Abstract
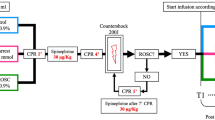
We studied the effect of thiopental loading during resuscitation of 53 patients following cardiopulmonary arrest and compared the outcome with that found in 54 patients treated conventionally in the 30 previous months. Thiopental therapy (10 mg/kg i.v.) was begun within 30 min of the arrest once hemodynamic stability had been established. Thiopental infusion (20 mg/kg over 6 h) was followed by phenobarbital sodium (125 mg every 12 h), tolerance to the initial dose having been assessed. The in-hospital mortality rate for both groups was similar. In patients with ischemic heart disease, the mortality rate within the first 6 h was significantly higher in the thiopental group (p<0.05), although for the remaining patients there were more survivors among the thiopental treated patients (p<0.05). Excluding the patients who died within the first 6 h, 61% of the patients in the thiopental group survived cardiac arrest with normal cerebral performance, whereas only 37% in the standard treatment group showed normal functional outcome (p<0.03). These results suggest a favorable neurologic effect of thiopental loading durnig resuscitation of patients without ischemic heart disease. In patients with ischemic heart disease, an initial hemodynamic deterioration may contribute to minimising the beneficial effect of barbiturate therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson N, Safar P, Detre K, Kelsey S, Monroe J, Reinmuth O, Snyder J, Mullie A, Hedstrand U, Tammisto T, Lund I, Breivik H, Lind B, Jamstremski M (1983) Results of a randomized clinical trial of brain resuscitation with thiopental. Anesthesiology 59:A101
Bleyaert A, Lennox J, Willy J, Chang J, Kuperwasser B, Cohn N (1980) Essais aléatoires cliniques des barbituriques dans le traitment de l'arrêt cardiac aux Etats-Unis: aspects moraux et légaux relatifs. Anesth Analg Reanim 37:587
Bleyaert A, Nemoto E, Safar P, Stezoski S, Mickell J, Moossy J, Rao G (1978) Thiopental amelioration of brain damage after global ischemia in monkeys. Anesthesiology 49:390
Breivik H, Safar P, Sands P, Fabritius R, Lind B, Lust P, Mullie A, Orr M, Renck H, Snyder J (1978) Clinical feasibility of barbiturate therapy after cardiac arrest. Crit Care Med 6:228
Detre K, Abramson N, Safar P, Snyder J, Reinmuth O, Bitsko J, Kelsey S, Mullie A, Hedstrand U, Tammisto T, Lund I, Breivik H, Lind B, Jamstremski M, Bleyaert A, Alexander H, Stezoski W, Thompson M (1981) Collaborative randomized clinical study of cardiopulmonary-cerebral resuscitation. Crit Care Med 9:395
Gisvold S, Safar P, Sassano J, Bleyaert A, Alexander H, Stezoski W, Thompson M (1981) Cardiovascular depression by thiopental loading for brain resuscitation in monkeys. Crit Care Med 9:247
Gisvold S, Safar P, Hendrickx H, Rao G, Moossy J, Alexander H (1984) Thiopental treatment after global brain ischemia in pigtailed monkeys. Anesthesiology 60:88
Goldstein A, Wells B, Keats A (1966) Increased tolerance to cerebral anoxia by pentobarbital. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 161:138
Levy D, Brierley K (1979) Delayed pentobarbital administration limits ischemic brain damage in gerbils. Ann Neurol 5:59
Michenfelder J, Milde J, Sundt T (1976) Cerebral protection by barbiturate anesthesia. Use after middle cerebral artery occlusion in Java monkeys. Arch Neurol 33:345
Monsalve F, Bonastre J, Rucabado L, Cuñat J, Lacueva V, Ruano M (1984) Contraindicación del tratamiento barbitúrico de la encefalopatía post-paro cardiorespiratorio en la cardiopatía isquémica. Med Intensiva 8 [Suppl 1]:42
Monsalve F, Rucabado L, Romar A, Bonastre J, Simon J, Ruano M (1984) Indice pronostico de recuperacion neurológica tras situaciones de paro cardiorespiratorio. Med Intensiva 8 [Suppl 1]:50
Mullie A, Abramson N, Safar P, Lund I, Bjorgo S, Breivik H, Hedstrand U, Hoel T, Jamstremski M, Kampshulte S, Lind B, Snyder J, Tammisto T (1981) Clinical pilot studies of thiopental loading after cardiac arrest. Crit Care Med 9:184
Negovskii V (1977) Reanimatology: the science of resuscitation. In: Stephenson HE (ed) Cardiac arrest and resuscitation. CV Mosby, St. Louis, pp 3–28
Nemoto E, Kofke W, Keesler P, Hossman K, Stezoski W, Safar P (1977) Studies on the pathogenesis of ischemic brain damage and the mechanism of its amelioration by thiopental. Acta Neurol Scand 56 [Suppl 64]:142
Price H (1960) General anesthesia and circulatory homeostasis. Physiol Rev 40:187
Safar P (1977) Advances in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Proceedings of the Wolf Creek Conference. Springer, New York, pp 195–207
Safar P, Nemoto E (1978) Brain resuscitation. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand [Suppl] 70:60
Safar P, Stezoski W, Nemoto E (1976) Amelioration of brain damage after 12 minutes cardiac arrest in dogs. Arch Neurol 33:91
Snyder B, Ramirez-Lessepas M, Lippert D (1977) Neurologic status and prognosis after cardiopulmonary arrest. I. A retrospective study. Neurology 27:807
The brain resuscitation clinical trial study group (1984) Thiopental loading in cardiopulmonary arrest survivors. A randomized collaborative clinical study. Crit Care Med 12:227
Todd M, Chadwick H, Shapiro H, Dunlop B, Marshall L, Dueck R (1982) The neurologic effects of thiopental therapy following experimental cardiac arrest in cats. Anesthesiology 57:76
Wells B, Keats A, Cooley D (1963) Increased tolerance to cerebral ischemia produced by general anesthesia during temporary carotid artery occlusion. Surgery 54:216
Yatsu F, Diamond I, Graziana C, Wells B (1972) Experimental brain ischemia; protection from irreversible damage with a rapid acting barbiturate (metohexital). Stroke 3:726
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monsalve, F., Rucabado, L., Ruano, M. et al. The neurologic effects of thiopental therapy after cardiac arrest. Intensive Care Med 13, 244–248 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265112
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265112