Abstract.
Objective:
To investigate whether glutamine supplementation modulates intestinal nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activity and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression after traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Materials and methods:
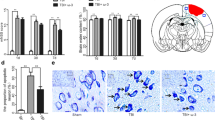
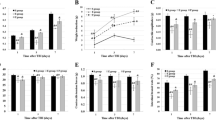
Right parietal cortical contusion in male rats was made by the weight-dropping method. After trauma, the rats were randomly given chow alone or glutamine mixed chow for 5 d. Gut samples were extracted at 5 d postinjury. We measured NF-κB binding activity by electrophoretic mobility shift assay; NF-κB subunits p50 and p65 expression by immunohistochemistry; the concentrations of interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; intestinal mucosal morphological changes by histopathological study and electron microscopy; and apoptosis by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling staining.
Results:
Administration of glutamine following TBI could decrease NF-κB binding activity, NF-κB p65 protein expression and concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the gut. TBI-induced damage of gut structure was ameliorated after glutamine supplementation.
Conclusion:
The results of the present study suggest that the therapeutic benefit of post-TBI glutamine supplementation might be due to its inhibitory effects on intestinal NF-κB activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 14 May 2007; returned for revision 9 July 2007; accepted by I. Ahnfeld-Rønne 16 August 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Shi, J., Qi, M. et al. Glutamine decreases intestinal nuclear factor kappa B activity and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression after traumatic brain injury in rats. Inflamm. res. 57, 57–64 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-007-7101-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-007-7101-7