Abstract
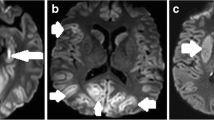
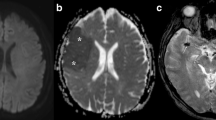
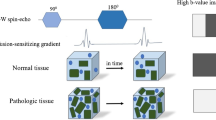
We carried out MRI on 16 male and three female comatose patients, aged 2 days to 79 years, with suspected cortical ischaemia referred from our intensive care units. Using a head coil, and following standard imaging, including coronal fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery images, we performed diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) using a whole-brain multislice single-shot echo-planar sequence with b 0 and 1000 s/mm2: 5-mm slices covering the whole brain, TR 7000 TE 106 ms, 128×128 pixels, field of view 250 mm, one excitation. Maps of apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) were generated automatically. DWI showed cortical, basal ganglia and watershed-area high signal in all cases, associated with a decrease in ADC to 60– 80% of normal. DWI showed lesions not seen (40%) or underestimated (40%) on conventional T2-weighted imaging. Within 24 h of the onset of symptoms, DWI showed changes not readily detectable on T2-weighted images. The cortical high signal on DWI and the ADC changes, suggesting severe ischaemia rather than oedema, was found in areas known to be affected by cortical laminar necrosis. Extension to the brain stem and white matter was associated with a higher likelihood of death.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valanne L, Paetau A, Suomalainen A, Ketonen L, Pihko H (1996) Laminar cortical necrosis in MELAS syndrome: MR and neuropathological observations. Neuropediatrics 27: 154–160
Hawes DR, Mishkin FS (1972) Brain scans in watershed infarction and laminar cortical necrosis. Radiology 103: 131–134
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M (1986) MR Imaging of intravoxel incoherent motion: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161: 401–407
Moseley ME, Cohen Y, Mintorovitch J, et al (1990) Early detection of regional cerebral ischemia in cats: comparison of diffusion- and T2-weighted MRI and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 14: 330–346
van Gelderen P, de Vleeschouwer MHM, DesPres D, Pekar J, van Zijl PCM, Moonen C TW (1994) Water diffusion and acute stroke. Magn Reson Med 31: 154–163
Warach S, Chien D, Li W, Ronthal M, Edelman RR (1992) Fast magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging of acute stroke. Neurology 42: 1717–1723
Warach S, Gaa J, Siewert B, Wielopolski P, Edelman RR (1995) Acute human stroke studies by whole brain echo planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 37: 231–241
Sorensen AG, Buonano FS, Gonzalez RG, et al (1996) Hyperacute stroke: evaluation with combined multisection diffusion-weighted and hemodynamically-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 199: 391–401
Lövblad KO, Laubach HJ, Baird AE, et al (1998) Clinical experience with diffusion-weighted MR in patients with acute stroke. AJNR 19: 1061–1066
el Quessar A, Meunier JC, Delmaire C, Soto Ares G, Pruvo JP (1999) MRI imaging in cortical laminar necrosis J Radiol 80: 913–916
Komiyama M, Nakajima H, Nishikawa M, Yasui T (1998) Serial MR observation of cortical laminar necrosis caused by brain infarction. Neuroradiology 40: 771–777
Komiyama M, Nishikawa M, Yasui T (1997)Cortical laminar necrosis in brain infarcts: chronological changes on MRI. Neuroradiology 39: 474–479
Takahashi S, Higano S, Ishii K, et al (1993) Hypoxic brain damage: cortical laminar necrosis and delayed changes in white matter at sequential MR imaging. Radiology 189: 449–456
Sawada H, Udaka F, Seriu N, Shindou K, Kameyama M, Tsujimura M (1990) MRI demonstration of cortical laminar necrosis and delayed white matter injury in anoxic encephalopathy. Neuroradiology 32: 319–321
Goto Y, Wataya T, Arakawa Y, Hojo M, et al (2001) Magnetic resonance imaging findings of postresuscitation encephalopathy: sequential change and correlation with clinical outcome. No To Shinkei 53: 535–540
Bargallo N, Burrel M, Berenguer J, Cofan F, Bunesch L, Mercader JM (2000) Cortical laminar necrosis caused by immunosuppressive therapy and chemotherapy. AJNR 21: 479–484
Takeoka M, Soman TB, Yoshii A, et al (2002) Diffusion-weighted images in neonatal cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury. Pediatr Neurol. 26: 274–281
Christophe C, Clercx A, Blum D, Hasaerts D, Segebarth C, Perlmutter N (1994) Early MR detection of cortical and subcortical hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in full-term-infants. Pediatr Radiol. 24: 581–584
Christophe C, Fonteyne C, Ziereisen F, et al (2002) Value of MR imaging of the brain in children with hypoxic coma. AJNR 23: 716–723
Singhal AB, Topcuoglu MA, Koroshetz WJ (2002) Diffusion MRI in three types of anoxic encephalopathy. J Neurol Sci 196: 37–40
van der Knaap MS, Smit LS, Nauta JJ, Lafeber HN, Valk J (1993) Cortical laminar abnormalities—occurrence and clinical significance. Neuropediatrics 24: 143–148
Siskas N, Lefkopoulos A, Ioannidis I, Charitandi A, Dimitriadis AS (2003) Cortical laminar necrosis in brain infarcts: serial MRI. Neuroradiology 45: 283–288
Boyko OB, Burger PC, Shelburne JD, Ingram P (1992) Non-heme mechanisms for T1 shortening: pathologic, CT, and MR elucidation. AJNR 13: 1439–1445
Kawahara H, Takeda Y, Tanaka A, et al (2000) Does diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging enable detection of early ischemic change following transient cerebral ischemia? J Neurol Sci 181: 73–81
Arbelaez A, Castillo M, Mukherji SK (1999) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of global cerebral anoxia. AJNR 20: 999–1007
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant 3100-06634 from the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lövblad, K.O., Wetzel, S.G., Somon, T. et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in cortical ischaemia. Neuroradiology 46, 175–182 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1133-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1133-7