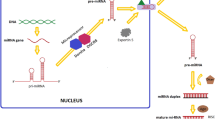
Abstract
Considering the high mortality rate encountered in lung cancer, there is a strong need to explore new biomarkers for early diagnosis and also improved therapeutic targets to overcome this issue. The implementation of microRNAs as important regulators in cancer and other pathologies expanded the possibilities of lung cancer management and not only. MiR-21 represents an intensively studied microRNA in many types of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Its role as an oncogene is underlined in multiple studies reporting the upregulated expression of this sequence in patients diagnosed with this malignancy; moreover, several studies associated this increased expression of miR-21 with a worse outcome within NSCLC patients. The same pattern is supported by the data existent in the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The carcinogenic advantage generated by miR-21 in NSCLC resides in the target genes involved in multiple pathways such as cell growth and proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis, but also chemo- and radioresistance. Therapeutic modulation of miR-21 by use of antisense sequences entrapped in different delivery systems has shown promising results in impairment of NSCLC. Hereby, we review the mechanisms of action of miR-21 in cancer and the associated changes upon tumor cells together a focused perspective on NSCLC signaling, prognosis and therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- LUAD:
-
Lung adenocarcinoma
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M et al (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136(5):E359–E386
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Austin JH, Beasley MB et al (2015) The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of lung tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances Since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol 10(9):1243–1260
Office of the Surgeon General (US), Office on Smoking and Health (US) (2004) The health consequences of smoking: a report of the surgeon general. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US), Atlanta, GA
Pikor LA, Ramnarine VR, Lam S, Lam WL (2013) Genetic alterations defining NSCLC subtypes and their therapeutic implications. Lung Cancer (Amst, Neth) 82(2):179–189
Voortman J, Goto A, Mendiboure J, Sohn JJ, Schetter AJ, Saito M et al (2010) MicroRNA expression and clinical outcomes in patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy after complete resection of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Can Res 70(21):8288–8298
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E et al (2002) Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(24):15524–15529
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL, Bradley A (2004) Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and transcription units. Genome Res 14(10A):1902–1910
Bortolin-Cavaille ML, Dance M, Weber M, Cavaille J (2009) C19MC microRNAs are processed from introns of large Pol-II, non-protein-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 37(10):3464–3473
Gulei D, Mehterov N, Nabavi SM, Atanasov AG, Berindan-Neagoe I (2017) Targeting ncRNAs by plant secondary metabolites: the ncRNAs game in the balance towards malignancy inhibition. Biotechnol Adv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.11.003
Redis RS, Berindan-Neagoe I, Pop VI, Calin GA (2012) Non-coding RNAs as theranostics in human cancers. J Cell Biochem 113(5):1451–1459
Pop-Bica C, Gulei D, Cojocneanu-Petric R, Braicu C, Petrut B, Berindan-Neagoe I (2017) Understanding the role of non-coding RNAs in bladder cancer: from dark matter to valuable therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci 18(7):1514
Hsu SD, Lin FM, Wu WY, Liang C, Huang WC, Chan WL et al (2011) miRTarBase: a database curates experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions. Nucl Acids Res 39(Database issue):D163–D169
Braicu C, Calin GA, Berindan-Neagoe I (2013) MicroRNAs and cancer therapy—from bystanders to major players. Curr Med Chem 20(29):3561–3573
Gulei D, Magdo L, Jurj A, Raduly L, Cojocneanu-Petric R, Moldovan A et al (2018) The silent healer: miR-205-5p up-regulation inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colon cancer cells by indirectly up-regulating E-cadherin expression. Cell Death Dis 9(2):66
Ouellet DL, Perron MP, Gobeil LA, Plante P, Provost P (2006) MicroRNAs in gene regulation: when the smallest governs it all. J Biomed Biotechnol 2006(4):69616
Berindan-Neagoe I, Monroig Pdel C, Pasculli B, Calin GA (2014) MicroRNAome genome: a treasure for cancer diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin 64(5):311–336
Xi X, Li T, Huang Y, Sun J, Zhu Y, Yang Y et al (2017) RNA biomarkers: frontier of precision medicine for cancer. Non-Coding RNA 3(1):9
Zhang HD et al. (2018) CircRNA: a novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast cancer 25(1):1–7
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP, Lawler S (2014) MicroRNAs in cancer: biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol Med 20(8):460–469
Bertoli G, Cava C, Castiglioni I (2015) MicroRNAs: new biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics 5(10):1122–1143
Budisan L, Gulei D, Zanoaga OM, Irimie AI, Sergiu C, Braicu C et al (2017) Dietary intervention by phytochemicals and their role in modulating coding and non-coding genes in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 18(6):1178
Berindan-Neagoe I, Calin GA (2014) Molecular pathways: microRNAs, cancer cells, and microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res 20(24):6247–6253
Cai X, Hagedorn CH, Cullen BR (2004) Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA 10(12):1957–1966
Krichevsky AM, Gabriely G (2009) miR-21: a small multi-faceted RNA. J Cell Mol Med 13(1):39–53
Zhou X, Ren Y, Moore L, Mei M, You Y, Xu P et al (2010) Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits EGFR pathway and suppresses the growth of human glioblastoma cells independent of PTEN status. Lab Investig 90(2):144–155
Iliopoulos D, Jaeger SA, Hirsch HA, Bulyk ML, Struhl K (2010) STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer. Mol Cell 39(4):493–506
Ma X, Choudhury SN, Hua X, Dai Z, Li Y (2013) Interaction of the oncogenic miR-21 microRNA and the p53 tumor suppressor pathway. Carcinogenesis 34(6):1216–1223
Berindan-Neagoe I, Balacescu O, Burz C, Braicu C, Balacescu L, Tudoran O et al (2009) p53 gene therapy using RNA interference. J BUON 14(Suppl 1):S51–S59
Braicu C, Pileczki V, Irimie A, Berindan-Neagoe I (2013) p53siRNA therapy reduces cell proliferation, migration and induces apoptosis in triple negative breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 381(1–2):61–68
Chira S, Gulei D, Hajitou A, Berindan-Neagoe I (2018) Restoring the p53 ‘Guardian’ phenotype in p53-deficient tumor cells with CRISPR/Cas9. Trends Biotechnol 36(7):653–660
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Can Res 65(14):6029–6033
Lakomy R, Sana J, Hankeova S, Fadrus P, Kren L, Lzicarova E et al (2011) MiR-195, miR-196b, miR-181c, miR-21 expression levels and O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase methylation status are associated with clinical outcome in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Sci 102(12):2186–2190
Ivo D’Urso P, Fernando D’Urso O, Damiano Gianfreda C, Mezzolla V, Storelli C, Marsigliante S (2015) miR-15b and miR-21 as circulating biomarkers for diagnosis of glioma. Curr Genom 16(5):304–311
Huang GL, Zhang XH, Guo GL, Huang KT, Yang KY, Shen X et al (2009) Clinical significance of miR-21 expression in breast cancer: SYBR-Green I-based real-time RT-PCR study of invasive ductal carcinoma. Oncol Rep 21(3):673–679
Han JG, Jiang YD, Zhang CH, Yang YM, Pang D, Song YN et al (2017) A novel panel of serum miR-21/miR-155/miR-365 as a potential diagnostic biomarker for breast cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res 92(2):55–66
Pulito C, Mori F, Sacconi A, Goeman F, Ferraiuolo M, Pasanisi P et al (2017) Metformin-induced ablation of microRNA 21-5p releases Sestrin-1 and CAB39L antitumoral activities. Cell Discov 3:17022
Park SK, Park YS, Ahn JY, Do EJ, Kim D, Kim JE et al (2016) MiR 21-5p as a predictor of recurrence in young gastric cancer patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 31(8):1429–1435
Riccioni R, Lulli V, Castelli G, Biffoni M, Tiberio R, Pelosi E et al (2015) miR-21 is overexpressed in NPM1-mutant acute myeloid leukemias. Leuk Res 39(2):221–228
Oue N, Anami K, Schetter AJ, Moehler M, Okayama H, Khan MA et al (2014) High miR-21 expression from FFPE tissues is associated with poor survival and response to adjuvant chemotherapy in colon cancer. Int J Cancer 134(8):1926–1934
Li T, Li RS, Li YH, Zhong S, Chen YY, Zhang CM et al (2012) miR-21 as an independent biochemical recurrence predictor and potential therapeutic target for prostate cancer. J Urol 187(4):1466–1472
Huang W, Kang XL, Cen S, Wang Y, Chen X (2015) High-level expression of microRNA-21 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is a diagnostic and prognostic marker in prostate cancer. Genet Test Mol Biomark 19(9):469–475
Wang WY, Zhang HF, Wang L, Ma YP, Gao F, Zhang SJ et al (2014) miR-21 expression predicts prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 38(6):715–719
Guo X, Lv X, Lv X, Ma Y, Chen L, Chen Y (2017) Circulating miR-21 serves as a serum biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma and correlated with distant metastasis. Oncotarget 8(27):44050–44058
Wang L, Wang J (2012) MicroRNA-mediated breast cancer metastasis: from primary site to distant organs. Oncogene 31(20):2499–2511
Zhang H, Li Y, Lai M (2010) The microRNA network and tumor metastasis. Oncogene 29(7):937–948
Sahay D, Leblanc R, Grunewald TG, Ambatipudi S, Ribeiro J, Clezardin P et al (2015) The LPA1/ZEB1/miR-21-activation pathway regulates metastasis in basal breast cancer. Oncotarget 6(24):20604–20620
Hu Y, Wang C, Li Y, Zhao J, Chen C, Zhou Y et al (2015) MiR-21 controls in situ expansion of CCR6(+) regulatory T cells through PTEN/AKT pathway in breast cancer. Immunol Cell Biol 93(8):753–764
Zhang L, Zhan X, Yan D, Wang Z (2016) Circulating MicroRNA-21 Is Involved in Lymph Node Metastasis in Cervical Cancer by Targeting RASA1. Int J Gynecol Cancer 26(5):810–816
Liu LZ, Li C, Chen Q, Jing Y, Carpenter R, Jiang Y et al (2011) MiR-21 induced angiogenesis through AKT and ERK activation and HIF-1alpha expression. PLoS One 6(4):e19139
Yang Z, Fang S, Di Y, Ying W, Tan Y, Gu W (2015) Modulation of NF-kappaB/miR-21/PTEN pathway sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer to cisplatin. PLoS One 10(3):e0121547
Su Q, Li L, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Wang J, Wen W (2015) Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-mediated microRNA-21 transfection regulated PDCD4/NF-kappaB/TNF-alpha pathway to prevent coronary microembolization-induced cardiac dysfunction. Gene Ther 22(12):1000–1006
Gui F, Hong Z, You Z, Wu H, Zhang Y (2016) MiR-21 inhibitor suppressed the progression of retinoblastoma via the modulation of PTEN/PI3 K/AKT pathway. Cell Biol Int 40(12):1294–1302
Song L, Liu S, Zhang L, Yao H, Gao F, Xu D et al (2016) MiR-21 modulates radiosensitivity of cervical cancer through inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/Akt/HIF-1alpha feedback loop and the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Tumour Biol 37(9):12161–12168
Zhang JG, Wang JJ, Zhao F, Liu Q, Jiang K, Yang GH (2010) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin Chim Acta 411(11–12):846–852
Liu ZL, Wang H, Liu J, Wang ZX (2013) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem 372(1–2):35–45
Jiang LP, He CY, Zhu ZT (2017) Role of microRNA-21 in radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting PDCD4 gene. Oncotarget 8(14):23675–23689
Forgacs E, Biesterveld EJ, Sekido Y, Fong K, Muneer S, Wistuba II et al (1998) Mutation analysis of the PTEN/MMAC1 gene in lung cancer. Oncogene 17(12):1557–1565
Kohno T, Takahashi M, Manda R, Yokota J (1998) Inactivation of the PTEN/MMAC1/TEP1 gene in human lung cancers. Genes Chromosom Cancer 22(2):152–156
Hosoya Y, Gemma A, Seike M, Kurimoto F, Uematsu K, Hibino S et al (1999) Alteration of the PTEN/MMAC1 gene locus in primary lung cancer with distant metastasis. Lung cancer (Amst, Neth) 25(2):87–93
Zhong Z, Dong Z, Yang L, Gong Z (2012) miR-21 induces cell cycle at S phase and modulates cell proliferation by down-regulating hMSH2 in lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138(10):1781–1788
Lin L, Tu HB, Wu L, Liu M, Jiang GN (2016) MicroRNA-21 regulates non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion and chemo-sensitivity through SMAD7. Cell Physiol Biochem 38(6):2152–2162
Jiang S, Wang R, Yan H, Jin L, Dou X, Chen D (2016) MicroRNA-21 modulates radiation resistance through upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-promoted glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 13(5):4101–4107
Fujita S, Ito T, Mizutani T, Minoguchi S, Yamamichi N, Sakurai K et al (2008) miR-21 Gene expression triggered by AP-1 is sustained through a double-negative feedback mechanism. J Mol Biol 378(3):492–504
Li C, Nguyen HT, Zhuang Y, Lin Y, Flemington EK, Guo W et al (2011) Post-transcriptional up-regulation of miR-21 by type I collagen. Mol Carcinog 50(7):563–570
Jajoo S, Mukherjea D, Kaur T, Sheehan KE, Sheth S, Borse V et al (2013) Essential role of NADPH oxidase-dependent reactive oxygen species generation in regulating microRNA-21 expression and function in prostate cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal 19(16):1863–1876
Muppala S, Mudduluru G, Leupold JH, Buergy D, Sleeman JP, Allgayer H (2013) CD24 induces expression of the oncomir miR-21 via Src, and CD24 and Src are both post-transcriptionally downregulated by the tumor suppressor miR-34a. PLoS One 8(3):e59563
Mathew R, Hartmuth K, Mohlmann S, Urlaub H, Ficner R, Luhrmann R (2008) Phosphorylation of human PRP28 by SRPK2 is required for integration of the U4/U6-U5 tri-snRNP into the spliceosome. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15(5):435–443
Yin J, Park G, Lee JE, Choi EY, Park JY, Kim TH et al (2015) DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX23 modulates glioma malignancy via elevating miR-21 biogenesis. Brain 138(Pt 9):2553–2570
Liu X, Winey M (2012) The MPS1 family of protein kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 81:561–585
Maachani UB, Tandle A, Shankavaram U, Kramp T, Camphausen K (2016) Modulation of miR-21 signaling by MPS1 in human glioblastoma. Oncotarget 7(33):52912–52927
Loffler D, Brocke-Heidrich K, Pfeifer G, Stocsits C, Hackermuller J, Kretzschmar AK et al (2007) Interleukin-6 dependent survival of multiple myeloma cells involves the Stat3-mediated induction of microRNA-21 through a highly conserved enhancer. Blood 110(4):1330–1333
Ferraro A, Kontos CK, Boni T, Bantounas I, Siakouli D, Kosmidou V et al (2014) Epigenetic regulation of miR-21 in colorectal cancer: ITGB4 as a novel miR-21 target and a three-gene network (miR-21-ITGBeta4-PDCD4) as predictor of metastatic tumor potential. Epigenetics 9(1):129–141
Zhou M, Zeng J, Wang X, Wang X, Huang T, Fu Y et al (2015) Histone demethylase RBP2 decreases miR-21 in blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 6(2):1249–1261
Markou A, Tsaroucha EG, Kaklamanis L, Fotinou M, Georgoulias V, Lianidou ES (2008) Prognostic value of mature microRNA-21 and microRNA-205 overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Clin Chem 54(10):1696–1704
Cho WC, Chow AS, Au JS (2009) Restoration of tumour suppressor hsa-miR-145 inhibits cancer cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Eur J Cancer 45(12):2197–2206
Xie Y, Todd NW, Liu Z, Zhan M, Fang H, Peng H et al (2010) Altered miRNA expression in sputum for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 67(2):170–176
Wei J, Gao W, Zhu CJ, Liu YQ, Mei Z, Cheng T et al (2011) Identification of plasma microRNA-21 as a biomarker for early detection and chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Cancer 30(6):407–414
Shen H, Zhu F, Liu J, Xu T, Pei D, Wang R et al (2014) Alteration in Mir-21/PTEN expression modulates gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One 9(7):e103305
Geng Q, Fan T, Zhang B, Wang W, Xu Y, Hu H (2014) Five microRNAs in plasma as novel biomarkers for screening of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Respir Res 15:149
Zhang H, Mao F, Shen T, Luo Q, Ding Z, Qian L et al (2017) Plasma miR-145, miR-20a, miR-21 and miR-223 as novel biomarkers for screening early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett 13(2):669–676
Yang JS, Li BJ, Lu HW, Chen Y, Lu C, Zhu RX et al (2015) Serum miR-152, miR-148a, miR-148b, and miR-21 as novel biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer screening. Tumour Biol 36(4):3035–3042
Cortez MA, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferdin J, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Calin GA (2011) MicroRNAs in body fluids–the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8(8):467–477
Zaharie F, Muresan MS, Petrushev B, Berce C, Gafencu GA, Selicean S et al (2015) Exosome-carried microRNA-375 inhibits cell progression and dissemination via Bcl-2 blocking in colon cancer. J Gastrointest Liver Dis JGLD 24(4):435–443
Heijnen HF, Schiel AE, Fijnheer R, Geuze HJ, Sixma JJ (1999) Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood 94(11):3791–3799
Braicu C, Tomuleasa C, Monroig P, Cucuianu A, Berindan-Neagoe I, Calin GA (2015) Exosomes as divine messengers: are they the Hermes of modern molecular oncology? Cell Death Differ 22(1):34–45
Thery C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S (2002) Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol 2(8):569–579
Gulei D, Irimie AI, Cojocneanu-Petric R, Schultze JL, Berindan-Neagoe I (2018) Exosomes-small players, big sound. Bioconjugate Chem 29(3):635–648
Greening DW, Gopal SK, Xu R, Simpson RJ, Chen W (2015) Exosomes and their roles in immune regulation and cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol 40:72–81
Fevrier B, Raposo G (2004) Exosomes: endosomal-derived vesicles shipping extracellular messages. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16(4):415–421
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9(6):654–659
Gonzalez-Begne M, Lu B, Han X, Hagen FK, Hand AR, Melvin JE et al (2009) Proteomic analysis of human parotid gland exosomes by multidimensional protein identification technology (MudPIT). J Proteome Res 8(3):1304–1314
Gallo A, Tandon M, Alevizos I, Illei GG (2012) The majority of microRNAs detectable in serum and saliva is concentrated in exosomes. PLoS One 7(3):e30679
Bullock M, Silva A, Kanlikilicer-Unaldi P, Filant J, Rashed M, Sood A et al (2015) Exosomal non-coding RNAs: diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic applications in cancer. Non-Coding RNA 1(1):53
Zhou X, Wen W, Shan X, Zhu W, Xu J, Guo R et al (2017) A six-microRNA panel in plasma was identified as a potential biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma diagnosis. Oncotarget 8(4):6513–6525
Liu Q, Yu Z, Yuan S, Xie W, Li C, Hu Z et al (2017) Circulating exosomal microRNAs as prognostic biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 8(8):13048–13058
Gallach S, Jantus-Lewintre E, Calabuig-Farinas S, Montaner D, Alonso S, Sirera R et al (2017) MicroRNA profiling associated with non-small cell lung cancer: next generation sequencing detection, experimental validation, and prognostic value. Oncotarget 8:56143
Saito M, Schetter AJ, Mollerup S, Kohno T, Skaug V, Bowman ED et al (2011) The association of microRNA expression with prognosis and progression in early-stage, non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma: a retrospective analysis of three cohorts. Clin Cancer Res 17(7):1875–1882
Gao W, Lu X, Liu L, Xu J, Feng D, Shu Y (2012) MiRNA-21: a biomarker predictive for platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 13(5):330–340
Tian L, Shan W, Zhang Y, Lv X, Li X, Wei C (2016) Up-regulation of miR-21 expression predicate advanced clinicopathological features and poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Oncol Res POR 22(1):161–167
Capodanno A, Boldrini L, Proietti A, Ali G, Pelliccioni S, Niccoli C et al (2013) Let-7g and miR-21 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: correlation with clinicopathological and molecular features. Int J Oncol 43(3):765–774
Li C, Yin Y, Liu X, Xi X, Xue W, Qu Y (2017) Non-small cell lung cancer associated microRNA expression signature: integrated bioinformatics analysis, validation and clinical significance. Oncotarget 8(15):24564–24578
Shen Y, Tang D, Yao R, Wang M, Wang Y, Yao Y et al (2013) microRNA expression profiles associated with survival, disease progression, and response to gefitinib in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer with EGFR mutation. Med Oncol 30(4):750
Wang ZX, Bian HB, Wang JR, Cheng ZX, Wang KM, De W (2011) Prognostic significance of serum miRNA-21 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol 104(7):847–851
Zhao W, Zhao JJ, Zhang L, Xu QF, Zhao YM, Shi XY et al (2015) Serum miR-21 level: a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(9):14759–14763
Stenvold H, Donnem T, Andersen S, Al-Saad S, Valkov A, Pedersen MI et al (2014) High tumor cell expression of microRNA-21 in node positive non-small cell lung cancer predicts a favorable clinical outcome. BMC Clin Pathol 14(1):9
Dejima H, Iinuma H, Kanaoka R, Matsutani N, Kawamura M (2017) Exosomal microRNA in plasma as a non-invasive biomarker for the recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett 13(3):1256–1263
Markou A, Sourvinou I, Vorkas PA, Yousef GM, Lianidou E (2013) Clinical evaluation of microRNA expression profiling in non small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 81(3):388–396
Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, Ma LN, Zhou SQ, Wang YK et al (2012) High expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol 29(2):618–626
Zhu J, Qi Y, Wu J, Shi M, Feng J, Chen L (2016) Evaluation of plasma microRNA levels to predict insensitivity of patients with advanced lung adenocarcinomas to pemetrexed and platinum. Oncol Lett 12(6):4829–4837
Dong J, Zhang Z, Gu T, Xu SF, Dong LX, Li X et al (2017) The role of microRNA-21 in predicting brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther 10:185–194
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W (2009) Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 136(4):629–641
Tuck AC, Tollervey D (2013) A transcriptome-wide atlas of RNP composition reveals diverse classes of mRNAs and lncRNAs. Cell 154(5):996–1009
Schmitt AM, Chang HY (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 29(4):452–463
Martens-Uzunova ES, Bottcher R, Croce CM, Jenster G, Visakorpi T, Calin GA (2014) Long noncoding RNA in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer. Eur Urol 65(6):1140–1151
Cao L, Chen J, Ou B, Liu C, Zou Y, Chen Q (2017) GAS5 knockdown reduces the chemo-sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell to cisplatin (DDP) through regulating miR-21/PTEN axis. Biomed Pharmacother 93:570–579
Zhou Y, Sheng B, Xia Q, Guan X, Zhang Y (2017) Association of long non-coding RNA H19 and microRNA-21 expression with the biological features and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 24:317
Geretto M, Pulliero A, Rosano C, Zhabayeva D, Bersimbaev R, Izzotti A (2017) Resistance to cancer chemotherapeutic drugs is determined by pivotal microRNA regulators. Am J Cancer Res 7(6):1350–1371
Li B, Ren S, Li X, Wang Y, Garfield D, Zhou S et al (2014) MiR-21 overexpression is associated with acquired resistance of EGFR-TKI in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Amst, Neth) 83(2):146–153
Ma Y, Xia H, Liu Y, Li M (2014) Silencing miR-21 sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells to ionizing radiation through inhibition of PI3 K/Akt. Biomed Res Int 2014:617868
Jiang Y, Chen X, Tian W, Yin X, Wang J, Yang H (2014) The role of TGF-beta1-miR-21-ROS pathway in bystander responses induced by irradiated non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Br J Cancer 111(4):772–780
Pereira DM, Rodrigues PM, Borralho PM, Rodrigues CM (2013) Delivering the promise of miRNA cancer therapeutics. Drug Discovery Today 18(5–6):282–289
Castanotto D, Rossi JJ (2009) The promises and pitfalls of RNA-interference-based therapeutics. Nature 457(7228):426–433
Tomuleasa C, Braicu C, Irimie A, Craciun L, Berindan-Neagoe I (2014) Nanopharmacology in translational hematology and oncology. Int J Nanomed 9:3465–3479
Ananta JS, Paulmurugan R, Massoud TF (2016) Tailored nanoparticle codelivery of antimiR-21 and antimiR-10b augments glioblastoma cell kill by temozolomide: toward a “Personalized” anti-microRNA therapy. Mol Pharm 13(9):3164–3175
Song H, Oh B, Choi M, Oh J, Lee M (2015) Delivery of anti-microRNA-21 antisense-oligodeoxynucleotide using amphiphilic peptides for glioblastoma gene therapy. J Drug Target 23(4):360–370
Aldea MD, Petrushev B, Soritau O, Tomuleasa CI, Berindan-Neagoe I, Filip AG et al (2014) Metformin plus sorafenib highly impacts temozolomide resistant glioblastoma stem-like cells. J BUON 19(2):502–511
Leone E, Morelli E, Di Martino MT, Amodio N, Foresta U, Gulla A et al (2013) Targeting miR-21 inhibits in vitro and in vivo multiple myeloma cell growth. Clin Cancer Res 19(8):2096–2106
Shu D, Li H, Shu Y, Xiong G, Carson WE 3rd, Haque F et al (2015) Systemic delivery of anti-miRNA for suppression of triple negative breast cancer utilizing RNA nanotechnology. ACS Nano 9(10):9731–9740
Dong H, Ding L, Yan F, Ji H, Ju H (2011) The use of polyethylenimine-grafted graphene nanoribbon for cellular delivery of locked nucleic acid modified molecular beacon for recognition of microRNA. Biomaterials 32(15):3875–3882
Zhi F, Dong H, Jia X, Guo W, Lu H, Yang Y et al (2013) Functionalized graphene oxide mediated adriamycin delivery and miR-21 gene silencing to overcome tumor multidrug resistance in vitro. PLoS One 8(3):e60034
Li Y, Chen Y, Li J, Zhang Z, Huang C, Lian G et al (2017) Co-delivery of microRNA-21 antisense oligonucleotides and gemcitabine using nanomedicine for pancreatic cancer therapy. Cancer Sci 108(7):1493–1503
Liu C, Wen J, Meng Y, Zhang K, Zhu J, Ren Y et al (2015) Efficient delivery of therapeutic miRNA nanocapsules for tumor suppression. Adv Mater 27(2):292–297
Lin Q, Ma L, Liu Z, Yang Z, Wang J, Liu J et al (2017) Targeting microRNAs: a new action mechanism of natural compounds. Oncotarget 8(9):15961–15970
Sethi S, Li Y, Sarkar FH (2013) Regulating miRNA by natural agents as a new strategy for cancer treatment. Curr Drug Targets 14(10):1167–1174
Braicu C, Pilecki V, Balacescu O, Irimie A, Neagoe IB (2011) The relationships between biological activities and structure of flavan-3-ols. Int J Mol Sci 12(12):9342–9353
Cojocneanu Petric R, Braicu C, Raduly L, Zanoaga O, Dragos N, Monroig P et al (2015) Phytochemicals modulate carcinogenic signaling pathways in breast and hormone-related cancers. OncoTargets Ther 8:2053–2066
Zhang J, Zhang C, Hu L, He Y, Shi Z, Tang S et al (2015) Abnormal expression of miR-21 and miR-95 in cancer stem-like cells is associated with radioresistance of lung cancer. Cancer Invest 33(5):165–171
Acknowledgements
This work was granted by Competitiveness Operational Program, 2014–2020, entitled “Clinical and economical impact of personalized targeted anti-microRNA therapies in reconverting lung cancer chemoresistance”—CANTEMIR, no. 35/01.09.2016, MySMIS 103375 and PhD fellowship (PCD 2017) no. 1300/51/13.01.2017 entitled, “Next Generation sequencing (NGS) in personalized medicine”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bica-Pop, C., Cojocneanu-Petric, R., Magdo, L. et al. Overview upon miR-21 in lung cancer: focus on NSCLC. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 75, 3539–3551 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2877-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2877-x