Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to correlate the imaging features with surgical histology for tibial osteofibrous dysplasia (OFD), osteofibrous dysplasia-like adamantinoma (OFD/LA) and classical adamantinoma and to determine the additional role of imaging in suggesting a correct diagnosis in cases of needle biopsy misdiagnosis.
Materials and methods
This is a retrospective audit of 24 patients presenting over a 9-year period to a specialist orthopaedic oncology unit. Radiographic and axial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) characteristics were recorded for each patient. The needle biopsy diagnosis and resection specimen histological diagnoses were retrospectively reviewed and compared with the imaging findings.
Results
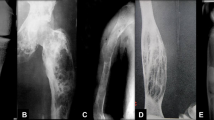
The 24 cases comprised five OFD, 11 OFD/LA and eight adamantinoma based on surgical resection histology. The mean length of OFD was 6.1 cm (range 2–8.5 cm), for OFD/LA was 6.5 cm (range 2–13 cm) and for adamantinoma was 13.2 cm (range 6.5–26 cm). Seven of eight adamantinomas had moth-eaten margins compared to five of 11 OFD/LA and two of five OFDs. Three of eight adamantinomas demonstrated cortical destruction, with seven of eight cases completely involving the marrow cavity. In comparison, only one of 11 OFD/LA cases and one of five OFD cases demonstrated cortical destruction, and complete marrow involvement was rare. Four of 19 cases had a different needle biopsy result compared to the final histology, three cases being upgraded from an OFD/LA or OFD to classical adamantinoma. The radiological features of these three cases were more in keeping with a diagnosis of adamantinoma.
Conclusions
A diagnosis of classical adamantinoma is suggested by an extensive lesion with moth-eaten margins and complete involvement of the medullary cavity on axial MR imaging. Misdiagnosis on needle biopsy may occur in up to one fifth of cases, and radiological features can assist in making the correct diagnosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahn LB. Adamantinoma, osteofibrous dysplasia and differentiated adamantinoma. Skelet Radiol 2003; 32: 245–258.
Iravani S, Walling A, Gilbert-Barness E. Pathological case of the month. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1997; 151: 427–428.
Unni KK. Dahlin’s bone tumors: general aspects and data on 11,087 cases. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven; 1996. p. 333–42.
Moon NF, Mori H. Adamantinoma of the appendicular skeleton-updated. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1986; 204: 215–237.
Hazelberg HM, Taminiau AH, Fleuren GJ, Hogendoorn PC. Adamantinoma of the long bones. A clinicopathologic study of 32 patients with emphasis on histological subtype, precursor lesion and biological behaviour. J Bone Jt Surg Am 1994; 76: 1482–1499.
Van der Woude HJ, Hazelbag HM, Bloem JL, Taminiau AH, Hogendoorn PC. MRI of adamantinoma of long bones in correlation with histopathology. AJR 2004; 183: 1737–44.
Campanacci M, Laus M. Osteofibrous dysplasia of the tibia and fibula. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 1981; 69-A: 367–375.
Wang J, Shih C, Chen W. Osteofibrous dysplasia (ossifying fibroma of long bones): a report of four cases and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1992; 69-A: 367–375.
Bohndorf K, Nidecker A, Mathias K, Zidkova H, Kauffmann H, Jundt G. The radiologic findings in adamantinoma of the long tubular bones. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstrahl Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 1992; 157: 239–244.
Bloem JL, Van der Heul RO, Schuttevaer HM, Kuipers D. Fibrous dysplasia vs adamantinoma of the ibia: differentiation based on discriminant analysis of clinical and plain film findings. AJR 1991; 156: 1017–1023.
De Keyser F, Vansteenkiste J, Van Den Brande P, Demedts M, Van de Woestijne KP. Pulmonary metastasis of a tibial adamantinoma. Case report and review of the literature. Acta Clin Belg 1990; 45: 31–33.
Keeney GL, Unni KK, Beabout JW, Pritchard DJ. Adamantinoma of long bones. A clinicopathological study of 85 cases. Cancer 1989; 64: 730–737.
Qureshi AA, Shott S, Mallin BA, Gitelis S. Current trends in the management of adamantinoma of long bones. An international study. J Bone Jt Surg Am 2000; 82: 1122–1131.
Park YK, Unni KK, McLeod RA, Pritchard DJ. Osteofibrous dysplasia: clinicopathological study of 80 cases. Hum Pathol 1993; 24: 1339–1347.
Lee RS, Weitzel S, Eastwood DM, Monsell F, Pringle J, Cannon SR, Briggs TWR. Osteofibrous dysplasia of the tibia. Is there a need for a radical surgical approach? J Bone Jt Surg 2006; 88-B: 658–664.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khanna, M., Delaney, D., Tirabosco, R. et al. Osteofibrous dysplasia, osteofibrous dysplasia-like adamantinoma and adamantinoma: correlation of radiological imaging features with surgical histology and assessment of the use of radiology in contributing to needle biopsy diagnosis. Skeletal Radiol 37, 1077–1084 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-008-0553-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-008-0553-1