Abstract
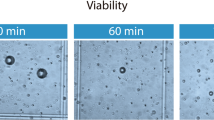
The results of transplantation of free autologous fat obtained by blunt syringe suction lipectomy are unpredictable. We examined if adipose tissue viability is compromised by using syringe suction lipectomy and by infiltration of the tissue with local anesthetics. As reference, we used adipose tissue samples excised during elective surgery. Fat obtained intraoperatively and by lipectomy was digested with collagenase to isolate adipocytes. The mechanical damage associated with sample handling and cell isolation in both procedures was similar and did not exceed 6% of the total cell mass. In addition, cells isolated from intraoperative and lipectomy samples did not differ functionally, responded similarly to insulin stimulation of glucose transport and epinephrine-stimulated lipolysis, and retained the same growth pattern in culture. Since during fat transplantation the graft is exposed to local anesthetics at both the donor and the recipient sites, we reexamined adipocyte function in the presence of lidocaine. Lidocaine potently inhibited glucose transport and lipolysis in adipocytes and their growth in culture. That effect, however, persisted only as long as lidocaine was present; after washing, the cells were able to fully regain their function and growth regardless of whether the exposure was as short as 30 minutes or as long as 10 days. These results indicate that adipose tissue obtained by syringe lipectomy consists of fully viable and functional adipocytes, but local anesthetics may halt their metabolism and growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arner P, Arner O, Ostman J: The effect of local anesthetic agents on lipolysis by human adipose tissue. Life Sci 13:161, 1973
Arner P, Bolinder J, Hellmer J, Engfeldt P: Studies on human fat cell metabolism in small adipose tissue samples. In: Larner J, Pohl S (eds): Methods in Diabetes Research, Vol. II, Clinical Methods. New York: Wiley, 1984, p 233
Chajchir A, Benzaquen I, Wexler E, Arellano A: Fat injection. Aesth Plast Surg 14:127, 1990
Eggstein M, Kreutz FH: Eine neue Bestimmung der Neutralfette im Blutserum und Gewebe. Klin Wschr 44:262, 1966
Ersek RA: Transplantation of purified autologous fat: a 3-year follow-up is disappointing. Plast Reconstr Surg 87:219,1991
Gormley DE, Eremia S: Quantitative assessment of augmentation therapy. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 16: 1147, 1990
Horl HW, Feller AM, Biemer E: Technique for liposuction fat reimplantation and long-term volume evaluation by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Plast Surg 26:248, 1991
Kolaczynski JW, Taskinen M-R, Hilden H, Kiviluoto T, Cantell K, Koivisto VA: Effects of interferon alpha on insulin binding and glucose transport in human adipocytes. Eur J Clin Invest 22:292, 1992
Kononas TC, Bucky LP, Hurley C, May JW: The fate of suctioned and surgically removed fat after reimplantation for soft-tissue augmentation: a volumetric and histologic study in the rabbit. Plast Reconstr Surg 91:763, 1993
Lewis CA: The current status of autologous fat grafting. Aesth Plast Surg 17:109, 1993
Linde B, Hjemdahl, Freyschuss U, Juhlin-Dannfelt A: Adipose tissue and skeletal muscle blood flow during metabolic stress. Am J Physiol (Endocrine Metab) 19:E12, 1989
Peer LA: Loss of weight and volume in human fat grafts: With postulation of a “cell survival theory.” Plast Reconstr Surg 5:217, 1950
Rodbell M: Metabolism of isolated fat cells. I. Effects of hormones on glucose metabolism and lipolysis. J Biol Chem 239:375, 1964
Rosell S, Belfrage E: Blood circulation in adipose tissue. Physiol Rev 59:1078, 1979
Sugihara H, Yonemitsu N, Miyabara S, Yun K: Primary cultures of unilocular fat cells: characteristics of growth in vitro and changes in differentiation properties. Differentiation 31:42, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, J.H., Kolaczynski, J.W., Morales, L.M. et al. Viability of fat obtained by syringe suction lipectomy: effects of local anesthesia with lidocaine. Aesth. Plast. Surg. 19, 335–339 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451659
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451659