Summary
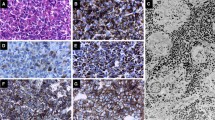
In a series of 39 adenomas from patients with the clinical hyperfunction syndrome of acromegaly and in one from a case of prolactinoma we studied the mRNA expression of growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL) andβ-human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) by using the technique of in situ hybridization (ISH). This technique allows the direct identification and localization of cells expressing mRNA and thus synthesizing the respective hormone. The aim of our study was to demonstrate the frequent co-expression of PRL mRNA and HCG mRNA in pituitary adenomas of acromegalic patients. Probes for ISH of the above-mentioned hormones were obtained by subcloning cDNA fragments into pGEM plasmids. Subsequent Sp6-polymerase catalysed in vitro transcription with35S-CTP revealed radio-labelled single-stranded antisense RNA probes [the probe forβHCG detectsβ-luteinizing hormone (βLH) simultaneously because of a sequence homology of 90%]. To localize the labelled hybrids, autoradiography was carried out. Light microscopical evaluation of the tissue sections demonstrated positive signals in all cases for GH, in 80% of cases for PRL and in 25% of cases for HCG [LH] mRNA. The comparison of mRNA content shown by ISH with immunocytochemical (ICC) hormone detection revaled that in all cases the detection of GH corresponded to GH mRNA content of the cells. For PRL and HCG [LH] positive mRNA detection (ISH) and negative hormone detection (ICC) occurred in some cases (PRL 17.5%; HCG [LH] 15%). In contrast, negative mRNA detection (ISH) and positive hormone content (ICC) was also demonstrated (PRL 5%; HCG [LH] 37.5%). The remaining adenomas showed both mRNA and the respective hormone, as well as negative ISH and ICC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkan AL (1989) Acromegaly. Diagnosis and therapy. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 18:277–310
Brinboim HC, Doly J (1979) A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 7:1513–1523
Cooke NE, Coit D, Shine J, Baxter JD, Martial JA (1981) Human prolactin cDNA structural analysis and evolutionary comparisons. J Biol Chem 256:4007–4016
Fehr S, Ivel R, Schams D, Fields M, Richter D (1987) Expression of the oxytocin gene in the large cells of the bovine corpus luteum. FEBS Lett 210:45–50
Fiddes JC, Talmadge K (1984) Structure, expression, and evolution of the genes for the human glycoprotein hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res 40:43–78
Goeddel DV, Heynecker HL, Hozumi T, Arentzen R, Itakura K, Yansura DG, Ross M, Miozari G, Crea R, Seeburg PH (1979) Direct expression inEscherichia coli of a DNA sequence coding for human growth hormone. Nature 281:544–548
Grody WW, Cheng L, Lewin KJ (1987) Application of in situ DNA hybridization technology to diagnostic surgical pathology. Pathol Annu 22:151–175
Hanahan D (1983) Studies of transformation ofE. coli with plasmid. J Mol Biol 155:557–580
Höfler H (1987) What's new in “in situ hybridization”. Pathol Res Pract 182:421–430
Jameson JL, Lindell CM, Habener JF (1987) Gonadotropin and thyrotropinα- andβ-subunit gene expression in normal and neoplastic tissues characterized using specific messenger ribonucleic acid hybridization probes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 64:319–327
Jameson JL, Lindell CM, Hsu DW, Habener JF, Ridgeway EC (1987) Expression of chorionic gonadotropin-β-like messenger ribonucleic acid in anα-subunit-secreting pituitary adenoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 62:1271–1278
Kanie N, Kageyama N, Kuwayama A, Nakane T, Watanabe M, Kawaoi A (1983) Pituitary adenomas in acromegalic patients: an immunohistochemical and endocrinological study with special reference to prolactin-secreting adenoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 57:1093–1101
Klibanski A, Zervas NT, Kovacs K, Ridgway EC (1987) Clinically silent hypersecretion of growth hormone in patients with pituitary tumors. J Neurosurg 66:806–811
Klibanski A, Jameson JL, Biller BMK, Crowley WF Jr, Zervas NT, Rivier J, Vale WW, Bikkal H (1989) Gonadotropin andα-subunit responses to chronic gonadotropin-releasing hormone analog administration in patients with glycoprotein hormone-secreting pituitary tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 68:81–86
Levy A, Lightman SL (1988a) Quantiative in-situ hybridization histochemistry studies on growth hormone (GH) gene expression in acromegalic somatotrophs. Effects of somatostatin, GH-releasing factor and cortisol. J Mol Endocrinol 1:19–26
Levy A, Lightman SL (1988b) Quantitative in-situ hybridization histochemistry of anterior pituitary hormone mRNA species in human pituitary adenomas. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 119:397–404
Lloyd RV (1987) Use of molecular probes in the study of endocrine diseases. Hum Pathol 18:1199–1211
Lloyd RV, Cano M, Chandler WF, Barkan AL, Horvath E, Kovacs K (1989) Human growth hormone and prolactin secreting pituitary adenomas analyzed by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol 134:605–613
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Melmed S (1990) Acromegaly. N Engl J Med 322:966–977
Miura M, Matsukado Y, Kodama T, Mihara Y (1985) Clinical and histopathological characteristics of gonadotropin-producing pituitary adenomas. J Neurosurg 62:376–382
Mulcahy SS, Jaffe RB (1988) Detection of a potential progenitor cell in the human fetal pituitary that secretes both growth hormone and prolactin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 66:24–32
Penschow JD, Haralambidis J, Darlinr DE, Darby IA, Wintour EM, Tregear GW, Coghlan JP (1987) Hybridization histochemistry. Experientia 43:741–750
Pixley S, Weiss M, Melmed S (1987) Identification of human growth hormone messenger ribonucleic acid in pituitary adenoma cells by in situ hybridization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 65:575–580
Rentrop M, Knapp B, Winter H, Schweizer J (1986) Aminoalkylsilane-treated glass slides as support for in situ hybridization of keratin cDNAs to frozen tissue sections under varying fixation and pretreatment conditions. Histochem J 18:271–276
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Colson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Scheithauer BW, Kovacs K, Randall RV, Horvath E, Laws ER Jr (1986) Pathology of excessive production of growth hormone. Clin Endocrinol Metab 15:655–681
Snyder PJ, Bashey HM, Kim SU, Chappel SC (1984) Secretion of uncombined subunits of luteinizing hormone by gonadotroph cell adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 59:1169–1175
Talmadge K, Vamvakopoulos NC, Fiddes JC (1984) Evolution of the genes for theβ-subunits of human chorionic gonadotropin and luteinizing hormone. Nature 307:37–40
Uhlig H (1991) Nachweis von STH-, Prolaktin- undβ-HCG-Genexpression in STH-bildenden Hypophysenadenomen bei Akromegalie durch in situ-Hybridisierung. Thesis, University of Hamburg
Wilson MC, Higgins GA (1989) In situ hybridization. In: Boulton AA, Baker GB, Campagnoni AT (eds) Neuromethods, vol 16. Molecular neurobiological techniques. Human Press, Clifton, NY, pp 239–284
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uhlig, H., Saeger, W., Fehr, S. et al. Detection of growth hormone, prolactin and human β-chorionic gonadotropin messenger RNA in growth-hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas by in situ hybridization. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 418, 539–546 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01606505
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01606505