Abstract
Objective
The present study aimed to examine the changes in pro-inflammatory cytokines and body weight during 6-month risperidone treatment in drug naïve, first-episode schizophrenia.
Methods
Sixty-two drug naïve, first-episode schizophrenia (SZ group) and 60 healthy individuals (control group) were enrolled in the study. Serum interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels, and body weight were measured at baseline for both groups, and repeated for the SZ group at five different time points during 6-month risperidone treatment.
Results
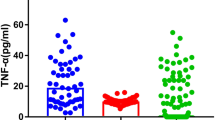
At baseline, serum IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in the SZ group (53.28 ± 12.62, 33.98 ± 14.13, 50.08 ± 12.86 pg/mL, respectively) were significantly higher than those in the control group (23.49 ± 15.27, 15.53 ± 7.16, 32.12 ± 15.23 pg/mL, respectively) (p's < 0.001). Within the SZ group, serum IL-1β levels decreased significantly at 2 weeks (48.02 ± 16.00 pg/mL, p < 0.01) and 1 month (44.70 ± 16.63 pg/mL, p < 0.001), but then gradually increased at 2 months (48.49 ± 18.87 pg/mL), 3 months (50.59 ± 18.48 pg/mL) and 6 months (53.64 ± 16.22 pg/mL) to the levels comparable to baseline; serum IL-6 levels changed significantly over the course of treatment (p = 0.001), but reached the levels comparable to baseline at 6 months (37.13 ± 13.23 pg/mL); serum levels of TNF-α increased significantly at 3 months (55.02 ± 16.69 pg/mL, p < 0.01) and 6 months (58.69 ± 13.57 pg/mL, p < 0.001); steady and significant weight gain was observed at each follow-up time point (p's < 0.001), from 56.71 ± 9.25 kg at baseline to 62.72 ± 9.53 kg at 6 months.
Conclusions
Risperidone treatment is associated with changes in serum pro-inflammatory cytokines levels and weight. There is an initial anti-inflammatory effect that reduces with treatment, potentially due to its weight gain side effect.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrami-Weizman A, Maayan R, Gil-Ad I, Pashinian A, Fuchs C, Kotler M, Poyurovsky M (2013) The effect of reboxetine co-administration with olanzapine on metabolic and endocrine profile in schizophrenia patients. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 230:23–27
Barzilay JI, Forsberg C, Heckbert SR, Cushman M, Newman AB (2006) The association of markers of inflammation with weight change in older adults: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Int J Obes (London) 30:1362–1367
Bushe CJ, Slooff CJ, Haddad PM, Karagianis JL (2013) Weight change by baseline BMI from 3-year observational data: findings from the Worldwide Schizophrenia Outpatient Health Outcomes Database. J Psychopharmacol 27:358–365, Oxford, England
Chen C, Lu FC, Department of Disease Control Ministry of Health, P.R.C. (2004) The guidelines for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults. Biomed Environ Sci: BES 17:1–36
Chen SL, Lee SY, Chang YH, Chen SH, Chu CH, Tzeng NS, Lee IH, Chen PS, Yeh TL, Huang SY, Yang YK, Lu RB, Hong JS (2012) Inflammation in patients with schizophrenia: the therapeutic benefits of risperidone plus add-on dextromethorphan. J Neuroimmune Pharm 7:656–664
Davey KJ, O'Mahony SM, Schellekens H, O'Sullivan O, Bienenstock J, Cotter PD, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2012) Gender-dependent consequences of chronic olanzapine in the rat: effects on body weight, inflammatory, metabolic and microbiota parameters. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 221:155–169
Drzyzga L, Obuchowicz E, Marcinowska A, Herman ZS (2006) Cytokines in schizophrenia and the effects of antipsychotic drugs. Brain Behav Immun 20:532–545
el-Mallakh RS, Suddath RL, Wyatt RJ (1993) Interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-2 in cerebrospinal fluid of schizophrenic subjects. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 17:383–391
Fan X, Goff DC, Henderson DC (2007) Inflammation and schizophrenia. Expert Rev Neurother 7:789–796
Fan X, Borba CP, Copeland P, Hayden D, Freudenreich O, Goff DC, Henderson DC (2013) Metabolic effects of adjunctive aripiprazole in clozapine-treated patients with schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 127:217–226
Fawzi MH, Fawzi MM, Fawzi MM, Said NS (2011) C-reactive protein serum level in drug-free male Egyptian patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 190:91–97
Fineberg AM, Ellman LM (2013) Inflammatory cytokines and neurological and neurocognitive alterations in the course of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 73:951–966
Garver DL, Tamas RL, Holcomb JA (2003) Elevated interleukin-6 in the cerebrospinal fluid of a previously delineated schizophrenia subtype. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1515–1520
Holz T, Thorand B, Doring A, Schneider A, Meisinger C, Koenig W (2010) Markers of inflammation and weight change in middle-aged adults: results from the prospective MONICA/KORA S3/F3 study. Obesity 18:2347–2353, Silver Spring, Md
Hotamisligil GS (2006) Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444:860–867
Jassim G, Skrede S, Vazquez MJ, Wergedal H, Vik-Mo AO, Lunder N, Dieguez C, Vidal-Puig A, Berge RK, Lopez M, Steen VM, Ferno J (2012) Acute effects of orexigenic antipsychotic drugs on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in rat. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 219:783–794
Kemp DE, Correll CU, Tohen M, Delbello MP, Ganocy SJ, Findling RL, Chang K (2013) Associations Among Obesity, Acute Weight Gain, and Response to Treatment with Olanzapine in Adolescent Schizophrenia. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol
Kim YK, Myint AM, Verkerk R, Scharpe S, Steinbusch H, Leonard B (2009) Cytokine changes and tryptophan metabolites in medication-naive and medication-free schizophrenic patients. Neuropsychobiology 59:123–129
Leonard BE, Schwarz M, Myint AM (2012) The metabolic syndrome in schizophrenia: is inflammation a contributing cause? J Psychopharmacol 26:33–41, Oxford, England
Licinio J, Seibyl JP, Altemus M, Charney DS, Krystal JH (1993) Elevated CSF levels of interleukin-2 in neuroleptic-free schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 150:1408–1410
Lin A, Kenis G, Bignotti S, Tura GJ, De Jong R, Bosmans E, Pioli R, Altamura C, Scharpe S, Maes M (1998) The inflammatory response system in treatment-resistant schizophrenia: increased serum interleukin-6. Schizophr Res 32:9–15
Martinez-Gras I, Garcia-Sanchez F, Guaza C, Rodriguez-Jimenez R, Andres-Esteban E, Palomo T, Rubio G, Borrell J (2012) Altered immune function in unaffected first-degree biological relatives of schizophrenia patients. Psychiatry Res 200:1022–1025
Meyer JM, McEvoy JP, Davis VG, Goff DC, Nasrallah HA, Davis SM, Hsiao JK, Swartz MS, Stroup TS, Lieberman JA (2009) Inflammatory markers in schizophrenia: comparing antipsychotic effects in phase 1 of the clinical antipsychotic trials of intervention effectiveness study. Biol Psychiatry 66:1013–1022
Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, Mellor A, Kirkpatrick B (2011) Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry 70:663–671
Myint AM, Schwarz MJ, Verkerk R, Mueller HH, Zach J, Scharpe S, Steinbusch HW, Leonard BE, Kim YK (2011) Reversal of imbalance between kynurenic acid and 3-hydroxykynurenine by antipsychotics in medication-naive and medication-free schizophrenic patients. Brain Behav Immun 25:1576–1581
Na KS, Kim YK (2007) Monocytic, Th1 and th2 cytokine alterations in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 56:55–63
Naudin J, Capo C, Giusano B, Mege JL, Azorin JM (1997) A differential role for interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in schizophrenia? Schizophr Res 26:227–233
Nunes SO, Matsuo T, Kaminami MS, Watanabe MA, Reiche EM, Itano EN (2006) An autoimmune or an inflammatory process in patients with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, and in their biological relatives. Schizophr Res 84:180–182
O'Brien SM, Scully P, Dinan TG (2008) Increased tumor necrosis factor-alpha concentrations with interleukin-4 concentrations in exacerbations of schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 160:256–262
Odegaard JI, Chawla A (2013) Pleiotropic actions of insulin resistance and inflammation in metabolic homeostasis. Science 339:172–177
Ou JJ, Xu Y, Chen HH, Fan X, Gao K, Wang J, Guo XF, Wu RR, Zhao JP (2013) Comparison of metabolic effects of ziprasidone versus olanzapine treatment in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 225:627–635
Pollmacher T, Hinze-Selch D, Mullington J (1996) Effects of clozapine on plasma cytokine and soluble cytokine receptor levels. J Clin Psychopharmacol 16:403–409
Potvin S, Stip E, Sepehry AA, Gendron A, Bah R, Kouassi E (2008) Inflammatory cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: a systematic quantitative review. Biol Psychiatry 63:801–808
Rapaport MH, McAllister CG, Pickar D, Tamarkin L, Kirch DG, Paul SM (1997) CSF IL-1 and IL-2 in medicated schizophrenic patients and normal volunteers. Schizophr Res 25:123–129
Ritchie SA, Connell JM (2007) The link between abdominal obesity, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis: NMCD 17:319–326
Rudolf S, Peters M, Rothermundt M, Arolt V, Kirchner H (2002) The influence of typical and atypical neuroleptic drugs in the production of interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma in vitro. Neuropsychobiology 46:180–185
Runeson BS, Rich CL (1994) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 3rd ed. (DSM-III), adaptive functioning in young Swedish suicides. Ann Clin Psychiatry: Off J Am Acad Clin Psychiatr 6:181–183
Schattner A, Cori Y, Hahn T, Sirota P (1996) No evidence for autoimmunity in schizophrenia. J Autoimmun 9:661–666
Song XQ, Lv LX, Li WQ, Hao YH, Zhao JP (2009) The interaction of nuclear factor-kappa B and cytokines is associated with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 65:481–488
Tateya S, Kim F, Tamori Y (2013) Recent advances in obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4:93
Vasunilashorn S (2013) Retrospective reports of weight change and inflammation in the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Obes 2013:601534
Acknowledgments
Funding for this study was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30971058 to X-QS; No.81071090to L-XL), the Natural Science Foundation of Henan (No.102300413208, 112300413226 to L-XL), and the Youth Fund of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (to X-QS).
Financial disclosures
Dr. Fan has received research support or honoraria from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myer-Squibb, Janssen, and Pfizer. Other authors report no competing interests.
Contributors
Dr. Song and Dr. Fan were responsible for the analysis and interpretation of the data for this paper. All authors contributed to the writing of the paper.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any actual or potential conflict of interest including any financial, personal, or other relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence, or be perceived to influence, their work as submitted in the uploaded material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xueqin Song and Xiaoduo Fan share co-first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Fan, X., Li, X. et al. Changes in pro-inflammatory cytokines and body weight during 6-month risperidone treatment in drug naïve, first-episode schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 231, 319–325 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3382-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3382-4