Abstract
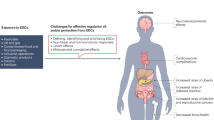
Recently published papers have alleged that exposures to endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are causing substantial disease burdens in the EU and US and are consequently costing society hundreds of billions of dollars annually. To date, these cost estimates have not undergone adequate scientific scrutiny, but nevertheless are being used aggressively in advocacy campaigns in an attempt to fundamentally change how chemicals are tested, evaluated and regulated. Consequently, we critically evaluated the underlying methodology and assumptions employed by the chief architects of the disease burden cost estimates. Since the vast majority of their assigned disease burden costs are driven by the assumption that “loss of IQ” and “increased prevalence of intellectual disability” are caused by exposures to organophosphate pesticides (OPPs) and brominated flame retardants (PBDEs), we have taken special care in describing and evaluating the underlying toxicology and epidemiology evidence that was relied upon. Unfortunately, our review uncovered substantial flaws in the approach taken and the conclusions that were drawn. Indeed, the authors of these papers assumed causal relationships between putative exposures to EDCs and selected diseases, i.e., “loss of IQ” and “increased prevalence of intellectual disability”, despite not having established them via a thorough evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of the underlying animal toxicology and human epidemiology evidence. Consequently, the assigned disease burden costs are highly speculative and should not be considered in the weight of evidence approach underlying any serious policy discussions serving to protect the public and regulate chemicals considered as EDCs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal V et al (2014) Biosynthesis of polybrominated aromatic organic compounds by marine bacteria. Nat Chem Biol 10:640–647. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1564
Allen S et al (2016) An appeal for the integrity of science and public policy. Toxicology 371:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.tox2016.08.015
Aschner M et al (2016) Reference compounds for alternative test methods to indicate developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) potential of chemicals: example lists and criteria for their selection and use. Altex 34:1. doi:10.14573/altex.1604201
Attina T et al (2016) Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the USA: a population-based disease burden and cost analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 4:996–1003. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30275-3
Attina TM, Trasande L (2013) Economic costs of childhood lead exposure in low- and middle-income countries. Environ Health Perspect 121:1097–1102
Beausoleil C et al (2016) Review of non-monotonic dose-responses of substances for human risk assessment. Support Publ 13(5). doi:10.2903/sp.efsa.2016.EN-1027
Becker K et al (2007) German environmental survey for children, 2003/06. Available at http://www.umweltbundesamt.de/sites/default/files/medien/publikation/long/3355.pdf. Accessed 4 Jan 2017
Bellanger M et al (2015) Neurobehavioral deficits, diseases, and associated costs of exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the European Union. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(4):1256–1266. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-432
Bergman A et al (2013) State of the science of endocrine disrupting chemicals, 2012. United Nations Environment Programme and the World Health Organization. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/78101/1/9789241505031_eng.pdf?ua=1
Bonde JP et al (2016) The epidemiologic evidence linking prenatal and postnatal exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals with male reproductive disorders: a systematic review and meta analysis. Hum Reprod Update. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmw036
Borgert C et al (2013) Potency matters: thresholds govern endocrine activity. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 67(1):83–88. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2013.06.007
Bruce N et al (2014) WHO Indoor air quality guidelines: household fuel combustion. Methods used for assessment. Available at http://www.who.int/indoor/guidelines/hhfc/Evidence_review_methods.pdf Accessed 1 Mar 2015
Burns C et al (2013) Pesticide exposure and neurodevelopmental outcomes: review of the epidemiologic and animal Studies. J Toxicol Environ Health 16(3–4):127–283. doi:10.1080/10937404.2013.783383
Chen A et al (2014) Prenatal polybrominated diphenyl ether exposures and neurodevelopment in US children through 5 years of age: the HOME Study. Environ Health Perspect 122(8):856–862
Chen H et al (2016) BDE-47 and BDE-49 inhibit axonal growth in primary rat hippocampal neuron-glia co-cultures via ryanodine receptor-dependent mechanisms. Toxicol Sci. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfw259
Choksi NY et al (2003) Role of thyroid hormones in human and laboratory animal reproductive health. Birth Defects Res (Part B) 68:479–491. doi:10.1002/bdrb.10045
Covaci A et al (2014) Urinary BPA measurements in children and mothers from six European member states: overall results and determinants of exposure. Environ Res. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2014.08.008i
Crofton KM (2008) Thyroid disrupting chemicals: mechanisms and mixtures. Int J Androl 31:209–223. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2605.2007.00857.x
Crofton KM, Zoller RT (2005) Mode of action: neurotoxicity induced by thyroid hormone disruption during development—hearing loss resulting from exposure to PHAHs. Crit Rev Toxicol 35:757–769. doi:10.1080/10408440591007304
Danish EPA (2011) Establishment of criteria for endocrine disruptors and options for regulation. http://eng.mst.dk/media/mst/Attachments/DKEDcriteria110517_finalcorr1.pdf. Accessed on 2 Nov 2016
DE-UK (2011) Joint DE-UK Position Paper. Regulatory definition of an endocrine disrupter in relation to potential threat to human health. Proposal applicable in the regulatory context of plant protection products, biocidial products, and chemicals targeted within REACH. www.bfr.bund.de
Den Hond E et al (2015) First steps toward harmonized human biomonitoring in Europe: demonstration project to perform human biomonitoring on a European scale. Environ Health Perspect. doi:10.1289/ehp.1408616
Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2009) Fourth national report on human exposure to environmental chemicals 2009. http://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/pdf/fourthreport.pdf. Accessed on 2 Nov 2016
Dietrich D et al (2016) Allowing pseudoscience into EU risk assessment processes is eroding public trust in science experts and in science as a whole: the bigger picture. Chemico-Biol Interact 257(2016):1–3
Dietrich DR, Hengstler JG (2016) Highlight report: from bisphenol A to bisphenol F and a ban of mustard due to chronic low dose exposures? Arch Toxicol 90(2):489–491. doi:10.1007/s00204-016-1671-5
Dingemans MML et al (2011) Review: neurotoxicity of brominated flame retardants: (In)direct effects of parent and hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers on the (developing) nervous system. Environ Health Perspect. doi:10.1289/ehp.1003035
Dohler KD et al (1979) The rat as a model for the study of drug effects on thyroid function: consideration of methodological problems. Pharmacol Ther 5:305–318
Eaton D et al (2008) Review of the toxicology of chlorpyrifos with an emphasis on human exposure and neurodevelopment. Crit Rev Toxicol 38(Sup 2):1–125. doi:10.1080/10408440802272158
Eskenazi B et al (2013) In utero and childhood polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) exposures and neurodevelopment in the CHAMACOS study. Environ Health Perspect 121:257–262
European Commission (2013) JRC scientific and policy reports: key scientific issues relevant to the identification and characterization of endocrine disrupting substances. Rep Endocr Disrupt Expert Advisory Group. doi:10.2788/8659 (online)
European Commission (2016a) Staff working document: defining criteria for identifying endocrine disruptors in the context of the implementation of the plant protection products regulation and biocidal products regulation http://ec.europa.eu/health/endocrine_disruptors/docs/2016_impact_assessment_en.pdf
European Commission (2016b) Rules of procedure for the scientific committees on consumer safety (SCCS) and health, environmental and emerging risks (SCHEER). http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/docs/rules_procedure_2016_en.pdf. Accessed on 2 Nov 2016
Fritsche E et al (2005) Polychlorinated biphenyls disturb differentiation of normal human neural progenitor cells: clue for involvement of thyroid hormone receptors. Environ Health Perspect 113:871–876. doi:10.1289/ehp.7793
Govarts E et al (2012) Birth weight and prenatal exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE): a meta-analysis within 12 European birth cohorts. Environ Health Perspect 120:162–170. doi:10.1289/ehp.1103767 (online 13 October)
Gray E (2013) Non-monotonic dose response curves (NMDRCs) are common after estrogen or androgen signaling pathway disruption. Fact or falderal? Presented at Risk Assessment Specialty Section, Society of Toxicology sponsored RASS Webinar, May 08, 2013. Available on-line at https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?dirEntryId=257864
Hauser R et al (2015) Male reproductive disorders, diseases, and costs of exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the European Union. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(4):1267–1277. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-4325
Herbstman J et al (2010) Prenatal exposure to PBDEs and neurodevelopment. Environ Health Perspect 118:712–719
Hsu CC, Sanford B (2007) The Delphi technique: making sense of consensus. Pract Assess Res Eval 12(10):1–8
Hunt PA et al (2016) Female reproductive disorders, diseases, and costs of exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals in the European Union. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-2873#sthash.uhE1pZY.dpuf
Huwe JK, Smith DJ (2007) Accumulation, whole-body depletion, and debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether in male Sprague−Dawley rats following dietary exposure. Environ Sci Technol 41(7):2371–2377. doi:10.1021/es061954d
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (2005) Guidance notes for lead authors of the IPCC fourth assessment report on addressing uncertainties. http://www.ipcc.ch/meetings/ar4-workshops-express-meetings/uncertainty-guidance-note.pdf. Accessed on 2 Nov 2016
Ioannidis J (2005) Why most published research findings are false. PLoS Med 2(8):124
Ioannidis J (2016) We have an epidemic of deeply flawed meta-analyses, says John Ioannidis. Retraction Watch. http://retractionwatch.com/2016/09/13/we-have-an-epidemic-of-deeply-flawed-meta-analyses-says-john-ioannidis/
Kim YR et al (2014) Health consequences of exposure to brominated flame retardants: a systematic review. Chemosphere 106:1–19. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.12.064
LaKind J et al (2015) Improving concordance in environmental epidemiology: a three-part proposal. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B 18(3):105–120. doi:10.1080/10937404.2015.1051612
Lamb J et al (2014) Critical comments on the WHO-UNEP state of the science of endocrine disrupting chemicals–2012. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 69:22–40
Legler J et al (2015) Obesity, diabetes, and associated costs of exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the European Union. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(4):1278–1288. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-4326
Li A et al (2012) Evaluation of epidemiology and animal data for risk assessment: chlorpyrifos developmental neurobehavioral outcomes. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B 15(2):109–184. doi:10.1080/10937404.2012.645142Journal
Linares V et al (2015) Human exposure to PBDE and critical evaluation of health hazards. Arch Toxicol 89:335. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1457-1
Mercè Garí M, Grimalt JO (2013) Inverse age-dependent accumulation of decabromodiphenyl ether and other PBDEs in serum from a general adult population. Environ Int 54:119–127. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2013.01.012
Middelbeek RJ, Veuger SA (2015) Letter to the Editor: Re: neurobehavioral deficits, diseases, and associated costs of exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the European Union. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-2010
Ntzani E et al (2013) Literature review of epidemiology studies linking exposure to pesticides and health effects. EFSA Supporting Publication EN:497, pages 159. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/store/10.2903/sp.efsa.2013.EN-497/asset/efs3497e.pdf?v=1&t=iv1eeoou&s=9b9545d83a1e7ed6c627ba935e169519e9058a8c
OECD (2012) Guidance document on standardised test guidelines for evaluating chemicals for endocrine disruption, series on testing and assessment, No. 150, ENV/JM/MONO 22 http://www.oecd.org/officialdocuments/publicdisplaydocumentpdf/?cote=env/jm/mono(2012)22&doclanguage=en. Accessed 2 Nov 2016
Polloca G et al (2016) Identification of transcriptome signatures and biomarkers specific for potential developmental toxicants inhibiting human neural crest cell migration. Arch Toxicol 90(1):159–180. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1658-7
Prueitt R et al (2011) Hypothesis-based weight of evidence evaluation of the neurodevelopmental effects of chlorpyrifos. Crit Rev Toxicol 41(10):822–903. doi:10.3109/10408444.2011.616877
Robbins J, Rall JE (1979) The iodine containing hormones. In: Gray CH, James YHT (eds) Hormones in blood, 3rd edn. Academic Press, London, p 576
Rochester JR, Bolden AL (2015) Bisphenol S and F: a systematic review and comparison of the hormonal activity of bisphenol A substitutes. Environ Health Perspect 123:643–650. doi:10.1289/ehp.1408989
Rooney A et al (2014) Systematic review and evidence integration for literature-based environmental health science assessments. Environ Health Perspect 122:711–718. doi:10.1289/ehp.1307972
Roth N, Wilks M (2014) Neurodevelopmental and neurobehavioural effects of polybrominated and perfluorinated chemicals: a systematic review of the epidemiological literature using a quality assessment scheme. Toxicol Lett 230(2):271–281. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.02.015
Runkle D, Frankel M (2012) Advocacy in science: summary of a workshop convened by the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Washington, DC. https://mcmprodaaas.s3.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/reports/Advocacy_Workshop_Report_FINAL.pdf
Schalock R et al (2010) Intellectual disability: Definition, classification, and systems of supports (11th Edition) association on intellectual and developmental disabilities. ISBN: 978-1-935304-04-3
Schreiber et al (2010) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers induce developmental neurotoxicity in a human in vitro model: evidence for endocrine disruption. Environ Health Perspect 118:572–578. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901435
Stapleton HM et al (2009) Detection of organophosphate flame retardants in furniture foam and US house dust. Environ Sci Technol 43(19):7490–7495
Staskal et al (2006) Toxicokinetics of polybrominated diphenyl ether congeners 47, 99, 100, and 153 in mice. Tox Sci 94(1):28–37. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfl091
Sumner P et al (2014) The association between exaggeration in health related science news and academic press releases: retrospective observational study. Br Med J. doi:10.1136/bmj.g7015
Swenberg et al (1992) Species-specific mechanisms of carcinogenesis in: mechanisms of carcinogenesis in risk identification. Edited by H. Vainio. Lyon, Internat. Agency for Research on Cancer, pp 477–500
Teuten EL et al (2005) Two abundant bioaccumulated halogenated compounds are natural products. Science 307:917–920
Trasande L et al (2015) Estimating burden and disease costs of exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the European Union. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(4):1245–1255. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-4324
Trasande L et al (2016) Burden of disease and costs of exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals in the European Union: an updated analysis. Andrology 4(4):565–572. doi:10.1111/andr.12178
Trasande L, Liu Y (2011) Reducing the staggering costs of environmental disease In children, estimated at $76.6 billion In 2008. Health Aff 30:863–870
US EPA FIFRA Scientific Advisory Panel (2016) Minutes No. 2016-01: A set of scientific issues being considered by the Environmental Protection Agency regarding chlorpyrifos: analysis of biomonitoring data April 19–21, 2016
US EPA (2011) Endocrine disruption screening program weight-of-evidence: evaluating results of EDSP tier 1 screening to identify the need for tier 2 testing. OPPT-2010-0877-0021
US FDA (2014) 2014 Updated safety assessment of Bisphenol A (BPA) for use in food contact applications. Memorandum dated June 17, 2014. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/NewsEvents/PublicHealthFocus/UCM424266.pdf
US EPA (2015a) Endocrine Disruption Screening Program (EDSP) Tier 1 weight of the evidence evaluation of the potential interaction of chlorpyrifos. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-06/documents/chlorpyrifos-059101_2015-06-29_txr0057162.pdf. Accessed on 2 Nov 2016
US EPA (2015b) Endocrine disruptor screening program tier 1 screening determinations and associated data evaluation records. https://www.epa.gov/endocrine-disruption/endocrine-disruptor-screening-program-tier-1-screening-determinations-and. Accessed on 2 Nov 2016
US EPA (2016a) Federal advisory committees at US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/faca/about-federal-advisory-committee-act-faca-epa, Accessed on 2 Nov 2016
US EPA (2016b) The Frank R. Lautenberg Chemical Safety for the 21st Century Act. https://www.epa.gov/assessing-and-managing-chemicals-under-tsca/frank-r-lautenberg-chemical-safety-21st-century-act
US EPA (2017) Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program (EDSP) Overview. https://www.epa.gov/endocrine-disruption/endocrine-disruptor-screening-program-edsp-overview
Vandenberg L et al (2016) A Proposed framework for the systematic review and integrated assessment (SYRINA) of endocrine disrupting chemicals. Environ Health 15:74–93. doi:10.1186/s12940-016-0156-6
Vergano D (2015) Poll reveals rift between scientists, regular folks. National Geographic. 29 Jan 2015
WHO Regional Office for Europe (2015). Human biomonitoring: facts and figures. Copenhagen
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Conflict of interest
GGB provides consulting services to the American Chemistry Council. DRD declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bond, G.G., Dietrich, D.R. Human cost burden of exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals. A critical review. Arch Toxicol 91, 2745–2762 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-1985-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-1985-y