Abstract
Patients with solitary thyroid nodules that are benign on aspiration biopsy are often treated nonsurgically. To find out if thyroxine therapy is effective, 74 patients were randomized to receive levothyroxine treatment or nothing. There were 8 males and 66 females. Their mean age was 39 years. The mean nodule size was 3.6 cm and the mean nodule duration was 11 months. All patients had normal serum thyroxine and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels, and positive thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) tests. The dose of thyroxine was adjusted until the TRH test was negative. Patients were followed at 6-month intervals in the first 2 years and yearly thereafter, with measurement of the nodule diameter. The mean follow-up period was 1.5 years.
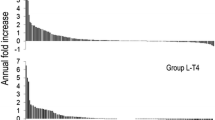
In the 37 patients receiving thyroxine therapy, 8 had disappearance of nodules, 6 had greater than 50% reduction in nodule size. In 19, the nodules were unchanged and in 4, the nodules were enlarged. In the 37 patients receiving no drug, 8 had disappearance of nodules, 5 had greater than a 50% reduction in nodule size, 17 had nodules unchanged, and 7 had enlarged nodules (p >0.9). The mean reduction in nodule diameter at various follow-up periods was greater in the thyroxine group, but the difference did not reach statistical significance. Carcinoma was found in 1 patient in each group and both of them experienced nodule enlargement.
We conclude that an adequate suppressive dose of levothyroxine does not alter the natural course of benign solitary thyroid nodules. An enlargement of the nodule or a change in its consistency should be further investigated to exclude malignancy.
Résumé
Les patients présentant un nodule thyroïdien solitaire bénin à la biopsie par aiguille ne sont souvent pas traités chirurgicalement. Pour évaluer 1'efficacité de la thyroxine dans ces cas, 74 patients ont été randomisés, recevant de la lévothyroxine ou rien. Il y avait 8 hommes et 66 femmes; 1'âge moyen était de 39 ans. La taille moyenne du nodule était de 3.6 cm, et 1'évolution moyenne était de 11 mois. Tous les patients avaient un taux sérique de thyroxine et de TSH normal; le test de la TRH était normal. La thyroxine a été dosée jusqu'à obtenir une réponse négative à la TRH. Les patients étaient suivis à intervalles de 6 mois pendant 2 ans puis une fois par an. Le diamètre du nodule etait mesuré à chaque examen. Le suivi moyen était de 1.5 ans.
Pour 37 patients qui recevaient de la thyroxine, le nodule a disparu chez 8 et s'est réduit de plus de 50% chez 6. Le nodule était inchangé chez 19 et a continué d'évoluer chez 4. Parmi les 37 patients n'ayant pas reçu de thyroxine, le nodule a disparu chez 8, s'est réduit en taille de plus de 50% chez 5, est resté inchangé chez 17 et a augmenté de volume chez 7 (p > 0.9). La réduction moyenne du diamètre du nodule était supérieure chez les patients dans le groupe thyroxine mais cette différence n'était pas statistiquement significative. Dans chaque groupe, il y avait un cancer, et dans les deux cas, le nodule avait grossi.
Nous concluons que la lévothyroxine aux doses suppressives ne modifie pas 1'évolution des nodules solitaires de la thyroïde. Une augmentation du volume ou une modification dans sa consistance demande des examens complémentaires pour exclure une évolution maligne.
Resumen
Los pacientes con nódulos tiroideos solitarios que demuestran ser benignos en la biopsia por aspiración frecuentemente reciben tratamiento no operatorio. Con el objeto de determinar si el tratamiento con tiroxina es efectivo, se estudiaron 74 pacientes mediante aleatorización: un grupo recibió levotiroxina y el otro ninguna terapia endocrina. El grupo tuvo 8 hombres y 66 mujeres; la edad promedio fue 39 años. El tamaño promedio de los nódulos fue 3.6 cm y el promedio de evolución del nódulo fue 11 meses. La totalidad de los pacientes exhibió niveles séricos de tiroxina y de TSH normales, y pruebas normales de TRH. La dosis de tiroxina fue ajustada hasta que la prueba de TRH resultó negativa. Los pacientes fueron seguidos a intervalos de 6 meses en el curso de los primeros 2 años, y anualmente de ahí en adelante, registrando en cada visita el diámetro del nódulo. El promedio del seguimiento fue 1.5 años.
En el grupo de 37 pacientes tratados con tiroxina, 8 exhibieron desaparición de los nódulos y 6 reducción de más del 50% en el tamaño del nódulo; en 19 los nódulos no demostraron cambio y en 4 aumentaron de tamaño. En los 37 pacientes que no recibieron terapia, 8 demostraron desaparición del nódulo y 5 reduccción de más del 50% en su tamaño; en 17 el nódulo no modificó el tamaño y en 7 el nódulo se agrandó (p > 0.9). La reducción promedio en el diámetro del nódulo observada en los diferentes períodos de seguimiento fue mayor en el grupo tratado con tiroxina, pero la diferencia no alcanzó significancia estadística. Se halló carcinoma en un paciente en cada grupo, y ambos mostraron crecimiento del nódulo.
Hemos concluído que una dosis supresiva de levotiroxina no altera la evolución natural de los nódulos tiroideos benignos. El crecimiento del nódulo o un cambio en su consistencia debe ser investigado para excluir posible malignidad.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson, N.W.: Current diagnostic techniques for single thyroid nodules. Curr. Surg.40:255, 1983
Ashcraft, M.W., van Herle, A.J.: Management of thyroid nodules. II. Scanning techniques, thyroid suppressive therapy, and fine needle aspiration. Head Neck Surg.3:297, 1981
Gharib, H., James, E.M., Charboneau, J.W., Naessens, J.M., Offord, K.P., Gorman, C.A.: Suppressive therapy with levothyroxine for solitary thyroid nodules. N. Engl. J. Med.317:70, 1987
Greenspan, F.S.: Thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer. West. J. Med.121:359, 1974
Thomas, Jr., C.G., Buckwalter, J.A., Staab, E.V., Kerr, C.Y.: Evaluation of dominant thyroid masses. Ann. Surg.183:463, 1976
Burrow, G.N., Mujtaba, Q., LiVolsi, V., Cornog, J.: The incidence of carcinoma in solitary “cold” thyroid nodules. Yale J. Biol. Med.51:13, 1978
Blum, M., Rothschild, M.: Improved nonoperative diagnosis of the solitary “cold” thyroid nodule: Surgical selection based on risk factors and three months of suppression. J.A.M.A.243:242, 1980
Getaz, E.P., Shimaoka, K., Razack, M., Friedman, M., Rao, U.: Suppressive therapy for postirradiation thyroid nodules. Can. J. Surg.23:558, 1980
Liechty, R.D., Stoffel, P.T., Zimmerman, D.E., Silverberg, S.G.: Solitary thyroid nodules. Arch. Surg.112:59, 1977
Reeve, T.S., Delbridge, L., Sloan, D., Crummer, P.: The impact of fine-needle aspiration biopsy on surgery for single thyroid nodules. Med. J. Aust.145:308, 1986
Hamberger, B., Gharib, H., Melton, L.J., Goellner, J.R., Zinsmeister, A.R.: Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules. Am. J. Med.73:381, 1982
Block, M.A., Miller, J.M., Kini, S.R.: The potential impact of needle biopsy on surgery for thyroid nodules. World J. Surg.4:737, 1980
Lo Gerfo, P., Starker, P., Weber, C., Moore, D., Feind, C.: Incidence of cancer in surgically treated thyroid nodules based on method of selection. Surgery98:1197, 1985
Taylor, S.: Physiologic considerations in the genesis and management of nodular goiter. Am. J. Med.20:698, 1956
Clark, O.H.: TSH suppression in the management of thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer. World J. Surg.5:39, 1981
Hoffman, D.P., Surks, M.I., Oppenheimer, J.H., Weitzman, E.D.: Response to thyrotropin releasing hormone: An objective criterion for the adequacy of thyrotropin suppression therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.44:892, 1977
Bartalena, L., Martino, E., Pacchiarotti, A., Grasso, L., Aghinilombardi, F., Buratti, L., Bambini, G., Breccia, M., Pinchera, A.: Factors affecting suppression of endogenous thyrotropin secretion by thyroxine treatment: Retrospective analysis in athyreotic and goitrous patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.64:849, 1987
Gordon, S.J., Pita, J.C., Watts, N.B., Wexler, C.B., Hamburger, J.I., Galli, C.: Suppressive therapy with levothyroxine for solitary thyroid nodules. N. Engl. J. Med.317:1663, 1987
Ramelli, F., Studer, H., Bruggisser, D.: Pathogenesis of thyroid nodules in multinodular goiter. Am. J. Pathol.109:215, 1982
Peter, H.J., Gerber, H., Studer, H., Smeds, S.: Pathogenesis of heterogeneity in human multinodular goiter. J. Clin. Invest.76:1992, 1985
Drexhage, H.A., Bottazzo, G.F., Doniach, D., Bitensky, L., Chayen, G.F.: Evidence for thyroid-growth-stimulating immunoglobulins in some goitrous thyroid diseases. Lancet2:287, 1980
Duh, Q.Y., Gum, E.T., Gerend, P.L., Raper, S.E., Clark, C.H.: Epidermal growth factor receptors in normal and neoplastic thyroid tissue. Surgery98:1000, 1985
Westermark, K.F., Karlson, L., Ericson, L.E., Westermark, B.: Epidermal growth factor: A regulator of thyroid growth and function in vitro. In Thyroglobulin—The Prothyroid Hormone. Progress in Endocrine Research and Therapy, vol. 2, M.C. Eggo, G.N. Burrow, editors, New York, Raven Press, 1985, pp. 255–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Research and Conference Grants and Lee Wing Tat Research Fund of the University of Hong Kong.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheung, P.S.Y., Lee, J.M.H. & Boey, J.H. Thyroxine suppressive therapy of benign solitary thyroid nodules: A prospective randomized study. World J. Surg. 13, 818–821 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01658447
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01658447