Abstract
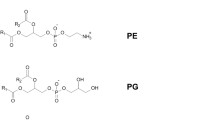
Analysis was performed on four different categories of phospholipids (phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidylinositol (PI), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and phosphatidic acid (PA)) from urine in patients with breast cancer. This quantitative analysis was conducted using nanoflow liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–tandem mass spectrometry (nLC-ESI-MS-MS). This study shows the profiling of the phospholipids (PLs) that can be identified by the negative ion mode of MS. A previous study (Kim et al. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 393:1649, 21) focused on only two PL classes: phosphatidylcholines (PCs) and phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) and were identified by positive ion mode. PLs were extracted by lyophilization of 1 mL of urine from both healthy normal females and breast cancer patients before and after surgery. Separation of PLs was performed by nLC followed by structural identification of PLs using data-dependent collision-induced dissociation. A total of 34 urinary PL molecules (12 PSs, 12 PIs, four PGs, and six PAs) were quantitatively examined. Among the four PL categories examined in this study, most PL classes showed an increase in the total amounts in the cancer patients, yet PIs exhibited some decreases. The present study suggests that the lipid composition found in the urine of breast cancer patients can be utilized for the possible development of disease markers, when the analysis is performed with negative ion mode of nLC-ESI-MS-MS.

Calibration curves of the concentration dependency (solid line) of each acyl chain length of PS standard deduced from the relationship (dotted lines) between relative peak area (vs. IS) and acyl chain length




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brouwers JFHM, Vernooji EAAM, Tielens AGM, van Golde LMG (1999) J Lipid Res 40:164–169
Wright MM, Howe AG, Zaremberg V (2004) Biochem Cell Biol 82:18–26
Wolf C, Quinn PJ (2008) Prog Lipid Res 47:15–36
Kuksis A, Myher JJ, Marai L (1984) J Am Oil Chem Soc 61:1582–1589
Heller DN, Murphy CM, Cotter RJ, Fenselau C, Uy OM (1988) Anal Chem 60:2787–2791
Fuchs B, Schiller J, Süβ R, Schürenburg M, Suckau D (2007) Anal Bioanal Chem 389:827–834
Rohlfing A, Muthing J, Pojlentz G, Distler I, Peter-Katalinc J, Berkenkamp S, Dreisewerd K (2007) Anal Chem 79:5793–5808
Helmy F, Rothenbacher F, Nosavanh L, Lowery J, Juracka A (2007) J Planar Chromatogr Modern TLC 20:209–215
Murray KE, Fried B, Sherma J (2007) Acta Chromatographica 18:190–198
Kaduce TL, Norton KC, Spector AA (1983) J Lipid Res 24:1398–1404
He FQ, Wang CT, Li XK, Liu XQ (2007) J Anal Chem 62:369–372
Kim HY, Wang TCL, Ma YC (1994) Anal Chem 66:3977–3982
Koivusalo M, Haimi P, Heikinheimo L, Kostiainen R, Somerharaju P (2001) J Lipid Res 42:663–672
Hsu FF, Turk J (2001) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 12:1036–1043
Hsu FF, Turk J (2001) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 11:986–999
Hsu FF, Turk J (2005) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 16:1510–1522
Taguchi R, Houjou T, Nakanishi H, Yamazaki T, Ishida M, Imagawa M, Shimizu T (2005) J Chromatogr B 823:26–36
Bang DY, Kang D, Moon MH (2006) J Chromatogr A 1104:222–229
Bang DY, Ahn E, Moon MH (2007) J Chromatogr B 852:268–277
Kim H, Ahn E, Moon MH (2008) Analyst 133:1656–1663
Kim H, Min HK, Kong G, Moon MH (2009) Anal Bioanal Chem 393:1649–1656
Hsu FF, Turk J (2000) J Am Mass Spectrom 11:797–803
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant (2008-03136) from the Korea Ministry of Science & Technology (MOST) and partly by a grant from the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation through the Center for Bioactive Molecular Hybrids (CBMH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, H.K., Kong, G. & Moon, M.H. Quantitative analysis of urinary phospholipids found in patients with breast cancer by nanoflow liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry: II. Negative ion mode analysis of four phospholipid classes. Anal Bioanal Chem 396, 1273–1280 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3292-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3292-9