Summary
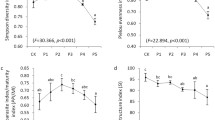
The abundance of nematodes was investigated in agricultural plots treated in three different ways, the first with no treatment, the second with 300 m3 ha-1 a-1 raw sewage sludge and the third with 300 m3 ha-1 a-1 sewage sludge with the addition of heavy metals. The nematodes were determined down to the genus and were assigned to five feeding groups. Total nematode numbers were highest in the site treated with sewage sludge and heavy metals. The smallest total numbers were found in the control site. The plant-feeding nematode genera showed different patterns of abundance depending on the sludge treatment and heavy metal content. For the mycophagic and bacteriophagic nematodes, numbers increased with the amount of sludge, especially in the sites with a higher heavy metal content. The family Rhabditidae was the most numerous group in the sludge plus heavy metals treatment. In contrast to these findings, the omnivorous nematodes were very rare in the sludgetreated plots and were completely absent in plots treated with sludge plus heavy metals, whereas predatory nematodes were numerous only after the application of sludge alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisessar S (1982) Effects of heavy metals on microorganisms in soil near a secondary lead smelter. Water Soil Air Pollut 17:305–308
Castagnone-Sereno P, Kermarrec A, Clairon M, Anais A (1988) Effets depresseure d'un apport de boue residuaire sur le parasitisme de Meloidogyne incognita. Meded Fac Landbouwwet Rijksuniv Gent 58:879–883
Clarke AJ, Shepherd AM (1966) Inorganic ions and the hatching of Heterodera spp. Ann Appl Biol 58:497–508
Dmowska E, Kozlowska J (1988) Communities of nematodes in soil treated with semi-liquid manure. Pedobiologia 32:323–330
Dreger K (1989) Dungfliegen (Sphaeroceriden) auf klärschlammgedüngten Feldern. Staatsexamens-Arbeit, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Germany
Dreger K (1990) Die Wirkung von Klärschlammdüngung und Schwermetallbelastung auf die Diptera eines Ackerbodens: 3. Die Sphaeroceriden eines klärschlammgedüngten Sommerweizenfeldes. Nachrichten der Deutschen Gesellschaft für allgemeine und angewandte Entomologie, Ulm, Germany 4:11
Epstein E (1973) The physical processes in the soil as related to sewage sludge applications. In: Proc Joint Conf on Recycling Municipal Sludges and Effluents on Land, Environmental Protection Agency, US Dept of Agriculture and National Association of State Universities and Land-Grant Colleges, Champaign, Illinois, pp 67–73
Fliessbach A, Reber H (1991) Effects of longterm sewage sludge applications on soil microbial parameters. EG-COST 681 Symposium, Braunschweig, Germany, 6–8 June, 1990 (in press)
Glockemann B, Larink O (1989) Einfluss von Klärschlammdüngung und Schwermetallbelastung auf Milben, speziell Gamasiden, in einem Ackerboden. Pedobiologia 33:237–246
Habicht WA (1975) The nematicidal effects of varied rates of raw and composted sewage sludge as soil organic amendments on a root-knot nematode. Plant Dis Rep 59:631–634
Huhta V, Ikonen E, Vilkamaa P (1979) Succession of invertebrate populations in artificial soil made of sewage sludge and crushed bark. Ann Zool Fenn 16:223–270
Klingler J, Kunz P (1986) Die Beeinflussung der Bodennematoden durch Klärschlamm und mineralische Düngung. Schweiz Landwirtsch Forsch 25:45–61
Larink O, Lübben B, Glockemann B, Prescher S (1990) Klärschlamm, Schwermetalle und Bodentiere. Berichte der Norddeutschen Naturschutz Akademie, Schneverdingen, Germany 3:77–80
Linford MB, Yap F, Oliviera JM (1938) Reduction of soil populations of the root-knot nematode during decomposition of organic matter. Soil Sci 45:127–141
Lübben B (1989) Influence of sewage sludge and heavy metals on the abundance of collembola on two agricultural soils. In: Dallai R (ed) 3rd Int Semin on apterygota, University of Siena, Siena, Italy, pp 419–428
Mitchell MJ, Hartenstein R, Swift BL, Neuhauser EF, Abrams BI, Mulligan RM, Brown BA, Craig D, Kaplan D (1978) Effects of different sewage sludges on some chemical and biological characteristics of soil. J Environ Qual 7:551–559
Prescher S (1990) Die Wirkung von Klärschlammdüngung und Schwermetallbelastung auf die Diptera eines Ackerbodens: 1. Erfassung der Brachycera. Nachrichten der Deutschen Gesellschaft für allgemeine und angewandte Entomologie, Ulm, Germany 4:9–10
Samoiloff MR (1987) Nematodes as indicators of toxic environmental contaminants. In: Veech JA, Dickson DW (ed) Vistas on nematology: A commemoration of the 25th Anniversary of the Society of Nematology. E O Painter Printing Co, De Leon Springs, Canada, pp 433–439
Sauerbeck D (1987) Effects of agricultural practices on the physical, chemical and biological properties of soils: Part II — Use of sewage sludge and agricultural wastes. In: Barth H, Hermite PL (ed) Scientific basis for soil protection in the European Community. Elsevier, London New York, pp 181–210
Sauerbeck D, Styperek P (1988) Schwermetallakkumulation durch Klärschlammanwendung — Ergebnisse aus 25 langjährigen Feldversuche. VDLUFA-Schriftenreihe 23 (Kongressband 1987 Koblenz), pp 489–506
Schiemer F (1983) Comparative aspects of food dependence and energetics of freeliving nematodes. Oikos 41:32–42
Schrader S (1991) Energy-dispersive X-ray microanalysis of the califerous glands of Lumbricus terrestris L. (Oligochaeta) contaminated with heavy metals. Proc 4th Int Symp on Earthworm Ecology, June 1990. Avignon, France. Soil Biol Biochem (in press)
Sohlenius B, Boström S (1986) Short term dynamics of nematode communities in arable soil — influence of nitrogen fertilization in barley crops. Pedobiologia 29:183–191
Southey JF (1986) Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes. Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, London
Stadelmann FX (1982) Die Wirkung steigender Gaben von Klärschlamm und Schweinegülle in Feldversuchen: II. Auswirkungen auf Population und Aktivität von Bodenmikroorganismen. Schweiz Landwirtsch Forsch 21:239–259
Stevenson BG, Parkinson CM, Mitchell MJ (1984) Effect of sewage sludge on decomposition processes in soils. Pedobiologia 26:95–105
Wasilewska L (1989) The role of nematodes in agroecosystems. Zesz Probl Postepow Nauk Roln 358:8–16
Wasilewska L (1971) Trophic classification of soil and plant nematodes. Wiad Ekol 17:379–388
Weber G (1990) Die Wirkung von Klärschlammdüngung und Schwermetallbelastung auf die Diptera eines Ackerbodens: 2. Erfassung der Nematocera-Imagines und Auswertung von Köderversuchen. Nachrichten der Deutschen Gesellschaft für allgemeine und angewandte Entomologie, Ulm, Germany 4:10–11
Weiss B (1990) Einfluss von Klärschlammdüngung und Schwermetallbelastung auf die Nematoden eines Ackerbodens. Diplomarbeit, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Germany
Zibilske LM, Wagner GH (1982) Bacterial growth and fungal genera distribution in soil amended with sewage sludge containing cadmium, chromium and copper. Soil Sci 134:364–370
Zullini A, Peretti E (1986) Lead pollution and moss-inhabiting nematodes of an industrial area. Water Soil Air Pollut 27:403–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, B., Larink, O. Influence of sewage sludge and heavy metals on nematodes in an arable soil. Biol Fert Soils 12, 5–9 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369381
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369381