Abstract
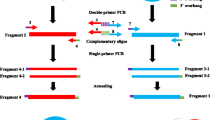
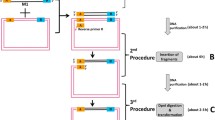
A simple and efficient method for the rapid isolation of specific sequences from PCR-amplified cDNA mixtures has been developed. cDNA mixtures obtained using lone linker PCR (Ko et al. 1990) appeared to be highly representative even though the starting material, 100 ng-2 μg of total RNA, is much less than is required for making an ordinary cDNA library. With this method, cDNA mixtures were obtained from limited materials, including early mouse embryos and primordial germ cells. For selective enrichment of desired cDNAs, biotinylated probe was hybridized with the lone linker-linked cDNA in solution and the resulting probe-cDNA hybrid was captured by Streptavidin-coated magnetic beads. After appropriate washing, cDNA was released from the beads and subjected to amplification followed by cloning into a vector. Using genomic fragments isolated during chromosomal walking in the T/t complex of mouse Chromosome (Chr) 17, cDNAs encoding novel germ cell specific genes have been readily isolated by the above procedures. The method, termed random access retrieval of genetic information through PCR (RARGIP), will streamline the entire process from RNA to cDNA greatly. Its application potentials in various areas of molecular genetics will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, K., Wei, J.-F., Wei, F.-S., Hsu, Y.-C., Uehara, H., Artzt, K., and Bennett, D.: Searching for coding sequences in the mammalian genome: The H-2K region of the mouse MHC is replete with genes expressed in embryos. EMBO J 7: 3441–3449, 1988.
Akowitz, A., and Manuelidis, L.: A novel cDNA/PCR strategy for efficient cloning of small amounts of undefined RNA. Gene 81: 295–306, 1989.
Anderson, L.M., and Young, B.D.: Quantitative filter hybridisation. In B.D. Hames and S.J. Higgins (eds.) Nucleic Acid Hybridization: A Practical Approach, pp 73–111, IRL Press, Oxford, 1985.
Bell, J.: Chromosome crawling in the MHC. Trends Genett 5: 289–290, 1989.
Belyavsky, A., Vinogradova, T., and Rajewsky K.: PCR-based cDNA library construction: General cDNA libraries at the level of a few cells. Nucl Acids Res 17: 2919–2932, 1989.
Bennett, D.: The T-locus of the mouse. Cell 6: 441–454, 1975.
Bird, A.P.: CpG islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature 321: 209–213, 1986.
Chirgwin, J.M., Przybyla, A.E., MacDonald, R.J., and Ratler, W.J.: Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18: 5294–5299, 1979.
Djabali, M., Nguyen, C., Roux, D., Demengeot, J., Yang, H.M., and Jordan, B.R.: A simple method for the direct use of total cosmid clones as hybridization probes. Nucl Acids Res 18: 6166, 1990.
Dressler, G.R., and Gruss, P.: Do multigene families regulate vertebrate development? Trends Genet 4: 214–219, 1988.
Elvin, P., Slynn, G., Black, D., Graham, A., Butler, R., Riley, J., Anand, R., and Markham, A.F.: Isolation of cDNA clones using yeast artificial chromosome probes. Nucl Acids Res 18:3913–3917, 1990.
Gelfand, D.H.: Taq DNA polymerase. In PCR Technology, pp 17–22. Stockton Press, New York, 1989.
Ha, H., Howard, C.A., Yeom, I. Y., Abe, K., Uehara, H., Artzt, K., and Bennett, D.: Testis-expressed genes in the mouse t-complex have expression differences between wild-type and t-mutant mice. Develop Genet, in press, 1991.
Hashimoto, N., Kubokawa, R., Yamazaki, K., Noguchi, M., and Kato, Y.: Germ cell deficiency causes testis cord differentiation in reconstructed mouse fetal ovaries. J Exp Zool 253: 61–70, 1990.
Innis, M.A., and Gelfand, D.H.: Optimization of PCRs In M.A. Innis, D.H. Gelfand, J.J. Snisky, and T.J. White (eds); PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications, pp. 3–12, Academic Press, New York, 1990.
Jefferys, A.J., Wilson, V., Neumann, R., and Keyte, J.: Applification of human minisatellites by the polymerase chain reaction: Towards DNA fingerprinting of single cells. Nucl Acids Res 16: 10953–10971, 1988.
Keohavong, P. and Thilly, W.G.: Fidelity of DNA polymerases in DNA amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 9253–9257, 1989.
Kinzler, K.W. and Vogelstein, B.: Whole genome PCR: Application to the identification of sequences bound by gene regulatory proteins. Nucl Acids Res 17: 3645–3653, 1989.
Ko, M.S.H.: An “equalized cDNA library” by the reassociation of short double-stranded cDNAs. Nucl Acids Res 18: 5705–5711, 1990.
Ko, M.S.H., Ko, S.B.H., Takahashi, N., Nishiguchi, K., and Abe, K.: Unbiased amplification of a highly complex mixture of DNA fragments by “lone linker”-tagged PCR. Nucl Acids Res 18: 4293–4294, 1990.
Lee, C.C. and Caskey, T.: cDNA cloning using degenerate primers. In M.A. Innis, D.H. Gelfand, J.J. Snisky, and T. J. White (eds.); PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications, pp. 46–53. Academic Press, 1990.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F. and Sambrook, J.: molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1982.
Meyerhans, A., Vatanian, J.-P. and Wain-Hobson, S.: DNA recombination during PCR. Nucl Acids Res 18: 1787–1791, 1990.
Ochman, H., Gerber, A.S., and Hartl, D.L.: Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics 120: 621–625, 1988.
Schwarz, K., Hansen-Hagge, T., and Bartram, C.: Improved yields of long PCR products using gene 32 protein. Nucl Acids Res, 18: 1079, 1990.
Silver, L.M.: Mouse t-haplotypes. Ann Rev Genet 19: 179–208, 1985.
Tiemeier, D.C., Tilghman, S.M., and Leder, P.: Purification and cloning of a mouse ribosomal gene fragment in coliphage λ. Gene 2: 173–191, 1977.
Tokunaga, K., Taniguchi, H., Yoda, K., Shimizu, M., and Sakiyama, S.: Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for mouse cytoskeletal β-actin mRNA. Nucl Acids Res. 14: 2829, 1986.
Triglia, T., Peterson, M.G., and Kemp, D.J.: A procedure for in vitro amplification of DNA sequences that lie outside the boundaries of known sequences. Nucl Acids Res. 16: 8186, 1988.
Uhlen, M.: Magnetic separation of DNA. Nature 340: 733–734, 1989.
Watson, C.J. and McConnel, J.: Construction of cDNA libraries for pre-implantation mouse embryos. In M. Monk (ed.) Mammalian Development: A Practical Approach, pp. 183–197, IRL Press, Oxford, 1987.
Welsh, J., Liu, J.-P., and Efstratiadis, A.: Cloning of PCR-amplified total cDNA: Construction of a mouse oocyte cDNA library. Genet Anal Tech Appl 7: 5–17, 1990.
Yeom, Y.I., Abe, K., Bennett, D., and Artzt, K.: Testis-/embryoexpressed genes are clustered in the mouse H-2K region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, in press, 1992.
Zabarovsky, E.R. and Allikmets, R.L.: An improved technique for the efficient construction of gene libraries by partial filling-in of cohesive ends. Gene 42: 119–123, 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abe, K. Rapid isolation of desired sequences from lone linker PCR amplified cDNA mixtures: Application to identification and recovery of expressed sequences in cloned genomic DNA. Mammalian Genome 2, 252–259 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355435
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355435