Abstract
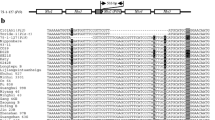
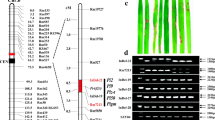
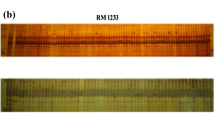
Blast resistance is one of the most important traits in rice breeding, and application of molecular markers for blast resistance breeding is likely to allow the rapid screening for the trait during early growth stages, without the need for inoculation of pathogen and phenotyping. Allele-specific PCR markers and insertion/deletion (InDel) markers, which genotype single-nucleotide polymorphisms and InDel polymorphisms, respectively, are useful tools for marker-assisted selections. We developed sets of allele-specific PCR and InDel markers for nine rice blast resistance genes—Piz, Piz-t, Pit, Pik, Pik-m, Pik-p, Pita, Pita-2, and Pib—which are commonly used in Japanese blast resistance rice breeding programs. For each resistance gene, we used the segregation information from thousands of progeny in several crosses or published gene locations to generate a marker that cosegregated with the gene and markers that closely flanked the gene on either side. The developed cosegregating markers uniquely discriminated among each of the lines with the individual resistance genes (except for Pita and Pita-2). Therefore, these markers will likely facilitate the development of multiline cultivars carrying one or a combination of these nine blast resistance genes. In addition, the systems we developed may be valuable tools in the quality control of seed production from blast-resistant multiline cultivars.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bryan GT, Wu KS, Farrall L, Jia Y, Hershey HP, McAdams SA, Faulk KN, Donaldson GK, Tarchini R, Valent B (2000) A single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 12:2033–2045
Ebitani T, Takeuchi Y, Nonoue Y, Yamamoto T, Takeuchi K, Yano M (2005) Construction and evaluation of chromosome segment substitution lines carrying overlapping chromosome segments of indica rice cultivar ‘Kasalath’ in a genetic background of japonica elite cultivar ‘Koshihikari’. Breed Sci 55:65–73
Feltus FA, Wan J, Schulze SR, Estill JC, Jiang N, Paterson AH (2004) An SNP resource for rice genetics and breeding based on subspecies indica and japonica genome alignments. Genome Res 14:1812–1819
Fjellstrom R, Conaway-Bormans CA, McClung AM, Marchetti MA, Shank AR, Park WD (2004) Development of DNA markers suitable for marker-assisted selection of three Pi genes conferring resistance to multiple Pyricularia grisea pathotypes. Crop Sci 44:1790–1798
Hayashi K, Hashimoto N, Daigen M, Ashikawa I (2004) Development of PCR-based SNP markers for rice blast resistance genes at the Piz locus. Theor Appl Genet 108:1212–1220
Hittalmani S, Parco A, Mew TV, Zeigler RS, Huang N (2000) Fine mapping and DNA marker-assisted pyramiding of the three major genes for blast resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 100:1121–1128
Inukai T, Nelson RJ, Zeigler RS, Sarkarung S, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Takamure I, Kinoshita T (1994) Allelism of blast resistance genes in near-isogenic lines of rice. Phytopathology 84:1278–1283
Jia Y, Wang Z, Singh P (2002) Development of dominant rice blast Pi-ta resistance gene markers. Crop Sci 42:2145–2149
Kaji R, Ogawa T, Nishimura M (1997) RFLP mapping of a blast resistance gene, Pit, in rice (in Japanese). Breed Sci 47(Suppl 1):37
Kiyosawa S (1969) The inheritance of blast-resistance in Indian rice variety, HR-22. Jpn J Breed 19:269–276
Kiyosawa S (1974) Studies on genetics and breeding of blast resistance in rice (in Japanese). Natl Inst Agric Sci Misc Publ D1:1–58
Kiyosawa S (1984) Establishment of differential varieties for pathogenicity test of rice blast fungus. Rice Genet Newsl 1:95–96
Kiyosawa S, Ling Z (2001) Genetic studies on rice blast relationships. In: Sreenivasaprasad S, Johnson R (eds) Major fungal diseases of rice. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 145–162
Koizumi S (2001) Rice blast control with multilines in Japan. In: Mew TW, Borromeo E, Hardy B (eds) In exploiting biodiversity for sustainable pest management. IRRI, Los Banos, pp 143–157
Koizumi S, Ashizawa T, and Zenbayashi KS (2004) Durable control of rice blast disease with multilines. In: Kawasaki S (ed) Rice blast: interaction with rice and control. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 191–199
Kumar LS (1999) DNA markers in plant improvement: an overview. Biotechnol Adv 17:143–182
Mohan M, Nair S, Bhagwat A, Krishna TG, Yano M, Bhatia CR, Sasaki T (1997) Genome mapping, molecular markers and marker-assisted selection in crop plants. Mol Breed 3:87–103
Monosi B, Wisser RJ, Pennill L, Hulbert SH (2004) Full-genome analysis of resistance gene homologues in rice. Theor Appl Genet 109:1434–1447
Mundt CC (2002) Use of multiline cultivars and cultivar mixtures for disease management. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:381–410
Nasu S, Suzuki J, Ohta R, Hasegawa K, Yui R, Kitazawa N, Monna L, Minobe Y (2002) Search for and analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and establishment of SNP markers. DNA Res 9:163–171
Sakata K, Nagamura Y, Numa H, Antonio BA, Nagasaki H, Idonuma A, Watanabe W, Shimizu Y, Horiuchi I, Matsumoto T, Sasaki T, Higo K (2002) RiceGAAS: an automated annotation system and database for rice genome sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 30:98–102
Yamada M, Kiyosawa S, Yamaguchi T, Hirano T, Kobayashi T, Kushibuchi K, Watanabe S (1976) Proposal of a new method for differentiating races of Pyricularia oryzae Cavara in Japan. Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 42:216–219
Yu J, Hu S, Wang J et al (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science 296:79–92
Yu J, Wang J, Lin W, Li S, Li H, Zhou J, Ni P et al (2005) The genomes of Oryza sativa: a history of duplications. PLoS Biol 3:266–281
Wang ZX, Yano M, Yamanouchi U, Iwamoto M, Monna L, Hayasaka H, Katayose Y, Sasaki T (1999) The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J 19:55–64
Wang C, Hirano K, Kawasaki S (2002) Cloning of Pita2 in the centromeric region of Chr 12 with HEGS: high efficiency genome scanning. Third International Rice Blast Conference, p 25
Zhou T, Wang Y, Chen JQ, Araki H, Jing Z, Jiang K, Shen J, Tian D (2004) Genome-wide identification of NBS genes in japonica rice reveals significant expansion of divergent non-TIR NBS-LRR genes. Mol Gen Genomics 271:402–415
Zhu Y, Chen H, Fan J, Wang Y, Li Y, Chen J, Fan J, Yang S, Hu L, Leung H, Mew TW, Teng PS, Wang Z, Mundt CC (2000) Genetic diversity and disease control in rice. Nature 406:718–722
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. M. Yano (National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences) for providing us with the seeds of 99SL-44 and OISL235. We also thank T. Nakajima, N. Yasuda, and M. Noguchi (National Agriculture Research Center) for their technical advice on assaying the blast resistance of the mapping population. This work was supported by a grant from the Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries under the project name “Development of DNA Marker-aided Selection Technology for Plants and Animals”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Y. Xue
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, K., Yoshida, H. & Ashikawa, I. Development of PCR-based allele-specific and InDel marker sets for nine rice blast resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 113, 251–260 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0290-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0290-6