Abstract
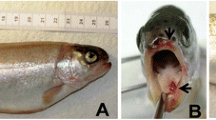
In 2004, a new disease was detected in cod (Gadus morhua) in western Norway. Affected cod had white granulomas in the visceral organs and skin. A species of Francisella was isolated on blood agar plates from moribund cod. The bacterium could be grown at temperatures ranging from 6 to 22°C, but did not grow at 37°C. Challenge experiments showed that Francisella sp. was the cause for the new disease. The 16S rDNA gene sequence from Francisella sp. showed 99.17% similarity to F. philomiragia, and the 16S–23S ribosomal RNA intergenic spacer (249 nt), shows a similarity with that from Francisella isolated from tilapia and F. tularensis of 96.8 and 35.9%, respectively. The 23S sequence is more similar to F. tularensis, 97.7% (2,862 nt), compared to the tilapia isolate 96.8% (2,131 nt). The partial putative outer membrane protein (FopA) sequence (781 nt) from Francisella sp. shows a similarity with that from F. tularensis and F. philomiragia of 77.3 and 98.2%, respectively. Based on sequence data, culturing temperatures and pathogenicity for cod, it is suggested that this Francisella sp. from cod could be a new species of Francisella, Family Francisellaceae.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd H, Johansson T, Golovliov I, Sanström G, Forsman M (2003) Survival and growth of Francisella tularensis in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Appl Envirion Microbiol 69(1):600–606
Agnalt AL, Ervik A, Kristiansen TS, Oppedal F (2004) Havbruksrapporten 2004 Fisken og Havet, 3 Bergen, Norway
Anda P, del Pozo JS, Garcia JMD et al (2001) Waterborne outbreak of tularemia associated with crayfish fishing. Emerg Infect Dis 7(3):575–582
Barns SM, Grow CC, Okinaka RT, Keim P, Kuske CR (2005) Detection of diverse new Francisella-like bacteria in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(9):5494–5500
Brown JA, Minkoff G, Puvanendran V (2003) Larviculture of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua): progress, protocols and problems. Aquaculture 227:357–372
Chen SC, Tung MC, Chen SP, Tsai JF, Wang PC, Chen RS, Lin SC, Adams A (1994) Sytematic granulomas caused by a rickettsia-like organism in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.), from southern Taiwan. J Fish Dis 17:591–599
Chen MF, Yun S, Marty GD, McDowell TS, House ML, Appersen JA, Guenther TA, Arkush KD, Hedrick RP (2000) A Piscirickettsia salmonis-like bacterium associated with mortality of white seabass Astractoscion nobilis. Dis Aquat Org 43:117–126
Chern RS, Chao CB (1994) Outbreaks of a disease caused by rickettsia-like organism in cultured tilapias in Taiwan. Fish Pathol 29:61–71
Dannevig BH, Brudeseth BE, Gjøen T, Rode M, Wergeland HI, Evensen Ø, Press CM (1997) Characterisation of a long-term cell line (SHK-1) developed from the head kidney of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 7:213–226
Devold M, Krossøy B, Aspehaug V, Nylund A (2000) Use of RT-PCR for diagnosis of infectious salmon anaemia virus (ISAV) in carrier sea trout Salmo trutta after experimental infection. Dis Aquat Organ 40:9–18
Giovannoni S (1991). The polymerase chain reaction. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 77–201
Hollis DG, Weaver RE, Steigerwalt AG, Wenger JD, Moss CW, Brenner DJ (1989) Francisella philomiragia comb. nov. (Formerly Yersinia philomiragia) and Francisella tularensis biogroup novicida (Formerly Francisella novicida) associated with human disease. J Clin Microbiol 27(7):1601–1608
Jensen WI, Owen CR, Jellison WL (1969) Yersinia philomiragia sp.n., a new member of the Pasturella group of bacteria, naturally pathogenic for the muskrat (Ondatra zibethica). J Bacteriol 100(3):1237–1241
Kamaishi T, Fukuda Y, Nishiyama M, Kawakami H, Matsuyama T, Yoshinaga T, Oseko N (2005) Identification and pathogenicity of intracellular Francisella bacterium in three-line grunt Parapristipoma trilineatum. Fish Pathol 40(2):67–71
Khoo L, Dennis PM, Lewbart GA (1995) Rickettsia-like organisms in the blue-eyed plecostomus, Panaque suttoni (Eigenmann & Eigenmann). J Fish Dis 18:157–164
Larsson P, Oyston PCF, Chain P, Chu MC et al (2005) The complete genome sequence of Francisella tularensis, the causative agent of tularemia. Nat Genet 37(2):153–159
Mauel MJ, Miller DL, Frazier K, Liggett AD, Styer L, Montgomery-Brock D, Brock J (2003) Characterization of piscirickettsiosis-like disease in Hawaiian tilapia. Dis Aquat Org 53:249–255
Nicholas KB, Nicholas HBJ, Deerfield DWI (1997) GeneDoc: Analysis and visualization of genetic variation. Embnew News 4:14
Niebylski ML, Peacock MG, Fisher ER, Porcella SF, Schwan TG (1997). Characterization of an endosymbiont infecting wood ticks, Dermacentor andersoni, as a member of the genus Francisella. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(19):3933–3940
Noda H, Munderloh UG, Kurtti TJ (1997). Endosymbionts of ticks and their relationship to Wolbachia spp. and tick-borne pathogens of humans and animals. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(19):3926–3932
Nylund A, Hovland T, Watanabe K, Endresen C (1995). Presence of infectious salmon anaemia virus (ISAV) in tissues of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., collected during three separate outbreaks of the disease. J Fish Dis 18:135–145
Oyston PCF, Sjøstedt A, Titball RW (2005) Tularemia: bioterrorism defence renews interest in Francisella tularensis. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:967–978
Page RD (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Scoles GA (2004) Phylogenetic analysis of the Francisella-like endosymbionts of Dermacentor ticks. J Med Entomol 41(3):277–286
Sjöstedt AB (2005a) Family III. Francisellaceae fam.nov. In: Garrity GM (ed) Bergeys manual of systematic bacteriology, 2nd edn. Springer, USA pp 199–210
Sjöstedt A (2005b) Intracellular survival mechanisms of Francisella tularensis, a stealth pathogen. Microbes Infect 8:561–567
Suitor EC, Weiss E (1961). Isolation of a rickettsialike microorganism (Wolbachia persica, n.sp.) from Argas persicus (Oken). J Infect Dis 108:95–106
Swofford DL (1998) Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony and other methods. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Timur G, Timur M, Akayli T, Korin J, Thompson KD (2005) First observation of rickettsia-like organisms in cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in Turkey. Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 25(5):196–202
Tomaso H, Dahouk SA, Hofer E, Splettstoesser WD, Treu TM, Dierich MP, Neubauer H (2005) Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Austrian Francisella tularensis holartica biovar II strains. Int J Antimicrob Agents 26:279–284
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nylund, A., Ottem, K.F., Watanabe, K. et al. Francisella sp. (Family Francisellaceae) causing mortality in Norwegian cod (Gadus morhua) farming. Arch Microbiol 185, 383–392 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0109-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0109-5