Abstract
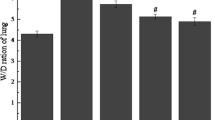
It is not known if alveolar macrophages (AM) play an important role in the development of interstitial changes in the lung. The purpose of the present study was to learn if AM are related to the initiation of paraquat-induced lung injury in rats. An intraperitoneal injection of 10 mg/kg paraquat was followed by a rapid increase in the number of viable AM. This effect reached a maximum at 24 h after injection. When 90 mg/kg of methylprednisolone was injected subcutaneously at the same time of the administration of paraquat there was no increase in the number of viable AM. After weekly injection of 5 mg/kg paraquat for six weeks, there were histological changes which were significantly supressed by the simultaneous administration of methylprednisolone. Methylprednisolone, however, did not show such suppressive effects when administered 4 d after the injection of paraquat. It is suggested that the emergence of viable AM is one of the key phenomena in the initiation of interstitial changes in paraquat-induced lung injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando M, Suga M, Sugimoto M, Tokuomi H (1979) Superoxide production in pulmonary alveolar macrophages and killing of BCG by superoxide-generating system with or without catalase. Infect Immun 24:404–410
Blussé van Oud Alblas A, Van der Linden-Schrever B, Mattie H, Van Furth R (1981) The effect of glucocorticosteroids on the kinetics of pulmonary macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc 30:1–14
Hamilton J, Vassalli JD, Reich E (1976) Macrophage plasminogen activator: induction by asbestos is blocked by anti-inflammatory steroids. J Exp Med 144: 1689–1694
Hesterberg TW, Last JA (1981) Ozone-induced acute pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Prevention of increased rates of collagen synthesis by methylprednisolone. Am Rev Respir Dis 123:47–52
Hocking WG, Golde DW (1979) The pulmonary-alveolar macrophage. Part II. N Engl J Med 301:639–645
Johnson KJ, Fantone JC III, Kaplan J, Ward PA (1981) In vivo damage of rat lungs by oxygen metabolites. J Clin Invest 67:983–993
Johnston RB Jr, Godzik CA, Cohn ZA (1978) Increased superoxide anion production by immunologically activated and chemically elicited macrophages. J Exp Med 148:115–127
Jones PA, Werb Z (1980) Degradation of connective tissue matrices by macrophages. II. Influence of matrix composition on proteolysis of glycoproteins, elastin, and collagen by macrophages in culture. J Exp Med 152:1527–1536
Leibovich SJ, Ross R (1976) A macrophage-dependant factor that stimulates the proliferation of fibroblasts in vitro. Am J Pathol 84:501–514
Martin WJ II, Gadek JE, Hunninghake GW, Crystal RG (1981) Oxidant injury of lung parenchymal cells. J Clin Invest 68::1277–1288
Nathan CF, Murray HW, Cohn ZA (1980) The macrophage as an effector cell. N Engl J Med 303:622–626
Smith P, Heath D, Kay JM (1974) The pathogenesis and structure of paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. J Pathol 114:57–67
Stevens JB, Autor AP (1977) Oxygen-induced synthesis of superoxide dismutase and catalase in pulmonary macrophages of neonatal rats. Lab Invest 37:470–478
Thompson J, Van Furth R (1970) The effect of glucocorticosteroids on the kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med 131:429–442
Van Furth R, Cohn ZA (1968) The origin and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med 128:415–433
Vijeyaratnam GS, Corrin B (1971) Experimental paraquat poisoning: a histological and electron-optical study of the changes in the lung. J Pathol 103:123–129
Volkman A (1966) The origin and turnover of mononuclear cells in peritoneal exudates in rats. J Exp Med 124:241–253
Weiss SJ, Lobuglio AF, Kessler HB (1980) Oxidative mechanisms of monocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:584–587
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Etoh, T., Shioya, S., Ohta, Y. et al. Role of alveolar macrophages in development of paraquat-induced lung injury. Lung 161, 47–55 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02713841
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02713841