Abstract
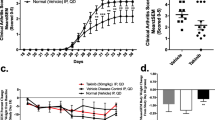
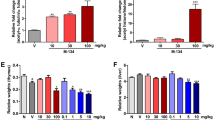
We previously demonstrated that treatments with rIL-1B accelerated the onset and progression of CIA in mice. In the present study, it was observed that IL-1 also enhanced the development of CIA in rats. Like the mouse model, maximal incidence (80–100%) of arthritis occurred within 7 days after the first treatment with IL-1 in rats. Thus, the acceleration of CIA by IL-1 (IL-1 CIA) may be an improved model for the rapid screening of anti-inflammatory and/or anti-arthritic drugs. As a first step to determining the utility of the IL-1 CIA model as a drug screen, we examined the ability of various known anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic drugs to modify the IL-1 mediated enhancement of CIA in both rats and mice. The results of these studies showed that when analyzed in the IL-1 CIA model, rats and mice exhibited differences in their responses to several of these drugs. For example, dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, various non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) as well as methotrexate were found active in the IL-1 CIA of rats. By contrast, the NSAIDs were found to be less effective in suppressing the IL-1 accelerated disease in mice. In both rats and mice, cyclosporine A and several disease modifying anti-arthritic drugs failed to the prevent the development of CIA that was potentiated by IL-1. Thus, in the IL-1 CIA model NSAIDs appeared to be less active in mice than rats. In conclusion, because of the shorter latent period required for the development of arthritis in the IL-1 treated animals, the IL-1 accelerated CIA model in both mice and rats may be useful for screening anti-inflammatory or anti-arthritic compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. Courtenay, M. J. Dallman, A. D. Dayan, A. Marten, and B. Mosedale,Immunization against heterologous type II collagen induces arthritis in mice. Nature283, 666–668 (1980).
D. E. Trentham, A. S. Townes, and A. H. Kang,Autoimmunity to type II collagen: an experimental model of arthritis. J. Exp. Med.146, 857–868.
K. Terato, R. Hashida, K. Miyamoto, T. Morimoto, Y. Kata, S. Kobayashi, T. Tajima, S. Otake, H. Horni, and Y. Nagai,Histological, immunological, and biochemical studies on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Biomed. Res.3, 495–523 (1982).
P. H. Wooley, H. S. Luthra, J. M. Stuart, and C. S. David,Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Major histocompatibility complex (I region) linkage and antibody correlates. J. Exp. Med.154, 688–700 (1981).
J. M. Stuart, A. S. Townes, and A. H. Kang,Nature and specificity of the immune responses to collagen in type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J. Clin. Invest.69, 673–683 (1982).
J. M. Stuart, M. A. Cremer, A. H. Kang and A. S. Townes,Collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Arth and Rheum.22, 1344–1351 (1979).
I. Gery, and B. H. Waksman,Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte responses to mitogens. II. The cellular source of potentiating mediator(s). J. Exp. Med.136, 143–155 (1972).
L. B. Lachman, M. P. Hacker, G. T. Blyden, and R. E. Handschuhmacher,Preparation of lymphocyte-activating factor from continous murine macrophage cell line. Cell Immunol34, 416–419 (1977).
D. N. Saunder, C. S. Carter, S. I. Katz, and J. J. Oppenheim,Epidermal cell production of thymocyte activating factor (ETAF). J. Invest. Dermatol.79, 34–39 (1982).
A. Fontana, F. Kreistensen, R. Dibs, D. Gemsa and E. Weber,Production of postaglandin E and an interleukin-1 like factor by cultured astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. J. Immunol.129, 2413–2419 (1982).
K. Tiku, M. L. Tiku, and S. L. Skosey,Interleukin-1 production by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J. Immunol.136, 3677–3685 (1986).
B. Tarkakovsky, E. J. Kovac, L. Takacs, and S. Duram,T cell clone producing an IL-1 like activity after stimulation by antigen-presenting B cells. J. Immunol.137, 160–166 (1986).
C. A. Dinarello, N. P. Goldin, and S. M. Wolff,Demonstration and characterization of two distinct human leukocytic pyrogens. J. Exp. Med.139, 1369–1381 (1974).
J. D. Sipe, S. N. Vogel, J. L. Ryan, K. P. W. J. McAdam and D. L. Rosenstreich,Detection of a mediator derived from endotoxin-stimulated macrophages that induces the acute phase serum amyloid A response in mice. J. Exp. Med.150, 597–606 (1979).
T. R. Ulich, J. del Castillo, M. Keyes, G. A. Granger, and R. X. Ni,Kinetics and mechanisms of recombinant human interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-a induced changes in circulating number of neutrophils and lymphocytes. J. Immunol.139, 3406–3415 (1988).
I. Gery, R. K. Gerson, and B. H. Waksman,Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte responses to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J. Exp. Med.136, 128–142 (1972).
J. Kaye, S. Gillis, S. B. Mizel, E. M. Shevach, T. R. Male, C. A. Dinarello, L. B. Lachman, and C. S. Janeway, Jr.,Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin-2. J. Immunol.133, 1339–1345 (1984).
S. Chiplunkar, J. Langhorne, and S. H. E. Kaufmann,Stimulation of B cell growth and differentation by murine recombinant interleukin-1. J. Immunol.137, 3748–3752 (1986).
J. R. Zucali, C. A. Dinarello, D. J. Oblon, M. A. Gross, L. Anderson, and R. S. Weiner,Interleukin-1 stimulates fibroblasts to produce granulocytes-macrophage colony-stimulating activity and prostaglandin E2. J. Clin Invest.77, 1857–1863 (1986).
S. B. Mizel, J.-M. Dayer, S. M. Krane, and S. E. Mergenhagen,Stimulation of rheumatoid synovial cell collagenase and prostaglandin production by partially purified lymphocyte activating factor (interleukin-1). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA78, 2474–2477 (1981).
J. Sakatvala, S. J. Sarsfield, and Y. J. Townsend,Pig interleukin-1: purification of two immunologically different leukocyte proteins that cause cartilage resorption, lymphocyte activation and fever. J. Exp. Med.162, 1208–1227 (1985).
T. Krakauer, J. J. Oppenheim and H. E. Jasin,Human interleukin-1 mediates cartilage matarix degradation. Cell Immunol.91, 92–99 (1985).
F. E. Dewhirst, P. P. Stashenko, J. E. Mole and T. Tsurumachi,Purification and partial sequence of human osteoclast activating factor: identity with interleukin-1B. J. Immunol.135, 2562–2568 (1985).
J. T. Hom, A. M. Bendele, and D. G. Carlson,In vivo administration with IL-1 accelerates the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J. Immunol.141, 834–841 (1988).
L. M. Killar and C. J. Dunn,Interleukin-1 potentiates the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Clin. Sci.76, 535–538 (1989).
E. J. Miller and R. K. Rhodes,Preparation and characterization of the different types of collagen. InMethods in enzymology vol 82. (Eds. S. P. Colowick and N. O. Kaplan) pp. 33–65 New York, USA, 1982.
L. B. Lachman, C. A. Dinarello, N. D. LLansa, and I. J. Fidler,Natural and recombinant human interleukin-1B is cytotoxic to human melanoma cells. J. Immunol.138, 3098–3102 (1986).
A. E. Sloboda, J. E. Birnbaum, A. L. Oronsky and S. Kerwar,Studies on type II collagen-induced polyarthritis in rats. Arthritis and Rheum.24, 616–624 (1981).
S. A. Jones, A. J. Kennedy and N. A. Roberts,Assessment of drugs for activity in established type II collagen arthritis. Agents and Action12, 650–656 (1982).
S. A. Stimpson, F. G. Dalldorf, I. G. Otterness, and J. H. Schwab,Exacerbation of arthritis by IL-1 in rat joints previously injured by peptidoglycan-polysaccharide. J. Immunol140, 2964–2969 (1988).
J. T. Hom, H. Cole and A. M. Bendele,Interleukin-1 enhances the development of spontaneous arthritis in MRL/lpr mice. Clin Immunol and Immunopath55, 109–119 (1990).
N. D. Staite, K. A. Richard, D. G. Aspar, K. A. Franz, L. A. Galinet and C. J. Dunn,Induction of an acute erosive monarticular arthritis in mice by interleukin-1 and methylated bovine serum albumin. Arthritis and Rheumatism33, 253–260 (1990).
K. Phadke, J. Caroll, and S. Nanda,Effects of various anti-inflammatory drugs on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Clin. Exp. Immunol.47, 579–586 (1982).
K. Yamaki, H. Nakagawa, and S. Tsurufuji,Inhibitory effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on type II collage induced arthritis in rats. Annals of the Rheum Diseases46, 543–548 (1987).
K. Phadke, R. L. Fouts, J. E. Parrish and L. D. Butler,Evaluation of the effects of various anti-arthritic drugs on type II collagen-induced mouse arthritis model. Immunopharm10, 51–60 (1985).
W. Paska, K. J. McDonald and M. Croft,Studies on type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Agents and Actions18, 413–420 (1986).
N. Kaibara, T. Hotokebuchi, K. Takagishi and I. Katsuki,Paradoxical effects of cyclosporin A on collagen arthritis in rats. J. Exp. Med.158, 2007–2015 (1983).
B. Henderson, N. Staines, I. Burrain and J. H. Cox,The anti-arthritic and immunosuppressive effects of cyclosporine on arthritis induced in the rat by type II collagen. Clin Exp Immunol57, 51–56 (1984).
K. Takagishi, N. Kaibara, T. Hotokebuchi, C. Arita, M. Morinaga, and K. Arai,Effects of cyclosporin on collagen induced arthritis in mice. Annals of Rheum Disease45, 339–344 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hom, J.T., Gliszczynski, V.L., Cole, H.W. et al. Interleukin 1 mediated acceleration of type II collagen-induced arthritis: Effects of anti-inflammatory or anti-arthritic drugs. Agents and Actions 33, 300–309 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01986577
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01986577