Abstract
Rationale
Altered cognitive function is a common feature of both the early and later stages of Parkinson’s disease (PD) that involves alterations in cortical dopamine content. Adenosine A2A antagonists, such as istradefylline, improve motor function in PD, but their effect on cognitive impairment has not been determined.
Objective
The present study investigated whether impairment of working memory due to the loss of dopaminergic input into the prefrontal cortex (PFC) is reversed by administration of istradefylline. We also evaluated whether A2A antagonist administration modulates dopamine levels in the PFC.
Methods
Bilateral lesions of the dopaminergic input to the PFC were produced in rats using 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). Cognitive performance was evaluated using an object recognition task and delayed alternation task. The effects of istradefylline, donepezil and methamphetamine on cognitive performance were examined. In addition, the effect of istradefylline on extracellular dopamine levels in the PFC was studied.
Results
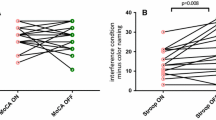
PFC dopamine levels and cognitive performance were significantly reduced by 6-OHDA lesioning. Istradefylline, donepezil and methamphetamine improved cognitive performance of PFC-lesioned rats. Istradefylline increased dopamine levels in the PFC in both normal and PFC-lesioned rats.
Conclusions
PFC dopaminergic input plays an important role in working memory performance. Blockade of A2A receptors using istradefylline reverses the changes in cognitive function, and this may be due to an increase in PFC dopamine content. Adenosine A2A receptor antagonists not only improve motor performance in PD but may also lead to improved cognition.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-Hydroxydopamine
- PFC:
-
Prefrontal cortex
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
References
Aarsland D, Zaccai J, Brayne C (2005) A systematic review of prevalence studies of dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 20:1255–1263
Acquas E, Tanda G, Chiara GD (2002) Differential effects of caffeine on dopamine and acetylcholine transmission in brain areas of drug-naive and caffeine-pretreated rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:182–193
Aoyama S, Koga K, Mori A, Miyaji H, Sekine S, Kase H, Uchimura T, Kobayashi H, Kuwana Y (2002) Distribution of adenosine A2A receptor antagonist KW-6002 and its effect on gene expression in the rat brain. Brain Res 953:119–125
Bohnen NI, Kaufer DI, Hendrickson R, Ivanco LS, Lopresti BJ, Constantine GM, Mathis CA, Davis JG, Moore RY, Dekosky ST (2006) Cognitive correlates of cortical cholinergic denervation in Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonian dementia. J Neurol 253:242–247
Brozoski TJ, Brown RM, Rosvold HE, Goldman PS (1979) Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey. Science 205:929–932
Chaudhuri KR, Schapira AHV (2009) Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: dopaminergic pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet Neurol 8:464–474
Clinton SM, Sucharski IL, Finlay JM (2006) Desipramine attenuates working memory impairments induced by partial loss of chtecholamines in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 183:404–412
Costenla AR, Diógenes MJ, Canas PM, Rodrigues RJ, Nogueira C, Maroco J, Agostinho PM, Ribeiro JA, Cunha RA, de Mendonça A (2011) Enhanced role of adenosine A2A receptors in the modulation of LTP in the rat hippocampus upon ageing. Eur J Neurosci 34:12–21
Cuadra G, Summers K, Giacobini E (1994) Cholinesterase inhibitor effects on neurotransmitters in rat cortex in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:277–284
Decamp E, Schneider JS (2004) Attention and executive function deficits in chronic low dose MPTP-treated non-human primates. Eur J Neurosci 20:1371–1378
Dixon AK, Gubitz AK, Sirinathsinghji DJ, Richardson PJ, Freeman TC (1996) Tissue distribution of adenosine receptor mRNAs in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 118:1461–1468
Dubois B, Pillon B (1997) Cognitive deficits in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 244:2–8
Ennaceur A, Meliani K (1992) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. III. Spatial vs. non-spatial working memory. Behav Brain Res 51:83–92
Floresco SB, Magyar O (2006) Mesocortical dopamine modulation of executive functions: beyond working memory. Psychopharmacology 188:567–585
Fraser CM, Fisher A, Cooke MJ, Thompson ID, Stone TW (1997) Purine modulation of dizocilpine effects on spontaneous alternation. Psychopharmacology 130:334–342
Giacobini E, Zhu XD, Williams E, Sherman K (1996) The effect of the selective reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor E200 on extracellular acetylcholine and biogenic amine levels in rat cortex. Neuropharmacology 35:205–211
Giménez-Llort L, Schiffmann SN, Shmidt T, Canela L, Camón L, Wassholm M, Canals M, Terasmaa A, Fernández-Teruel A, Tobeña A, Popova E, Ferré S, Agnati L, Ciruela F, Martínez E, Scheel-Kruger J, Lluis C, Franco R, Fuxe K, Bader M (2007) Working memory deficits in transgenic rats overexpressing human adenosine A2A receptors in the brain. Neurobiol Learn Mem 87:42–56
Izaki Y, Maruki K, Hori K, Nomura M (2001) Effects of rat medial prefrontal cortex temporal inactivation on a delayed alternation task. Neurosci Lett 315:129–132
Jenner P (2005) Istradefylline, a novel adenosine A2A receptor antagonist, for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 14:729–738
Jenner P, Mori A, Hauser R, Morelli M, Fredholm BB, Chen JF (2009) Adenosine, adenosine A2A antagonists, and Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15:406–413
Kanda T, Jackson MJ, Smith LA, Pearce RK, Nakamura J, Kase H, Kuwana Y, Jenner P (2000) Combined use of the adenosine A2A antagonist KW-6002 with l-DOPA or with selective D1 or D2 dopamine agonists increases antiparkinsonian activity but not dyskinesia in MPTP-treated monkeys. Exp Neurol 162:321–327
Kehagia AA, Barker RA, Robbins TW (2010) Neuropsychological and clinical heterogeneity of cognitive impairment and dementia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 9:1200–1213
Koga K, Kurokawa M, Ochi M, Nakamura J, Kuwana Y (2000) Adenosine A2A receptor antagonists KF17837 and KW-6002 potentiate rotation induced by dopaminergic drugs in hemi-Parkinsonian rats. Eur J Pharmacol 408:249–255
Kopf SR, Melani A, Pedata F, Pepeu G (1999) Adenosine and memory storage: effect of A1 and A2 receptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology 146:325–329
Liang YQ, Tang XC (2006) Comparative studies of huperzine A, donepezil, and rivastigmine on brain acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in freely-moving rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27:1127–1136
Lundblad M, Vaudano E, Cenci MA (2003) Cellular and behavioural effects of the adenosine A2a receptor antagonist KW-6002 in a rat model of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. J Neurochem 84:1398–1410
McKinlay A, Grace RC (2011) Characteristic of cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease: a 1-year follow-up. Appl Neuropsychol 18:269–277
Mihara T, MIhara K, Yarimizu J, Mitani Y, Matsuda R, Yamamoto H, Aoki S, Akahane A, Iwashita A, Matsuoka N (2007) Pharmacological characterization of a novel, potent adenosine A1 and A2A receptor dual antagonist, 5-[5-amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)pyrazin-2-yl]-1-isopropylpyridine-2(1H)-one (ASP5854), in models of parkinson’s disease and cognition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:708–719
Mishina M, Ishiwata K, Kimura Y, Naganawa M, Oda K, Kobayashi S, Katayama Y, Ishii K (2007) Evaluation of distribution of adenosine A2A receptors in normal human brain measured with [11C]TMSX PET. Synapse 61:778–784
Mizoguchi K, Shoji H, Tanaka Y, Murayama W, Tabira T (2009) Age-related spatial working memory impairment is caused by prefrontal cortical dopaminergic dysfunction in rats. Neuroscience 162:1192–1201
Mizuno Y, Hasegawa K, Kondo T, Kuno S, Yamamoto M, Japanese Istradefylline Study Group (2010) Clinical efficacy of istradefylline (KW-6002) in Parkinson’s disease: a randomized, controlled study. Mov Disord 25:1437–1443
Mori A, Shindou T (2003) Modulation of GABAergic transmission in the striatopallidal system by adenosine A2A receptors: a potential mechanism for the antiparkinsonian effects of A2A antagonists. Neurology 61:S44–S48
Mumby DG (2001) Perspectives on object-recognition memory following hippocampal damage: lessons from studies in rats. Behav Brain Res 127:159–181
Ochi M, Koga K, Kurokawa M, Kase H, Nakamura J, Kuwana Y (2000) Systemic administration of adenosine A2A receptor antagonist reverses increased GABA release in the globus pallidus of unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats: a microdialysis study. Neuroscience 100:53–62
O’Neill M, Brown VJ (2007) The effect of striatal dopamine depletion and the adenosine A2A antagonist KW-6002 on reversal learning in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 88:75–81
Pagonabarraga J, Kulisevsky J (2012) Cognitive impairment and dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 46:590–596
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic, New York
Pereira GS, Rossato JI, Sarkis JJ, Cammarota M, Bonan CD, Izquierdo I (2005) Activation of adenosine receptors in the posterior cingulate cortex impairs memory retrieval in the rat. Neurobiol Learn Mem 83:217–223
Prediger RDS, Takahashi RN (2005) Modulation of short-term social memory in rats by adenosine A1 and A2A receptors. Neurosci Lett 376:160–165
Prediger RDS, Da Cunha C, Takahashi RN (2005a) Antagonistic interaction between adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptors modulates the social recognition memory in reserpine-treated rats. Behav Pharmacol 16:209–218
Prediger RDS, Batista LC, Takahashi RN (2005b) Caffeine reverses age-related deficits in olfactory discrimination and social recognition memory in rats: involvement of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors. Neurobiol Aging 26:957–964
Prediger RDS, Fernandes D, Takahashi RN (2005c) Blockade of adenosine A2A receptors reverses short-term social memory impairments in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Behav Brain Res 159:197–205
Richard IH, Justus AW, Greig NH, Marshall F, Kurlan R (2002) Worsening of motor function and mood in a patient with Parkinson’s disease after pharmacologic challenge with oral rivastigmine. Clin Neuropharmacol 25:296–299
Rinne JO, Portin R, Ruottinen H, Nurmi E, Bergman J, Haaparanta M, Solin O (2000) Cognitive impairment and the brain dopaminergic system in Parkinson disease: [18F]fluorodopa positron emission tomographic study. Arch Neurol 57:470–475
Sánchez-Santed F, de Bruin JP, Heinsbroek RP, Verwer RW (1997) Spatial delayed alternation of rats in a T-maze: effects of neurotoxic lesions of the medial prefrontal cortex and of T-maze rotations. Behav Brain Res 84:73–79
Sawada Y, Nishio Y, Suzuki K, Hirayama K, Takeda A, Hosokai Y, Ishioka T, Itoyama Y, Takahashi S, Fukuda H, Mori E (2012) Attentional set-shifting deficit in Parkinson’s disease is associated with prefrontal dysfunction: an FDG-PET study. PLoS One 7:e38498
Scatton B, Javoy-Agid F, Rouquier L, Dubois B, Agid Y (1983) Reduction of cortical dopamine, noradrenaline, serotonin and their metabolites in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 275:321–328
Schrag A, Jahanshahi M, Quinn N (2000) What contributes to quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease? J Neurol Nerurosurg Psyhiatry 69:308–312
Sherman E, Rossi S, Szasz B, Juranyi Z, Fallon S, Pomara N, Sershen H, Lajtha A (2006) Changes in cerebral neurotransmitters and metabolites induced by acute donepezil and memantine administrations: a microdialysis study. Bran Res Bull 69:204–213
Shiozaki S, Ichikawa S, Nakamura J, Kitamura S, Yamada K, Kuwana Y (1999) Actions of adenosine A2A receptor antagonist KW-6002 on drug-induced catalepsy and hypokinesia caused by reserpine or MPTP. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 147:90–95
Takahashi RN, Pamplona FA, Prediger RDS (2008) Adenosine receptor antagonists for cognitive dysfunction: a review of animal studies. Front Biosci 13:2614–2632
van Laar T, De Deyn PP, Aarsland D, Barone P, Galvin JE (2011) Effects of cholinesterase inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease dementia: a review of clinical data. CNS Neurosci Ther 17:428–441
Ventura R, Pascucci T, Catania MV, Musumeci SA, Puglisi-Allegra S (2004) Object recognition impairment in Fmr1 knockout mice is reversed by amphetamine: involvement of dopamine in the medial prefrontal cortex. Behav Pharmacol 15:433–442
Wang JH, Ma YY, van den Buuse M (2006) Improved spatial recognition memory in mice lacking adenosine A2A receptors. Exp Neurol 199:438–445
Watanabe M, Kodama T, Hirosaka K (1997) Increase of extracellular dopamine in primate prefrontal cortex during a working memory task. J Neurophysiol 78:2795–2798
Wei CJ, Li W, Chen J-F (2011) Normal and abnormal functions of adenosine receptors in the central nervous system revealed by genetic knockout studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808:1358–1379
Zhou SJ, Zhu ME, Shu D, Du XP, Song XH, Wang XT, Zheng RY, Cai XH, Chen JF, He JC (2009) Preferential enhancement of working memory in mice lacking adenosine A2A receptors. Brain Res 1303:74–83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadowaki Horita, T., Kobayashi, M., Mori, A. et al. Effects of the adenosine A2A antagonist istradefylline on cognitive performance in rats with a 6-OHDA lesion in prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 230, 345–352 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3158-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3158-x