Abstract
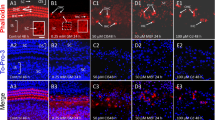
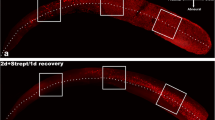
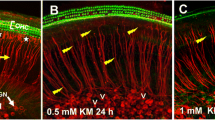
To clarify mechanisms of inner ear cell death induced by aminoglycosides, we used an in situ nick-end labelling method to examine guinea pig vestibular epithelia after chronic systemic treatments with gentamicin to produce apoptosis. Such changes occurred in damaged hair cells, suggesting that this process may be crucial for subsequent repair and cell regeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baroni GS, Marucci L, Benedetti A, Mancini R, Jezequel AM, Orlandi F (1994) Chronic ethanol feeding increases apoptosis and cell proliferation in rat liver. J Hepatol 20:508–513
Bright J, Khar J, Khar A (1994) Apoptosis: programmed cell death in health and disease. Biosci Rep 14:67–81
Dulon D, Zajic G, Aran JM, Schacht J (1989) Aminoglycoside antibiotics impair calcium entry but not viability and motility in isolated cochlear outer hair cells. Neurosci Res 24:338–346
Forge A, Li L, Corwin JT, Nevill G (1993) Ultrastructural evidence for hair cell regeneration in the mammalian inner ear. Science 259:1616–1619
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, BenSasson WA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labelling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–501
Hawkins JE, Johnson LG (1981) Histopathology of cochlear and vestibular ototoxicity in laboratory animals. In: Lerner SA, Matz GJ, Hawkins JE (eds) Aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 175–195
Heron A, Pollard H, Dessi F, Moreau J, Lesbennes F, Ben-Ari Y, Charriam-Mariangue C (1993) Regional variability in DNA fragmentation after global ischemia evidenced by combined histological and gel electrophoresis observations in the rat brain. J Neurochem 61:1973–1976
Hutchin T, Cortopassi G (1994) Proposed molecular and cellular mechanism for aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:2517–2520
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basis biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Lambert PR (1994) Inner ear hair cell regeneration in a mammal: identification of a trigger factor. Laryngoscope 104:701–718
Li L, Nevill G, Forge A (1995) Two modes of hair cell loss from the vestibular sensory epithelia of the guinea pig inner ear. J Comp Neurol 355:405–417
Nakagawa T, Aiba T, Shiotani H, Tomiyama K, Nakai Y (1997) Apoptosis in the normal olfactory epithelium of the adult guinea pig. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (in press)
Pellier V, Astic L (1994) Detection of apoptosis by electron microscopy and in situ labelling in the rat olfactory pit. Neuroreport 5:1429–1432
Potten CS, Meritt A, Hickman J, Hall P, Faranda A (1994) Characterization of radiation-induced apoptosis in the small intestine and its biological implication. Int J Radiat Biol 65:71–78
Rubel EW, Dew LA, Roberson DW (1995) Mammalian vestibular hair cell regeneration. Science 267:701–703
Schacht J (1986) Molecular mechanisms of drug-induced hearing loss. Hear Res 22:297–304
Seale J, Lawson TA, Abbott PJ, Harmon B, Kerr JF (1975) An electron-microscopic study of the model cell death induced by cancer chemotherapeutic agends in population of proliferating normal and neoplastic cells. J Pathol 116:129–138
Sonnenfeld MJ, Jacobs JR (1995) Macrophages and glia participate in the removal of apoptotic neurons from theDrosophila embryonic nervous system. J Comp Neurol 359:644–652
Tayeri H, Lopez I, Honrubia V (1995) Histological evidence for hair cell regeneration after ototoxic cell destruction with local application of gentamicin in the chinchilla crista ampullaris. Hear Res 89:194–202
Warchol ME, Lambert PR, Goldstein BJ, Forge A, Corwin JT (1993) Regenerative proliferation in inner ear sensory epithelia from adult guinea pigs and humans. Science 259:1619–1622
Wersäll J (1981) Structural damage to the organ of Corti and the vestibular epithelia caused by aminoglycoside antibiotics in the guinea pig. In: Lerner SA, Matz GJ, Hawkins JE (eds) Aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 197–214
Wyllie AH (1987) Apoptosis: cell death under homeostatic control. Arch Toxicol [Suppl] 11:3–10
Wyllie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR (1980) Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 68:251–30624
Yamane H, Nakagawa T, Iguchi H, Shibata S, Takayama M, Nishimura K, Nakai Y (1997) In vivo regeneration of vestibular hair cells of guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl] 520:174–177
Yamashita H, Osterle EC (1995) Induction of hair cell proliferation in mammalian inner ear sensory epithelia by transforming growth factor a and epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:3152–3155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakagawa, T., Yamane, H., Shibata, S. et al. Gentamicin ototoxicity induced apoptosis of the vestibular hair cells of guinea pigs. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 254, 9–14 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02630749
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02630749