Abstract
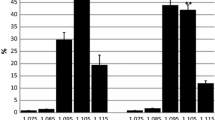
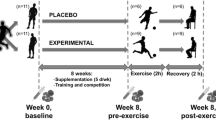
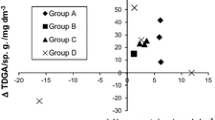
The effect on erythrocyte osmotic fragility of two anabolic agents, widely used to improve physical performance, has been studied. These agents, the steroid derivative, stanozolol, and a quaternary amine,l-carnitine, were administered to rats at rest and while performing running exercises, for 12 weeks. The results show that exercise does not alter the haemolysis curve. Administration of both agents in resting condition does increase the osmotic resistance of the erythrocytes. The combined effect of drug administration and physical exercise further increases the osmotic resistance in the case of stanozolol, presumably due to the steroid-erythrocyte membrane interaction as well as by an erthyropoietic effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn YS, Fernandez LF, Kim Chi, et al. (1989) Danazol therapy renders cells resistant to osmotic lysis. Faseb J 3:157–162
Alen M (1985) Androgenic steroid effects on liver and red cells. Br J Sports Med 19:15–20
Alvertazzi A, Capelli P, Di Paolo B et al. (1982) Endocrine-metabolic effects ofl-carnitine in patients on regular dialysis treatment. Proc EDTA 19:302–307
Avakumov VM, Smirnova TN, Clementeva IV et al. (1988) Pharmacotherapeutic properties of carnitine chloride, a nosteroid anabolic Khimiko-farmatseutichedkii Zh 22(3):379–382
Bauman DH, Ticherson JT, Britt ALL (1988) A comparison of body organ weights physiologic parameters, and pathological changes in target organs of rats given combinations of exercise, anabolic hormone and protein supplementation. Am J Sports Med 16:397–402
Bobyleva-Guarriero V, Iannone A, Bellei M et al. (1988) Effects of single or multiple doses of L-carnitine on liver energetic metabolism of rats forced to run. J Sports Med 28:298–303
Borum PR, Taggart EM (1986) Carnitine nutriture of dialysis patients. J Am Diet Assoc 86:644–647
Carlin JI, Reddan WG, Snajar M et al. (1983) Carnitine metabolism during prolonged exercise and recovery in humans. J Appl Physiol 55:489–495
Carter CH (1965) The anabolic steroid stanozolol. Its evaluation in debilitated children. Clin Pediatr 4:671–680
Chan MK, Varghese Z, Moorhead JF (1981) Lipid abnormalities in uraemia, dialysis and transplantation. Kidney Int 19:625–637
Cooper RA, Jandl JH (1968) Bile salt and cholesterol in the pathogenesis of target cells in obstructive jaundice. J Clin Invest 47:809–822
Detraglia M, Cook FB, Stasiw DM et al. (1973) Erythrocyte fragility in aging, Biochem Biophys Acta 354:213–219
Di Marco V, Ginardi V, Dell'Arria D et al. (1982) La Carnina nel trattamento dei crampi muscolari nei pazienti in emodialisi periodica. Policlinico Sed Med 89:104–110
Goa KL, Brogden RN (1987)l-Carnitine. Drugs 34:1–24
Greig L, Finch KM, Jones AA et al. (1987) The effect of oral supplementation withl-carnitine on maximum and submaximum exercise capacity. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:457–460
Ji LL, Miller RH, Nagle FJ et al. (1987) Amino acid metabolism during exercise in trained rats. The potential role of carnitine in the metabolism fate of branched-chain amino-acids. Metabolism 36:748–752
Kaya H, Saito T (1985) Effect of progesterone and its 17-hydroxy derivative on human erythrocyte. Jpn J Pharmacol 39:299–306
Kiraly CL (1988) Androgenic anabolic steroid effects on serum and skin surface lipids, on red cells and on liver enzymes. Int J Sports Med 9:249–252
Marconi C, Sassi GG, Carpinelly A et al. (1985) Effects ofl-carnitine loading on the anaerobic and aerobic performance of endurance athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:131–135
Michiels M, Hendriks R, Heykants J, et al. (1982) The pharmacokinetics of mebendazole and flubendazole in animals and man. Arch. Int Pharmacodyn 256:180–191
Mioli BV, Tarchini R, Boggi R (1982) Use of DL- andl-carnitine in uraemic patients on intermittent haemodialysis. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 2:143–148
Murad F, Haynes RC (1985) Androgens. In: Goodman, Gilman's (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. Macmillan, New York, pp 1440–1458
Ross JH, Attwood EC (1984) Severe repetitive exercise and haematological status. Postgrad Med J 60:454–457
Seeman P (1966) Erythrocyte membrane stabilization by steroids and alcohols; a possible model for anaesthesia. Biochem Pharmacol 15:1632–1637
Simon TL (1988) Haematology of sports. In: Appenzeller O (ed) Sports medicine, 3rd edn., Urban & Schwarzenberg, Baltimore, pp 257–273
Streuli RA, Kanofsky JR, Gunn RB et al. (1981) Diminished osmotic fragility of human erythrocytes following the membrane insertion of oxygenated sterol compound. Blood 58;317–325
Vacha GM, Giorcelli G, Siliprandi N et al. (1983) Favourable effects ofl-carnitine treatment on hypertrylglyceremia in haemodialysis patients: decisive role of low levels of high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol. Am J Clin Nutr 38:532–540
Vacha GM, Corsi M, Giorcelli G et al. (1985) Serum and musclel-carnitine levels in haemodialyzed patients during and after long terml-carnitine treatment. Curr Ther Res 37:505–516
Warner C, Horl WL (1986) Potential role of carnitine in patients with renal insufficiency. Klin Wochenschr 64:579–586
Watanabe H, Kobayashyi H, Yamakazi N (1989) Effects of long-chain acyl carnitine on membrane fluidity of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 980:315–318
Weschler A, Aviram M, Levin M et al. (1984) High dose ofl-carnitine increases platelet aggregation and plasma triglyceride levels of uraemic patients on haemodialysis. Nephron 38:120–124
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayon, J.E., Alvarez, A.I., Barrio, J.P. et al. Effects of stanozolol and L-carnitine on erythrocyte osmotic fragility during aerobic exercise in rats. Comparative Haematology International 3, 196–200 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02341966
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02341966