Abstract
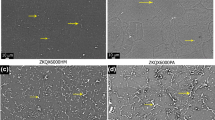
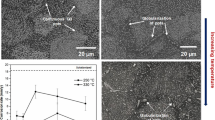
In the present study, the corrosion behavior of an as-cast magnesium alloy was studies focusing on the galvanic corrosion between a precipitate and Mg-rich matrix. Through immersion and electrochemical tests, the variation of the corrosion behavior with the alloy composition and alloy system was discussed in detail. The corrosion rate of an as-cast alloy increased abruptly to 9 wt.% Al in both alloys, but in the composition range of over 12 wt.% Al, the corrosion rate reveals a different tendency than the alloy system. The β-phase that is a typical precipitate in an Mg-xAl alloy is a more potent cathodic phase than is the ternary precipitate in a Mg-xAl-LZn alloy. In the case of the Mg-xAl alloy, the formation of a galvanic cell between the precipitate and matrix promotes the preferred dissolution of the matrix, but the precipitate in the Mg-xAl-lZn alloy has a minor effect on the corrosion behavior of the Mg-rich matrix. However, the corrosion rate of as-cast Mg-xAl and Mg-xAl-lZn alloys which contain precipitate, depends mainly upon the corrosion behavior of the Mg-rich matrix, which is influenced by the Al content. It depends additionally upon the variation of the Anode-Cathode Area Ratio (ACAR) and the chunk breakage of precipitate during corrosion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. D. Hanawalt, C. E. Nelson and J. A. Peloubet,Trans. AIME 147, 273 (1942).
K. N. Reichek, K. J. Clark and J. E. Hillis,SAE-Technical Paper #850417 (1985).
J. E. Hillis and K. N. Reichek,SAE-Technical Paper #860288 (1986).
O. Lunder, T. Kr. Aune and K. Nisancioglu,Corrosion 43, 291 (1987).
C. Baliga and P. Tsakiropoulos,Mater. Sci. Tech. A 134, 1029 (1991).
C. Baliga and P. Tsakiropoulos,Mater. Sci. Eng. 9, 507 (1991).
G. A. Marsh and E. Schaschl,J. Electrochem. Soc. 107, 960 (1960).
R. Tunold, H. Holfen, M. H. Berge, A. Lasson and R. S.Hansen,Corros. Sci. 17, 353 (1977).
C. D. Lee,Ph. D Thesis, Seoul National University, Korea (1996).
E. A. Brandes and G. B. Brook,Smithells Metals Reference Book,7th., p. 10.
P. F. King,J. Electrochem. Soc. 113, 536 (1966).
J. L. Robison and P. F. King,J. Electrochem. Soc. 108, 36 (1961).
O. Lunder, K. Nisancioglu and R. S. Hansen,SAE-Technical Paper #930755 (1993).
D. A. Jone,Principles and Prevention of Corrosion, p. 31, Macmillan Publishing Co. (1992).
M. Stern,Corrosion-NACE 14, 329t (1958).
R. F. Steigerwald and N. D. Greene,J. Electrochem. Soc. 109, 1026 (1962).
M. E. Strumanis and B. K. Bhatia,J. Electrochem. Soc. 110, 357 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.D., Kang, C.S. & Shin, K.S. Effect of galvanic corrosion between precipitate and matrix on corrosion behavior of As-cast magnesium-aluminum alloys. Metals and Materials 6, 351–358 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03028082
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03028082