Abstract
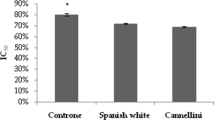
Natto is a traditional Japenese fermented food made by fermenting boiled soy beans withBacillus natto. Its contents of inhibitors against the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE, EC3.4.15.1) were investigated. Relatively strong inhibitory activity (IC50:0.4 mg/ml, 11.8 inhibition units/g natto) was detected in natto extracts and the inhibitory activity observed in the viscous fraction was more potent than in the bean extract. Two groups of inhibitors in the viscous material, high and low molecular weight inhibitors, were resolved by dialysis test. The inhibitor of high molecular weight was a protein with low IC50 value (0.12 mg/ml). The two types of low molecular weight inhibitors were detected in ethanol extracts (IC50: 0.53 mg/ml and 0.95 mg/ml) and they were found to be stable over a wide range of pH and temperature up to 100°C. They were different in the mode of ACE inhibition. One is competitive, and the other noncompetitive against the hydrolysis of Bz-Gly-His-Leu by ACE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith-Vaniz GT (1970) Diet-induced hypertension and cardiovascular lesions in mice. Yale J Bio Med 43: 61–70.
Wynn A (1987) Inequalities in nutrition. Nutr Health 5: 79–94.
Nestle PJ (1989) Current strategies for atherosclerosis and lowering cholesterol. Clin Exp Hypertens [A]11: 915–925.
Kim S, Yamamoto K (1992) The in vivo role of renin-angiotensin system. Cell Science 8: 146–151.
Hayashi U, Nagao K, Tosa Y, Yoshioka Y (1977) Natto no Eiyoka ni Kansuru Jikkenteki Kenkyu. Natto Kagaku Kenkyu Kaishi 1: 85–93.
Cushman DW, Cheng HS (1971) Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochemical Pharmacol 20: 1637–1648.
Lineweaver H, Burk D (1934) Determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J Am Chem Soc 56: 658–666.
Ohkubo K (1992) Natto. In: Yamauchi F, Ohkubo K, eds. Daizu no Kagaku. Tokyo Asakurashoten, pp 117–123.
Fujii H (1963) On the formation of mucilage byBacillus natto, Part III: Chemical constituents of mucilage in natto (1). Nippon Nogei Kagaku Kaishi 37: 407–411.
Fujii H (1963) On the formation of mucilage byBacillus natto, Part IV: Chemical constituents of mucilage in natto (2). Nippon Nogei Kagaku Kaishi 37: 474–477.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okamoto, A., Hanagata, H., Kawamura, Y. et al. Anti-hypertensive substances in fermented soybean, natto. Plant Food Hum Nutr 47, 39–47 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01088165
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01088165