Abstract
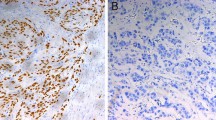
In view of the significance of MDM2 as a regulator as well as critical target of wild type p53, this study was undertaken to determine the alteration in MDM2 expression in esophageal squamons cell carcinoma (ESCC) and its relationship to clinicopathological parameters as well as p53 gene and protein status. Immunohistochemical analysis of MDM2 and p53 proteins on paraffin embedded sections from 64 surgically resected ESCCs and matched histologically normal tissues showed overexpression of MDM2 protein in 23/64 (36%) ESCCs, while the histopathologically normal esophageal tissues did not show detectable level of MDM2 immunoreactivity. Interestingly, MDM2−/p53+ phenotype was observed in 37/64 (58%) cases. None of the cases with p53 missense mutations (12/30, 40%) showed detectable level of MDM2 protein. Missense p53 mutations were significantly associated with discordant p53+/MDM2− immunophenotype (p= 0.004). The most intriguing feature of the study was accumulation of MDM2 in the absence of detectable p53 in 11% of and overexpression of MDM2 and p53 in 25% of ESCCs, suggesting a p53-independent role for MDM2 in a subset of tumors. These results underscore the involvement of MDM2 in p53-dependent and -independent pathways in the pathogenesis of esophageal cancer in the Indian population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESCC:
-
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- MDM2:
-
murine double minute 2
- mAb:
-
monoclonal antibody
- SSCP:
-
single strand conformation polymorphism
References
Barak Y, Juven T, Hafner R, et al; MDM2 expression is induced by wild type p53 activity. EMBO J 12:461–468, 1993.
Cahilly Snyder L, Yang-Feng T, Francke U, et al; Molecular analysis and Chromosomal mapping of amplified genes isolated from a transformed mouse 3T3 cell line. Somat Cell Molec Genet 13: 235–244, 1987.
Cordon-Cardo C, Latres E, Drobnjak M, et al; Molecular abnormalities of mdm-2 and p53 genes in adult soft tissue sarcomas. Canc Res 54: 794–799, 1994.
El-Deiry WS, Harper JW, O’Connor PM, et al; p21 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Canc Res 54:1169, 1994.
Fakhar-Zadeh SS, Trusko SP, George DC; Tumorigenic potential associated with enhanced expression of a gene that is amplified in a mouse tumor cell line. EMBO J 10:1565–1569, 1991.
Foulkes WD, Stamp GWH, Afzal S, et al; MDM2 overexpression is rare in ovarian carcinoma irrespective of TP53 mutation status. Br J Cancer 72: 883–888, 1995.
Ganguli G, Abecassis J, Wasylyk B; MDM2 induces hyperplasia and premalignant lesions when expressed in the basal layer of the epidermis. EMBO J 19: 5135–5147, 2000.
Gaur D, Arora S, Mathur M, et al; High prevalence of p53 gene alterations and protein accumulation in human esophageal cancer: correlation with dietary risk factors in India. Clin Canc Res 3: 2129–2136, 1997.
Haines DS; The mdm2 proto-oncogene. Leukemia Lymphoma 26:227–238, 1997.
Haital A, Wiener GH, Baethge U, et al; Mdm2 expression as a prognostic indicator in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: comparison with p53 overexpression and clinicopathological parameters. Clin Cancer Res 6:1840–1844, 2000.
Itoshima T, Fujiwara T, Waku T, et al; Induction of apoptosis in human esophageal cancer cells by sequential transfer of the wild-type p53 E2F-1 Genes: Involvement of p53 accumulation via ARF-mediated MDM2 down-regulation. Clin Canc Res 6: 2851–2859, 2000.
Jones SN, Hancock AR, Vogel H, et al; Overexpression of Mdm2 in mice reveals a p53-independent role for Mdm2 in tumorigenesis. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 95:15608–15612, 1998.
Kern SE, Pietenpol JA, Thiagalingan S, et al; Oncogenic forms of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science 256: 827, 1992.
Kern SE, Kinzler KW, Bruskin A, et al; Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science 252: 1708, 1992.
Landis SH, Murray T, Bolden S, et al; Cancer Statistics-1999, CAJ Clini. Ame Canc Soci 49: 57–58, 1999.
Leach FS, Tokino T, Meltzer P, et al; p53 Mutation and MDM2 amplification in human soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res 53: 2231–2234, 1993.
Marchett A, Buttitta F, Girlando S, et al; Mdm gene alterations and mdm2 protein expression in breast carcinomas. J Pathol 17:31–38, 1995
Michalides R; Prognosis for G1 cell-cycle regulators:Useful for predicting course of disease and for assessment of therapy in Cancer. J Pathol 188:341–343, 1999.
Momand J, Wu HH, Dasgupta G; MDM2-master regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Gene 242:15–29, 2000.
Oliner JD, Kinzler KW, Meltzer PS, et al; Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature 358:80–83, 1992.
Ralhan R, Agarwal S, Mathur M, et al; Induction of MDM2-P2 transcripts correlates with stabilized wild type p53 in Betel-tobacco Related Human Oral Cancer. Am J Pathol 157:587–596, 2000.
Ralhan R, Arora S, Chattopadhyay TK, et al; Circulating p53 antibodies, p53 gene mutational profile and product accumulation in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma in India. Int J Cancer, 85:791–795, 2000.
Sandhya Agarwal, Mathur M, Shukla NK, et al; MDM2/p53 coexpression in oral premalignant and malignant lesions: potential prognostic implications. E J Canc Oral Oncol 35:209–216, 1999.
Sherr CJ, Weber JD; The ARF/p53 pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10, 94–99, 2000.
Villuendas R, Pezzella F, Gatter K, et al; p21 waf1/cip1 and MDM2 expression in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and their relationship to p53 status: A p53+, MDM2-, p21-immunophenotype associated with missense p53 mutations. J Pathol 181:51–61, 1997.
Wu X, Bayle JH, Olson D, Leumi AJ; The p53-mdm2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev 7:1126–1132, 1993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contract Grant Sponsor: Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, S., Mathew, R., Mathur, M. et al. Alterations in MDM2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Relationship with p53 status. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 7, 203–208 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03032350
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03032350