Abstract
Introduction
No previous study has investigated the relationship between intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (IV t-PA) and intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) according to the location of vessel occlusion. The aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship between preprocedural IV t-PA and endovascular treatment (EVT) and ICH according to the location of occlusion using data from the nationwide prospective registry of acute cerebral large vessel occlusion (LVO), the RESCUE-Japan Registry.
Methods
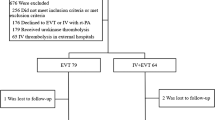
Among 1442 patients with acute LVO enrolled in the registry, we examined 410 patients who received EVT. Patients were divided into the following four groups according to the location of occlusion: the internal carotid artery (ICA), middle cerebral artery first division (M1), middle cerebral artery second division (M2), and vertebral artery (VA)/basilar artery (BA) groups.
Results
A total of 399 patients in whom the occlusion was located in these vessels were finally included. Any ICH (aICH) was identified in 127 (30.9 %) patients, and symptomatic ICH (sICH) was identified in 20 (4.9 %). Preprocedural IV t-PA did not increase the incidence of aICH in any group and tended to increase the incidence of sICH in only the M2 group. In multivariate analysis of the M2 group, IV t-PA was an independent risk factor for sICH.
Conclusion
Preprocedural IV t-PA did not increase the incidence of ICH in total, but could increase the incidence of sICH in those with M2 occlusion. IV t-PA before EVT may be an independent risk factor for sICH in patients with M2 occlusion.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emberson J, Lees KR, Lyden P, Blackwell L, Albers G, Bluhmki E, Brott T, Cohen G, Davis S, Donnan G, Grotta J, Howard G, Kaste M, Koga M, von Kummer R, Lansberg M, Lindley RI, Murray G, Olivot JM, Parsons M, Tilley B, Toni D, Toyoda K, Wahlgren N, Wardlaw J, Whiteley W, del Zoppo GJ, Baigent C, Sandercock P, Hacke W (2014) Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 384(9958):1929–1935. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60584-5
Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group (1995). N Engl J Med 333 (24):1581–1587. doi:10.1056/NEJM199512143332401
Heldner MR, Zubler C, Mattle HP, Schroth G, Weck A, Mono ML, Gralla J, Jung S, El-Koussy M, Ludi R, Yan X, Arnold M, Ozdoba C, Mordasini P, Fischer U (2013) National Institutes of Health stroke scale score and vessel occlusion in 2152 patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 44(4):1153–1157. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000604
Bhatia R, Hill MD, Shobha N, Menon B, Bal S, Kochar P, Watson T, Goyal M, Demchuk AM (2010) Low rates of acute recanalization with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in ischemic stroke: real-world experience and a call for action. Stroke 41(10):2254–2258. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.592535
Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, Schonewille WJ, Vos JA, Nederkoorn PJ, Wermer MJ, van Walderveen MA, Staals J, Hofmeijer J, van Oostayen JA, Lycklama a Nijeholt GJ, Boiten J, Brouwer PA, Emmer BJ, de Bruijn SF, van Dijk LC, Kappelle LJ, Lo RH, van Dijk EJ, de Vries J, de Kort PL, van Rooij WJ, van den Berg JS, van Hasselt BA, Aerden LA, Dallinga RJ, Visser MC, Bot JC, Vroomen PC, Eshghi O, Schreuder TH, Heijboer RJ, Keizer K, Tielbeek AV, den Hertog HM, Gerrits DG, van den Berg-Vos RM, Karas GB, Steyerberg EW, Flach HZ, Marquering HA, Sprengers ME, Jenniskens SF, Beenen LF, van den Berg R, Koudstaal PJ, van Zwam WH, Roos YB, van der Lugt A, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Majoie CB, Dippel DW (2015) A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372(1):11–20. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1411587
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, Roy D, Jovin TG, Willinsky RA, Sapkota BL, Dowlatshahi D, Frei DF, Kamal NR, Montanera WJ, Poppe AY, Ryckborst KJ, Silver FL, Shuaib A, Tampieri D, Williams D, Bang OY, Baxter BW, Burns PA, Choe H, Heo JH, Holmstedt CA, Jankowitz B, Kelly M, Linares G, Mandzia JL, Shankar J, Sohn SI, Swartz RH, Barber PA, Coutts SB, Smith EE, Morrish WF, Weill A, Subramaniam S, Mitha AP, Wong JH, Lowerison MW, Sajobi TT, Hill MD (2015) Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372(11):1019–1030. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1414905
Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, Yan B, Dowling RJ, Parsons MW, Oxley TJ, Wu TY, Brooks M, Simpson MA, Miteff F, Levi CR, Krause M, Harrington TJ, Faulder KC, Steinfort BS, Priglinger M, Ang T, Scroop R, Barber PA, McGuinness B, Wijeratne T, Phan TG, Chong W, Chandra RV, Bladin CF, Badve M, Rice H, de Villiers L, Ma H, Desmond PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM (2015) Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med 372(11):1009–1018. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1414792
Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, San Roman L, Serena J, Abilleira S, Ribo M, Millan M, Urra X, Cardona P, Lopez-Cancio E, Tomasello A, Castano C, Blasco J, Aja L, Dorado L, Quesada H, Rubiera M, Hernandez-Perez M, Goyal M, Demchuk AM, von Kummer R, Gallofre M, Davalos A (2015) Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372(24):2296–2306. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1503780
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Albers GW, Cognard C, Cohen DJ, Hacke W, Jansen O, Jovin TG, Mattle HP, Nogueira RG, Siddiqui AH, Yavagal DR, Baxter BW, Devlin TG, Lopes DK, Reddy VK, du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Singer OC, Jahan R (2015) Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med 372(24):2285–2295. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415061
Prabhakaran S, Ruff I, Bernstein RA (2015) Acute stroke intervention: a systematic review. JAMA 313(14):1451–1462. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.3058
Shi ZS, Loh Y, Walker G, Duckwiler GR (2010) Endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke in failed intravenous tissue plasminogen activator versus non-intravenous tissue plasminogen activator patients: revascularization and outcomes stratified by the site of arterial occlusions. Stroke 41(6):1185–1192. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.568451
Bhatia R, Shobha N, Menon BK, Bal SP, Kochar P, Palumbo V, Wong JH, Morrish WF, Hudon ME, Hu W, Coutts SB, Barber PA, Watson T, Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Hill MD (2014) Combined full-dose IV and endovascular thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke 9(8):974–979. doi:10.1111/j.1747-4949.2012.00890.x
Behme D, Gondecki L, Fiethen S, Kowoll A, Mpotsaris A, Weber W (2014) Complications of mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke-a retrospective single-center study of 176 consecutive cases. Neuroradiology 56(6):467–476. doi:10.1007/s00234-014-1352-0
Rubiera M, Ribo M, Pagola J, Coscojuela P, Rodriguez-Luna D, Maisterra O, Ibarra B, Pineiro S, Meler P, Romero FJ, Alvarez-Sabin J, Molina CA (2011) Bridging intravenous-intra-arterial rescue strategy increases recanalization and the likelihood of a good outcome in nonresponder intravenous tissue plasminogen activator-treated patients: a case–control study. Stroke 42(4):993–997. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.597104
Vora NA, Gupta R, Thomas AJ, Horowitz MB, Tayal AH, Hammer MD, Uchino K, Wechsler LR, Jovin TG (2007) Factors predicting hemorrhagic complications after multimodal reperfusion therapy for acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(7):1391–1394. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0575
Ginsberg MD, Hill MD (2015) Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage in the ALIAS Multicenter Trial: relationship to endovascular thrombolytic therapy. Int J Stroke 10(4):494–500. doi:10.1111/ijs.12476
Yoshimura S, Sakai N, Okada Y, Kitagawa K, Kimura K, Tanahashi N, Hyogo T, Yamagami H, Egashira Y (2014) Efficacy of endovascular treatment for acute cerebral large-vessel occlusion: analysis of nationwide prospective registry. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23(5):1183–1190. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.10.014
Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Davalos A, Ford GA, Grond M, Hacke W, Hennerici MG, Kaste M, Kuelkens S, Larrue V, Lees KR, Roine RO, Soinne L, Toni D, Vanhooren G (2007) Thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in the Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-Monitoring Study (SITS-MOST): an observational study. Lancet 369(9558):275–282
Nogueira RG, Gupta R, Jovin TG, Levy EI, Liebeskind DS, Zaidat OO, Rai A, Hirsch JA, Hsu DP, Rymer MM, Tayal AH, Lin R, Natarajan SK, Nanda A, Tian M, Hao Q, Kalia JS, Chen M, Abou-Chebl A, Nguyen TN, Yoo AJ (2015) Predictors and clinical relevance of hemorrhagic transformation after endovascular therapy for anterior circulation large vessel occlusion strokes: a multicenter retrospective analysis of 1122 patients. J Neurointerv Surg 7(1):16–21. doi:10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010743
Menon BK, Saver JL, Prabhakaran S, Reeves M, Liang L, Olson DM, Peterson ED, Hernandez AF, Fonarow GC, Schwamm LH, Smith EE (2012) Risk score for intracranial hemorrhage in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator. Stroke 43(9):2293–2299. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.660415
Soize S, Barbe C, Kadziolka K, Estrade L, Serre I, Pierot L (2013) Predictive factors of outcome and hemorrhage after acute ischemic stroke treated by mechanical thrombectomy with a stent-retriever. Neuroradiology 55(8):977–987. doi:10.1007/s00234-013-1191-4
Nahab F, Walker GA, Dion JE, Smith WS (2012) Safety of periprocedural heparin in acute ischemic stroke endovascular therapy: the multi MERCI trial. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 21(8):790–793. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2011.04.009
Diener HC, Foerch C, Riess H, Rother J, Schroth G, Weber R (2013) Treatment of acute ischaemic stroke with thrombolysis or thrombectomy in patients receiving anti-thrombotic treatment. Lancet Neurol 12(7):677–688. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70101-7
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by the Practical Research Project for Lifestyle-Related Diseases including Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes Mellitus from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED, and by the Center for Clinical Research and Education of Hyogo College of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the appropriate Ethics Committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takagi, T., Yoshimura, S., Uchida, K. et al. Intravenous tissue plasminogen activator before endovascular treatment increases symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage in patients with occlusion of the middle cerebral artery second division: subanalysis of the RESCUE-Japan Registry. Neuroradiology 58, 147–153 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1608-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1608-3