Summary
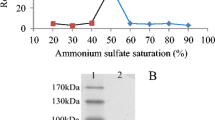
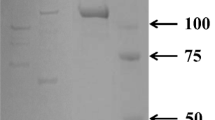
A novel enzyme degrading hyaluronic acid has been isolated, purified and characterized from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba). A combination of affinity chromatography (Con A-Sepharose), gel filtration (Superose 6) and fast protein liquid chromatography (Mono Q) was used for the purification. The hyaluronidase activity was determined by a radial diffusion method based on hyaluronic acid incorporated into an agarose gel. Moreover, the beta-glucuronidase and endo-(1,3)-beta-D-glucanase activities were also followed through the process using phenolphtalein mono beta-glucuronic acid and laminarin as substrates. After the final purification step on Mono Q column, the chromatogram showed three main peaks designated A, B and C. Peak C contained high hyaluronidase activity undetectable in peak A and B. The betaglucuronidase activity was associated with peak A, while the endo-(1,3)-beta-D-glucanase activity was found in peak B and slight in peak C. The hyaluronidase was purified about 85-fold. It had a pH optimum of 5.3, a temperature optimum of 37°C and a molecular weight of 80 000 Daltons. On polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis the enzyme fraction showed one major band associated with hyaluronic acid decomposition, slightly contaminated with a few other components. Isoelectric focusing in combination with a hyaluronic acid zymogram demonstrated one major band at pH 6.7 with high enzyme activity. Preliminary data on enzyme specificity suggest that krill hyaluronidase is a new endo-beta-glucuronidase and support the concept of krill enzymes as a remarkable and unusually effective digestive system adapted to the Antarctic marine ecosystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernfeld P (1955) Amylases, α and β. In: Colowick SP, Kapland NO (eds) Methods in enzymology, Vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 149–158
Chen C-S, Gau S-W (1981) Polysaccharidase and glycosidase activities of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba. J Food Biochem 5:63–68
Chen C-S, Lian K-T (1986) Purification and characterization of β-Dglucosidases from Euphausia superba. Agric Biol Chem 50:1229–1238
Fishman W, Springer B, Brunetti R (1948) Application of an improved glucuronidase assay method to the study of human blood β-glucuronidase. J Biol Chem 173:449–456
Karlstam B, Ljunglöf A (1986) Detection and partial purification of a hyaluronic acid-degrading enzyme from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba). Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 367:339
Linker A, Meyer K, Hoffman P (1960) The production of hyaluronate oligosaccharides by leech hyaluronidase and alkali. J Biol Chem 235:924–927
Linker A (1984) Hyaluronidase. In: Bergmeyer HU ed(3rd ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, Vol 4. Academic Press, New York, pp 256–262
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McConville MJ, Ikeda T, Bacic A, Clarke AE (1986) Digestive carbohydrases from the hepatopancreas of two Antarctic euphausiid species (Euphausia superba and E crystallorophias). Marine Biol 90:371–378
Meyer K, Hoffman P, Linker A (1960) Hyaluronidases. In: Boyer PD ed (2nd ed) The Enzymes, Vol 4. Academic Press, New York, pp 447–460
Osnes KK, Mohr V (1985) Peptide hydrolases of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba. Comp Biochem Physiol 82B:599–606
Richman P, Bear H (1980) A convenient plate assay for the quantition of hyaluronidase in Hymenoptera venoms. Anal Biochem 109:376–381
Spindler KD, Buchholz F (1988) Partial characterization of chitindegrading enzymes from two Euphausiids, Euphausia superba and Meganyctiphanes norvegica. Polar Biol 9:115–122
Turkiewicz M, Galas E, Zielinska M (1985) Purification and partial characterization of an endo-(1.3)-beta-D-glucanase from Euphausia superba Dana (Antarctic krill). Polar Biol 4:203–211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlstam, B., Ljunglöf, A. Purification and partial characterization of a novel hyaluronic acid-degrading enzyme from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba). Polar Biol 11, 501–507 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233086
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233086