal A, Saint-Cyr M, Garrido I (2009) Autologous fat transfer: controversies and current indications for breast surgery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62(5):708–710
Veronesi U, Salvadori B, Luini A, Greco M, Saccozzi R, del Vecchio M, Mariani L, Zurrida S, Rilke F (1995) Breast conservation is a safe method in patients with small cancer of the breast. Long-term results of three randomized trials on 1, 973 patients. Eur J Cancer 31:1574–1579
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rigotti, G., Marchi, A., Stringhini, P. et al. Determining the Oncological Risk of Autologous Lipoaspirate Grafting for Post-Mastectomy Breast Reconstruction. Aesth Plast Surg 34, 475–480 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9481-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9481-2